Existential themes explore the fundamental questions of human existence, freedom, and the search for meaning in an indifferent universe. These concepts challenge individuals to confront their own mortality and the responsibilities that come with making authentic choices. Discover how existential ideas impact your perspective and influence everyday life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
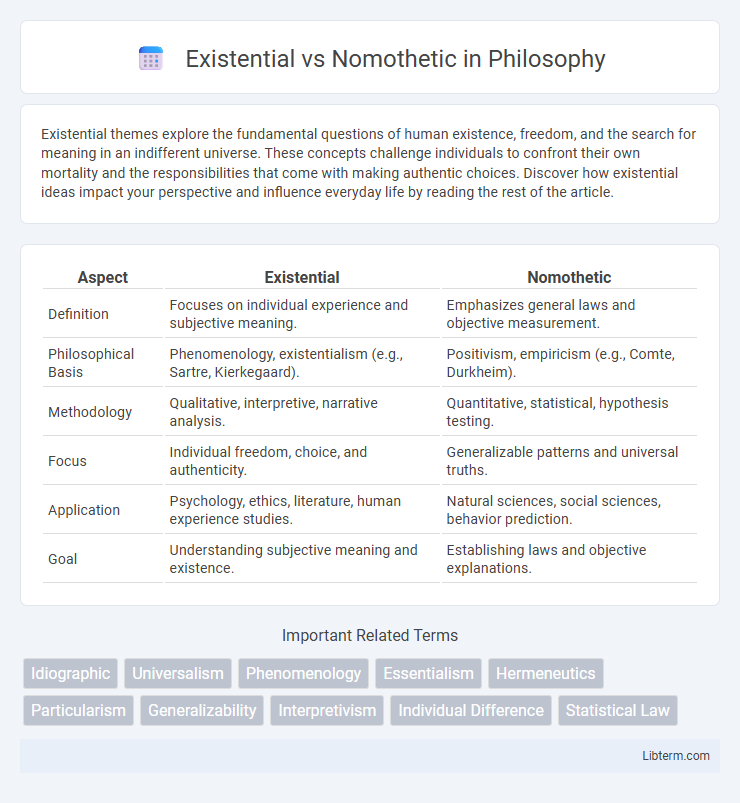
| Aspect | Existential | Nomothetic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on individual experience and subjective meaning. | Emphasizes general laws and objective measurement. |
| Philosophical Basis | Phenomenology, existentialism (e.g., Sartre, Kierkegaard). | Positivism, empiricism (e.g., Comte, Durkheim). |
| Methodology | Qualitative, interpretive, narrative analysis. | Quantitative, statistical, hypothesis testing. |
| Focus | Individual freedom, choice, and authenticity. | Generalizable patterns and universal truths. |
| Application | Psychology, ethics, literature, human experience studies. | Natural sciences, social sciences, behavior prediction. |
| Goal | Understanding subjective meaning and existence. | Establishing laws and objective explanations. |
Introduction to Existential and Nomothetic Approaches
Existential approaches emphasize individual experience, subjective meaning, and personal freedom, seeking to understand human existence in its unique, context-specific dimensions. Nomothetic approaches focus on identifying general laws and universal principles through quantifiable data, enabling prediction and explanation across populations. Together, these methodologies offer complementary perspectives in psychology and social sciences, balancing personal depth with broad generalizability.
Defining Existential Perspectives
Existential perspectives emphasize individual experience, freedom, and personal responsibility, highlighting the unique meaning each person creates in their life. Rooted in existential philosophy, this approach contrasts with nomothetic methods that seek general laws and patterns across populations. Central to defining existential perspectives is the focus on subjective meaning, authenticity, and confronting human conditions such as anxiety, death, and isolation.
Understanding the Nomothetic Approach
The nomothetic approach emphasizes the search for general laws and principles that apply across populations, relying heavily on quantitative data and statistical analysis to identify patterns and causal relationships. It contrasts with the existential perspective by prioritizing objective measurement and replicability, enabling broad generalizations in psychology and social sciences. This method is essential for developing standardized theories that guide empirical research and predict behavior on a large scale.
Key Differences: Existential vs Nomothetic
Existential approaches emphasize individual experience, subjective meaning, and personal freedom, while nomothetic methods focus on general laws, patterns, and statistical analysis across populations. Existential research often employs qualitative techniques to explore unique, context-specific phenomena, contrasting with the quantitative, objective measurements typical of nomothetic studies. The key difference lies in existentialism's prioritization of individual uniqueness versus nomothetic emphasis on universality and predictability.
Historical Background and Philosophical Roots
Existential psychology, rooted in 19th-century phenomenology and existential philosophy by thinkers like Kierkegaard and Heidegger, emphasizes individual experience and personal meaning. Nomothetic approaches derive from Enlightenment rationalism and positivist traditions, focusing on general laws and objective measurement pioneered by figures such as Galton and Cattell. The historical divergence reflects the tension between subjective human existence and scientific generalization in understanding behavior.
Applications in Psychology and Social Sciences
Existential approaches in psychology emphasize individual experience, meaning-making, and subjective reality, often applied in therapy to address personal crises and enhance self-awareness. Nomothetic methods focus on discovering general laws and patterns through quantitative research, widely used in social sciences to study behavior, cognition, and social phenomena at group or population levels. Combining existential and nomothetic perspectives fosters a comprehensive understanding of human behavior by balancing personal meaning with empirical generalization.
Strengths of the Existential Approach
The existential approach offers a deep understanding of individual human experiences by emphasizing personal meaning, freedom, and choice, which enhances psychological treatment tailored to unique subjective realities. It promotes authentic self-awareness and encourages personal responsibility, fostering profound emotional growth and resilience. This approach excels in addressing existential concerns such as anxiety, despair, and the search for purpose, making it highly effective in therapeutic settings focused on holistic human development.
Advantages of the Nomothetic Method
The nomothetic method offers the advantage of identifying generalizable laws and patterns across large populations, enhancing predictive power and replicability in research. This approach facilitates statistical analysis, enabling researchers to draw objective conclusions through quantifiable data. Its emphasis on broad applicability makes it essential for developing theories with universal relevance in social sciences.
Critiques and Limitations of Each Approach
Existential approaches face critiques for their subjective emphasis, which can lead to difficulties in generalizing findings across populations, limiting empirical validation and predictive power. Nomothetic methods are criticized for oversimplifying human experience by focusing on universal laws, often neglecting individual uniqueness and contextual variability. Both approaches exhibit limitations: existentialism struggles with scientific rigor, while nomothetic research may overlook the richness of personal lived experiences.
Integrating Existential and Nomothetic Perspectives
Integrating existential and nomothetic perspectives enhances psychological understanding by combining individual subjective experiences with generalizable scientific laws. This approach acknowledges the unique, meaning-driven nature of human existence while applying empirical research methods to identify patterns across populations. Using mixed methodologies, researchers can develop comprehensive models that respect personal narratives and ensure wider applicability in clinical and social interventions.
Existential Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com