Logical possibility refers to the concept that a proposition or scenario does not contain any contradictions and can exist within the framework of logical reasoning. It is a key consideration in philosophy, mathematics, and computer science when exploring what could potentially be true or feasible under given logical rules. Discover how logical possibility shapes our understanding of reality and hypothetical situations by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
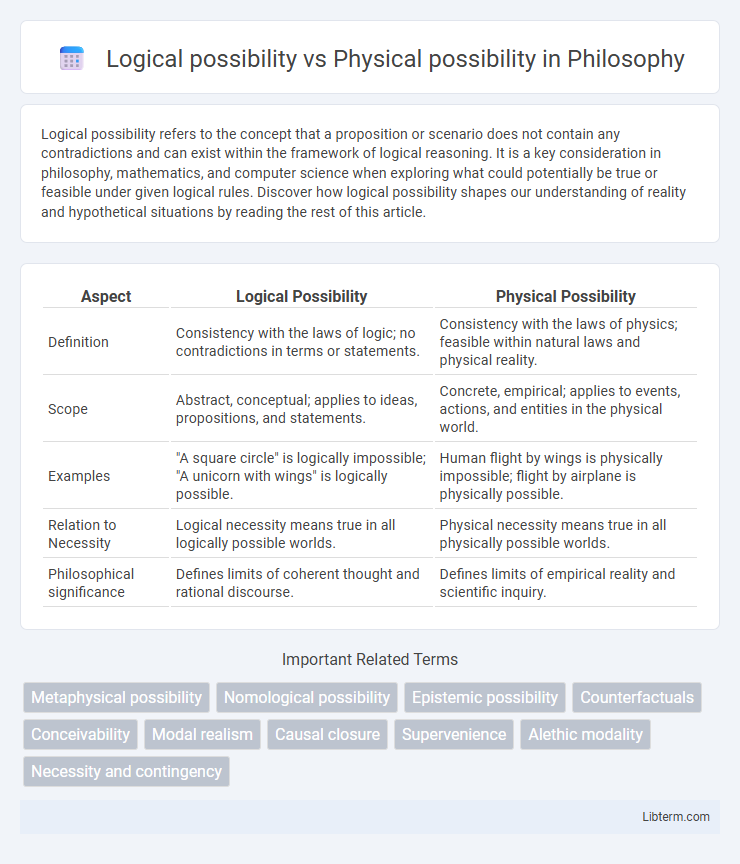
| Aspect | Logical Possibility | Physical Possibility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistency with the laws of logic; no contradictions in terms or statements. | Consistency with the laws of physics; feasible within natural laws and physical reality. |
| Scope | Abstract, conceptual; applies to ideas, propositions, and statements. | Concrete, empirical; applies to events, actions, and entities in the physical world. |
| Examples | "A square circle" is logically impossible; "A unicorn with wings" is logically possible. | Human flight by wings is physically impossible; flight by airplane is physically possible. |
| Relation to Necessity | Logical necessity means true in all logically possible worlds. | Physical necessity means true in all physically possible worlds. |
| Philosophical significance | Defines limits of coherent thought and rational discourse. | Defines limits of empirical reality and scientific inquiry. |
Understanding Logical Possibility
Logical possibility refers to the coherence of a proposition within the rules of logic, meaning it cannot contain any contradictions or violate logical principles. A scenario is logically possible if it can be conceived without inconsistency, regardless of real-world constraints or natural laws. Understanding logical possibility is crucial for distinguishing what can be thought or imagined from what can actually occur in the physical universe.
Defining Physical Possibility
Physical possibility refers to scenarios or events that can occur within the natural laws and constraints of the physical universe, such as gravity, thermodynamics, and causality. It limits what can actually happen based on empirical facts, material conditions, and scientific principles, distinguishing it from purely conceptual or logical coherence. Understanding physical possibility requires analyzing real-world factors like energy, matter, and space-time interactions to determine whether a situation can be realized in practice.
Key Differences Between Logical and Physical Possibility
Logical possibility refers to scenarios or propositions that do not contain any contradictions within the rules of logic, making them conceivable regardless of real-world constraints. Physical possibility concerns what can actually occur within the laws of nature and the structure of the physical universe, emphasizing empirical and scientific feasibility. The key difference lies in logical possibility being constrained solely by consistency of ideas, while physical possibility is bounded by natural laws and observable reality.
Role of Logic in Determining Possibility
Logic plays a crucial role in determining logical possibility by ensuring that a concept or event does not involve any contradictions within a given formal system. Logical possibility is defined purely by coherence with the rules of logic, independent of empirical facts or physical laws. Physical possibility, on the other hand, depends on natural laws and empirical conditions, where logic alone cannot determine whether something can occur in the actual world.
Physical Laws and Their Constraints
Physical possibility is strictly governed by the laws of physics, which impose constraints such as the speed of light limit and the conservation of energy, defining what can occur in the actual universe. Logical possibility merely requires coherence within a set of propositions, allowing scenarios that may violate physical laws but remain free of contradiction. Understanding physical laws as fundamental constraints clarifies why some logically conceivable events are physically impossible.
Examples of Logically Possible but Physically Impossible Scenarios
A classic example of a logically possible but physically impossible scenario is a square circle, which can be conceived without contradiction but cannot exist in the physical world due to geometric laws. Another example includes faster-than-light travel, which, while not logically contradictory, is prohibited by the constraints of Einstein's theory of relativity. Lastly, perpetual motion machines are logically conceivable but violate the laws of thermodynamics, making them physically impossible.
Why Some Physically Possible Events Are Logically Impossible
Some events may appear physically possible based on current scientific understanding but remain logically impossible due to contradictions inherent in their definitions, such as a square circle or a married bachelor. Logical possibility depends on the coherence of concepts and adherence to formal laws of logic, while physical possibility relates to what can occur given natural laws and conditions. Therefore, an event might be physically imaginable within a hypothetical framework yet logically impossible if it violates fundamental principles of logic and identity.
Philosophical Implications of Different Possibility Types
Logical possibility considers scenarios where propositions do not contradict any logical laws, allowing for a broad range of conceivable worlds, while physical possibility restricts these scenarios to those compatible with the actual laws of nature and physical constraints. Philosophically, this distinction challenges metaphysical debates about the nature of reality, as logical possibility permits hypothetical constructs ignored by physical possibility, influencing modal logic, epistemology, and theories of causation. Understanding these different possibility types informs discussions on determinism, free will, and the limits of human knowledge about what could exist or occur.
Logical Possibility in Thought Experiments
Logical possibility in thought experiments refers to scenarios that do not violate the laws of logic, allowing for conceptual exploration even if they defy physical laws. These thought experiments enable philosophers and scientists to analyze hypotheses, counterexamples, and abstract concepts by imagining worlds or situations consistent with logical coherence. Distinguishing logical possibility from physical possibility helps clarify boundaries between what can be conceived without contradiction and what can exist in the empirical universe.
Physical Possibility in Scientific Inquiry
Physical possibility in scientific inquiry refers to events or phenomena that can occur within the laws of nature and established physical principles. It involves evaluating whether a scenario is achievable under current scientific understanding, experimental evidence, and empirical constraints. Scientists rely on physical possibility to differentiate feasible hypotheses from those that, while logically conceivable, violate fundamental physical laws or practical limitations.
Logical possibility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com