Nothingness represents the absolute absence of anything, a concept deeply explored in philosophy and physics to understand existence and the void. It challenges human perception and sparks profound questions about reality, consciousness, and the nature of being. Discover how embracing the idea of nothingness can expand your understanding by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
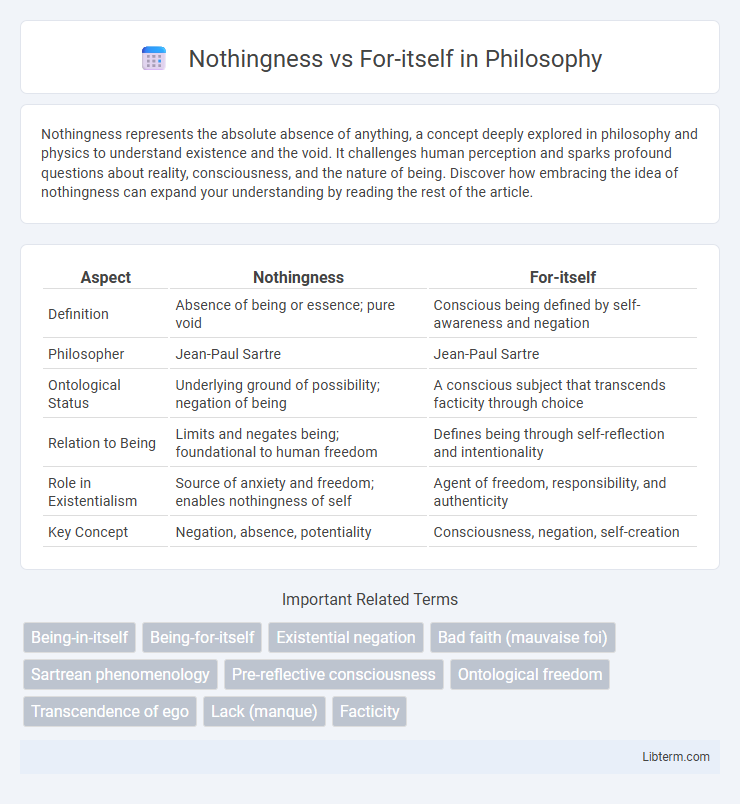
| Aspect | Nothingness | For-itself |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Absence of being or essence; pure void | Conscious being defined by self-awareness and negation |
| Philosopher | Jean-Paul Sartre | Jean-Paul Sartre |
| Ontological Status | Underlying ground of possibility; negation of being | A conscious subject that transcends facticity through choice |
| Relation to Being | Limits and negates being; foundational to human freedom | Defines being through self-reflection and intentionality |
| Role in Existentialism | Source of anxiety and freedom; enables nothingness of self | Agent of freedom, responsibility, and authenticity |
| Key Concept | Negation, absence, potentiality | Consciousness, negation, self-creation |
Understanding Nothingness: A Philosophical Perspective
Understanding nothingness involves exploring its role as a fundamental concept in existentialist philosophy, particularly in Jean-Paul Sartre's notion of For-itself (pour-soi). Nothingness represents the gap that enables consciousness to negate and transcend facticity, allowing freedom and self-definition beyond mere being-in-itself. This dynamic interplay highlights how for-itself consciousness is characterized by its awareness of non-being and the capacity for existential choice.
Defining the For-itself: Consciousness and Self-Awareness
The For-itself, a central concept in existential philosophy, is defined by its consciousness and self-awareness, distinguishing it from mere existence or Nothingness. This mode of being actively reflects on itself, creating a dynamic interplay between its sense of identity and its potential for freedom and choice. Unlike Nothingness, which denotes absence or negation, the For-itself embodies the presence of subjective experience and intentionality.
The Roots of Sartre’s Ontology: Being and Nothingness
Sartre's ontology in "Being and Nothingness" distinguishes Nothingness as the dynamic negation inherent in consciousness, contrasting with the For-itself, which represents self-aware being constantly defining itself through negation. Nothingness functions as the foundation for freedom, allowing the For-itself to transcend facticity and project possibilities beyond mere being-in-itself. This interplay illustrates Sartre's existential framework where human existence is characterized by continuous self-creation and the void that enables authentic choice.
The Nature of Existential Negation
Existential negation in existentialist philosophy distinguishes Nothingness as the fundamental absence enabling human consciousness, or For-itself, to define itself through negation of 'being-in-itself' or mere existence. Nothingness acts as a creative void, allowing For-itself to project possibilities and exercise freedom by negating predetermined essences. This dynamic interplay reveals the core of human freedom and self-awareness as rooted in the capacity to negate and transcend objective reality.
Nothingness: Absence or Creative Space?
Nothingness in existential philosophy represents both the absence of being and a fertile creative space for freedom and possibility. It serves as the foundation for self-awareness, enabling individuals to transcend facticity and create their own meaning. This dual nature of nothingness challenges static existence by opening a dynamic field for authentic self-definition.
For-itself: The Project of Becoming
For-itself represents consciousness defined by its inherent self-awareness and freedom to transcend mere being, continually projecting itself toward future possibilities. This ongoing project of becoming signifies a dynamic existence where identity is never fixed but always in the process of defining and redefining itself. Unlike nothingness, which denotes absence or void, the for-itself actively creates meaning through choice and negation, embodying existential freedom.
The Dynamic Relationship between Nothingness and For-itself
Nothingness and For-itself are central to Sartrean existentialism, where Nothingness represents the gap that enables freedom and self-awareness within the For-itself, the conscious being. This dynamic relationship fuels consciousness by negating being-in-itself, creating a space for choice, negation, and transcendence beyond mere facticity. The interplay between Nothingness and For-itself thus underpins the continuous self-creation and authenticity in human existence.
Freedom, Responsibility, and the Role of Nothingness
Freedom in the For-itself arises from its ability to negate and transcend the given, embodying nothingness as a space of infinite possibilities. Responsibility manifests as an inherent burden, compelling the For-itself to define itself through choices within this void of nothingness. Nothingness functions as the essential condition enabling consciousness to break free from facticity, framing existential freedom and ethical accountability.
Existential Anxiety: Encountering the Void
Existential anxiety arises from the confrontation between Nothingness and the For-itself, where the conscious self recognizes its own freedom and the inherent void at the core of existence. This encounter with Nothingness reveals the contingency of being, forcing the For-itself to grapple with its lack of predetermined essence and the burden of creating meaning. The tension between Nothingness and the For-itself drives the profound experience of existential anxiety, highlighting the individual's isolation and responsibility in an absurd world.
Implications for Authentic Living
Nothingness in existentialist thought signifies the inherent absence of predetermined essence, compelling the For-itself, or conscious being, to create meaning through free choices and self-awareness. This dynamic relationship forces individuals to confront anxiety and despair, yet it also empowers authentic living by embracing responsibility and rejecting external impositions. The implications for authentic living highlight the necessity of owning one's freedom and continuously redefining identity in the face of existential void.
Nothingness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com