Your appearance plays a significant role in shaping first impressions and can influence how others perceive your confidence and professionalism. Maintaining personal grooming and wearing appropriate attire can enhance your overall image and boost self-esteem. Discover effective tips to elevate your appearance and make a lasting impact by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
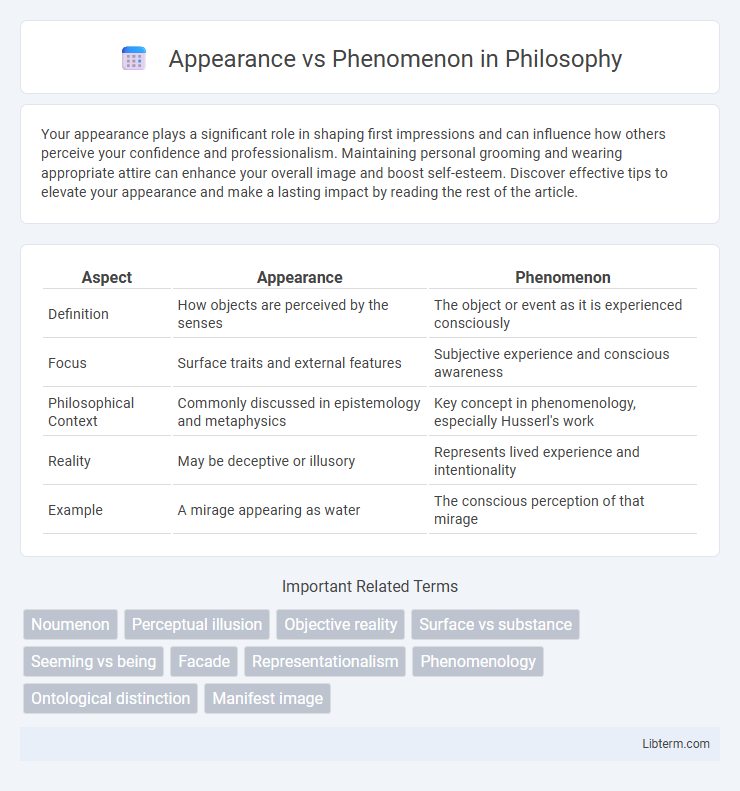
| Aspect | Appearance | Phenomenon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | How objects are perceived by the senses | The object or event as it is experienced consciously |
| Focus | Surface traits and external features | Subjective experience and conscious awareness |
| Philosophical Context | Commonly discussed in epistemology and metaphysics | Key concept in phenomenology, especially Husserl's work |
| Reality | May be deceptive or illusory | Represents lived experience and intentionality |
| Example | A mirage appearing as water | The conscious perception of that mirage |
Defining Appearance and Phenomenon
Appearance refers to the way an object is perceived by the senses, often emphasizing surface characteristics and external form. Phenomenon denotes an observable event or fact that can be analyzed scientifically, highlighting underlying processes or realities beyond mere visual impression. Defining appearance involves subjective sensory perception, while defining phenomenon centers on objective observable occurrence.
Historical Perspectives on Appearance vs Phenomenon
Historical perspectives on appearance versus phenomenon trace back to ancient Greek philosophy, where Plato distinguished between the illusory world of appearances and the true reality of forms or phenomena. In medieval scholasticism, thinkers like Thomas Aquinas grappled with reconciling sensory appearances with divine phenomena, emphasizing metaphysical realities beyond mere perception. The Enlightenment further advanced this debate through Kant's critical philosophy, which argued that phenomena areknowable through experience while appearances conceal the noumenal reality beyond human cognition.
Philosophical Foundations Explained
Appearance vs Phenomenon revolves around the distinction in philosophy where appearance refers to the way objects seem to us through perception, while phenomenon denotes the objective reality as it exists independent of perception. Immanuel Kant extensively explored this dichotomy, arguing that phenomena are the world as structured by human experience, whereas noumena represent things-in-themselves, inaccessible to direct knowledge. This philosophical foundation highlights the limits of human cognition and the difference between subjective experience and objective reality.
Appearance in Art and Literature
Appearance in art and literature often serves as the initial layer through which reality is interpreted and understood, shaping perception before deeper meaning emerges. Artists and writers manipulate visual and descriptive elements to evoke emotions, highlight themes, and construct identity, emphasizing how surface details influence audience interpretation. The exploration of appearance challenges readers and viewers to question the reliability of first impressions and to seek underlying truths beyond mere outward forms.
Phenomenon in Science and Nature
Phenomenon in science and nature refers to observable events or processes that can be studied and measured, revealing underlying principles and mechanisms of the natural world. Unlike mere appearance, phenomena provide concrete evidence that supports scientific theories and advances knowledge through empirical observation and experimentation. Understanding natural phenomena such as magnetic fields, chemical reactions, or weather patterns is fundamental for predicting outcomes and developing technologies.
Perception and Reality: Bridging the Gap
Perception often distorts reality by filtering external phenomena through subjective senses and cognitive biases, creating an appearance that may not reflect the true nature of what exists. Phenomena represent objective occurrences independent of observers, while appearances are the interpreted images shaped by individual perception. Bridging the gap requires critical analysis and empirical validation to reconcile perceptual illusions with factual reality for a coherent understanding of existence.
Cognitive Biases: Judging by Appearances
Cognitive biases such as the halo effect and confirmation bias often lead individuals to judge others based solely on appearances rather than underlying realities or phenomena. These biases distort perception, causing inaccurate assessments that favor superficial traits while ignoring deeper contextual information. Research in social psychology highlights how reliance on appearance can result in decision-making errors and flawed social judgments.
Illusions: When Appearance Distorts Phenomenon
Illusions reveal how appearance can distort phenomenon by misleading sensory perception and creating false interpretations of reality. Visual illusions like the Muller-Lyer or the Ponzo effect demonstrate how context alters size and distance judgment, affecting the brain's construction of the physical world. Neuropsychological studies confirm that these perceptual discrepancies arise from the brain's predictive coding mechanisms, emphasizing the difference between immediate appearance and underlying phenomenon.
Social Implications of Appearance vs Phenomenon
Appearance often shapes social interactions and judgments, influencing how individuals are perceived and treated within communities. Phenomenon, representing deeper realities beyond surface impressions, challenges stereotypes and promotes critical thinking about identity and social dynamics. Prioritizing understanding of phenomena over appearances can reduce prejudice and foster more equitable social environments.
Navigating Truth: Beyond Surface Perceptions
Appearance often conceals deeper realities, making it essential to distinguish phenomena from mere impressions when seeking truth. Phenomena represent surface-level experiences shaped by perception, while the essence lies beneath observable traits and initial judgments. Navigating truth requires critical analysis to unravel layers beyond appearance, revealing authentic understanding and overcoming cognitive biases.
Appearance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com