The Law of Noncontradiction states that contradictory propositions cannot both be true simultaneously, ensuring logical consistency in reasoning. Understanding this principle helps you critically evaluate arguments and avoid fallacies. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your grasp of this fundamental logical law.
Table of Comparison
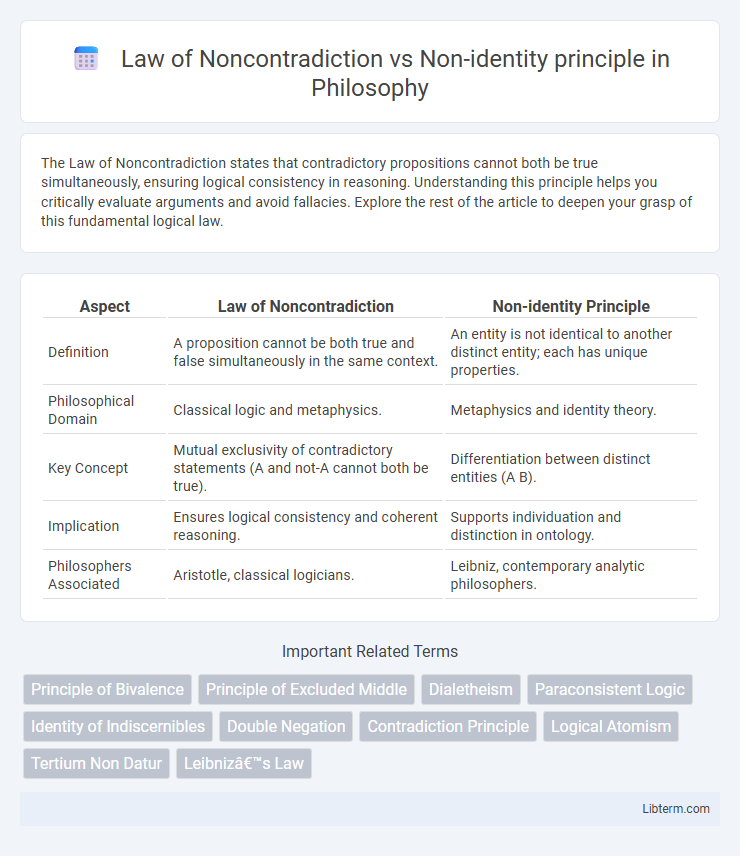
| Aspect | Law of Noncontradiction | Non-identity Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A proposition cannot be both true and false simultaneously in the same context. | An entity is not identical to another distinct entity; each has unique properties. |
| Philosophical Domain | Classical logic and metaphysics. | Metaphysics and identity theory. |
| Key Concept | Mutual exclusivity of contradictory statements (A and not-A cannot both be true). | Differentiation between distinct entities (A B). |
| Implication | Ensures logical consistency and coherent reasoning. | Supports individuation and distinction in ontology. |
| Philosophers Associated | Aristotle, classical logicians. | Leibniz, contemporary analytic philosophers. |
Introduction to Classical Logic: Core Principles
The Law of Noncontradiction asserts that a statement and its negation cannot both be true simultaneously, serving as a fundamental axiom in classical logic. The Non-identity Principle, by contrast, emphasizes that every entity is distinct from others, reinforcing the clarity of identity and differentiation in logical analysis. Together, these principles underpin the rigorous structure of classical logic, ensuring consistency and precise reasoning in formal arguments.
Defining the Law of Noncontradiction
The Law of Noncontradiction asserts that a statement cannot be both true and false simultaneously in the same context, serving as a fundamental axiom in classical logic. This principle ensures logical consistency by prohibiting contradictions within propositions, thereby underpinning deductive reasoning. In contrast, the Non-identity principle focuses on the distinctness of entities, emphasizing that each entity is not identical to any other, which addresses issues of identity rather than truth values.
Understanding the Non-identity Principle
The Non-identity Principle asserts that an entity is not identical to another if there exists at least one property or characteristic that differentiates them, emphasizing the uniqueness of each object in any given context. Unlike the Law of Noncontradiction, which prohibits contradictory properties from coexisting in the same entity simultaneously, the Non-identity Principle focuses on distinguishing separate entities based on their distinct attributes. Understanding this principle is crucial in fields like metaphysics and formal logic, where precise identification and differentiation underpin arguments about existence and identity.
Historical Context and Philosophical Roots
The Law of Noncontradiction, first systematically articulated by Aristotle in his Metaphysics, asserts that contradictory statements cannot both be true simultaneously, grounding classical logic and metaphysics. In contrast, the Non-identity principle, explored by philosophers such as Leibniz in the 17th century, emphasizes that no entity is identical to another, anchoring discussions in ontology and the philosophy of identity. Both principles emerged from efforts in ancient and early modern philosophy to establish clear criteria for truth, existence, and the nature of being.
Key Differences Between Noncontradiction and Non-identity
The Law of Noncontradiction asserts that a proposition cannot be both true and false simultaneously, emphasizing logical consistency within statements. In contrast, the Non-identity principle deals with the distinctness of entities, stating that no object is identical to another or to itself under different conditions or times. While Noncontradiction governs the truth values of propositions, Non-identity focuses on the ontological differentiation between objects or entities.
Practical Applications in Logical Arguments
The Law of Noncontradiction ensures that a proposition cannot be both true and false simultaneously, providing a foundational rule for consistent logical reasoning in debates and computational algorithms. The Non-identity Principle, which states that every entity is distinct from another, aids in clarifying ambiguous terms and avoiding equivocation in legal and philosophical arguments. Together, these principles support the construction of sound, unambiguous logical arguments crucial for decision-making and artificial intelligence systems.
Common Misconceptions and Confusions
The Law of Noncontradiction states that contradictory propositions cannot both be true simultaneously, such as "A is B" and "A is not B" being mutually exclusive, whereas the Non-identity Principle emphasizes that an entity is not identical to different entities or properties, preventing confusion between distinct objects. Common misconceptions arise by conflating these principles, mistakenly assuming that rejecting contradictions implies objects must be identical in all respects, which is false. Clarifying the distinction avoids errors in logic and metaphysics, reinforcing that noncontradiction governs truth values while non-identity addresses object distinctness.
Significance in Contemporary Philosophy
The Law of Noncontradiction, asserting that contradictory statements cannot both be true simultaneously, underpins logical consistency essential in analytic philosophy and formal reasoning. The Non-identity principle, emphasizing the distinctness of entities from themselves at different times or under varying conditions, challenges static notions of identity crucial for metaphysics and personal identity debates. Together, these principles inform contemporary discussions on language, ontology, and the limits of knowledge, shaping arguments in epistemology and cognitive science.
Illustrative Examples: Noncontradiction vs Non-identity
The Law of Noncontradiction states that a proposition cannot be both true and false simultaneously, as exemplified by the statement "The light is on" being either true or false, but not both. The Non-identity principle asserts that no entity is identical to another distinct entity, demonstrated by the fact that a tree cannot be the same as the rock beside it. These principles highlight contrasting logical rules: noncontradiction ensures consistency within a single proposition, while non-identity emphasizes uniqueness between separate entities.
Conclusion: The Interrelation of Logical Principles
The Law of Noncontradiction asserts that a statement cannot be both true and false simultaneously, while the Non-identity Principle emphasizes that no entity is identical to another. Together, these foundational logical principles establish consistency and distinctness within reasoning processes, ensuring coherent differentiation and reliable inference. Their interrelation underpins the structure of formal logic, reinforcing the integrity of argumentation frameworks and ontological clarity.
Law of Noncontradiction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com