Permission is the essential authorization that grants individuals or entities the right to perform specific actions, ensuring compliance with laws and regulations. Understanding the nuances of permission can protect your rights and prevent legal complications in personal or professional contexts. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to navigate permission requirements effectively.
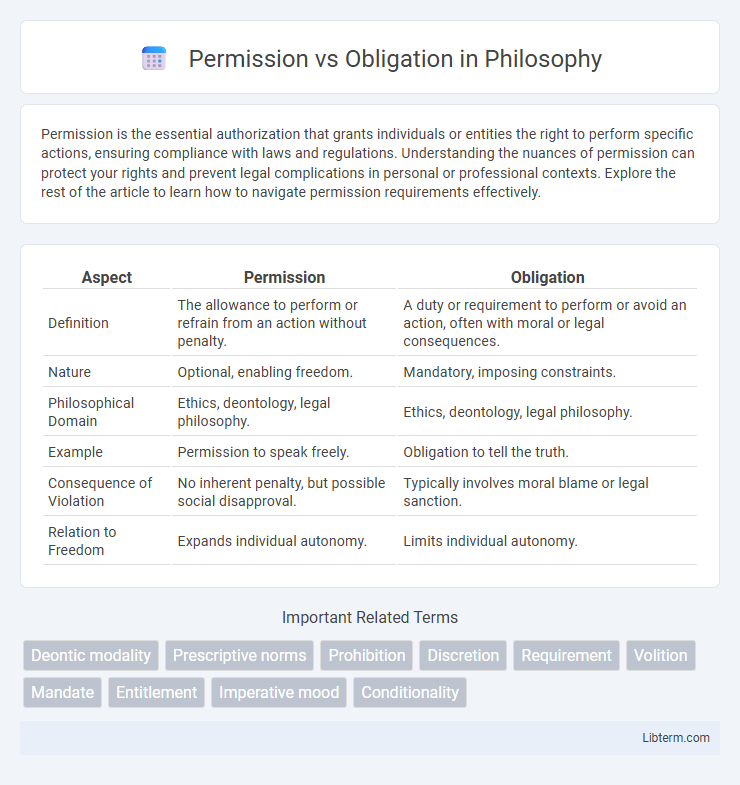
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Permission | Obligation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The allowance to perform or refrain from an action without penalty. | A duty or requirement to perform or avoid an action, often with moral or legal consequences. |
| Nature | Optional, enabling freedom. | Mandatory, imposing constraints. |
| Philosophical Domain | Ethics, deontology, legal philosophy. | Ethics, deontology, legal philosophy. |
| Example | Permission to speak freely. | Obligation to tell the truth. |
| Consequence of Violation | No inherent penalty, but possible social disapproval. | Typically involves moral blame or legal sanction. |
| Relation to Freedom | Expands individual autonomy. | Limits individual autonomy. |
Understanding Permission and Obligation
Permission allows an individual to perform an action without violating rules, granting authorized access or consent within legal or social frameworks. Obligation requires a mandated action, compelling adherence to duties or responsibilities under ethical, legal, or contractual conditions. Understanding permission and obligation clarifies the boundaries between voluntary actions and enforced requirements in various contexts.
Key Differences Between Permission and Obligation
Permission allows an individual to perform an action optionally, granting freedom without mandating compliance, while obligation requires an individual to perform a duty or adhere to a rule, often enforced by law or social norms. The key difference lies in the voluntary nature of permission versus the compulsory nature of obligation, affecting decision-making and accountability. Permission is typically associated with consent and choice, whereas obligation involves responsibility and potential consequences for non-compliance.
Legal Perspectives on Permission vs Obligation
Legal perspectives on permission and obligation delineate distinct roles within regulatory frameworks where permission denotes authorized consent to perform specific acts under defined conditions, while obligation imposes mandatory duties enforceable by law. Courts interpret permissions as granting lawful privileges that do not impose action, contrasting with obligations that require compliance to avoid penalties or legal sanctions. Understanding this dichotomy is critical in contractual law, statutory regulations, and administrative procedures, ensuring proper adherence and enforcement of legal rights and duties.
Social Implications of Permission and Obligation
Permission and obligation shape social behavior by defining acceptable actions and duties within communities. Permission grants individuals freedom, fostering autonomy and trust, while obligation enforces responsibility, promoting social order and accountability. The balance between permission and obligation influences social cohesion and the development of cultural norms.
Permission in Everyday Life Scenarios
Permission in everyday life scenarios involves granting individuals the autonomy to make choices within defined boundaries, such as parents allowing children to use electronic devices or employers authorizing remote work hours. It plays a crucial role in fostering trust, encouraging responsibility, and promoting personal freedom while maintaining social order and safety regulations. Understanding the balance between permission and its limits helps optimize interactions in educational, professional, and social environments.
Obligation in Professional and Personal Contexts
Obligation in professional and personal contexts involves a duty or commitment that individuals are expected to fulfill, often dictated by ethical standards, contracts, or social norms. In the workplace, obligations may include meeting deadlines, adhering to company policies, and maintaining confidentiality, while personal obligations often relate to family responsibilities, financial commitments, and caregiving. Understanding these obligations is crucial for balancing accountability and trust in both spheres, ensuring reliability and integrity.
The Role of Culture in Shaping Permission and Obligation
Cultural norms and values significantly influence the interpretation and enforcement of permission and obligation within societies, dictating what behaviors are allowed or required. In collectivist cultures, obligations often emphasize group harmony and social roles, whereas individualistic cultures may prioritize personal permission and autonomy. These cultural frameworks shape legal systems, organizational policies, and interpersonal interactions by defining the boundaries between voluntary actions and mandated duties.
Common Misconceptions about Permission and Obligation
Permission and obligation are often misunderstood, with many confusing permission as optional when it can impose implicit social expectations. Obligation is frequently perceived as strictly legal or formal, ignoring its presence in informal contexts like moral duties and social norms. Another common misconception is treating permission as a free choice rather than a conditional allowance subject to rules and limitations.
Balancing Permission and Obligation for Effective Relationships
Balancing permission and obligation is essential for fostering trust and respect in effective relationships. Granting permission encourages autonomy and personal growth, while well-defined obligations ensure accountability and commitment. Harmonizing these elements promotes mutual understanding and strengthens interpersonal connections.
Practical Examples: Navigating Permission vs Obligation
Understanding the difference between permission and obligation is critical in practical decision-making, such as workplace policies where employees have permission to work remotely but an obligation to meet deadlines. In legal contexts, individuals may be granted permission to use a property without the obligation to maintain it, highlighting distinct responsibilities and rights. Exploring real-world scenarios like school assignments, where students have the obligation to submit work but permission to select topics, clarifies how these concepts influence behavior and compliance.
Permission Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com