Action drives progress by turning intentions into tangible results that shape your environment. Effective decision-making and consistent effort amplify the impact of every step taken toward achieving goals. Explore the rest of the article to discover how deliberate action can transform your ambitions into reality.
Table of Comparison
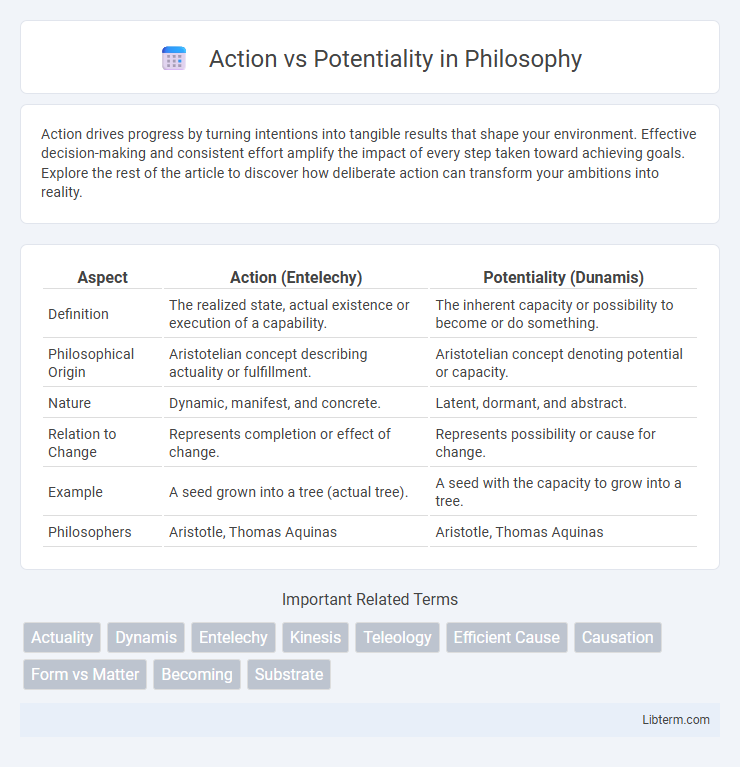
| Aspect | Action (Entelechy) | Potentiality (Dunamis) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The realized state, actual existence or execution of a capability. | The inherent capacity or possibility to become or do something. |
| Philosophical Origin | Aristotelian concept describing actuality or fulfillment. | Aristotelian concept denoting potential or capacity. |
| Nature | Dynamic, manifest, and concrete. | Latent, dormant, and abstract. |
| Relation to Change | Represents completion or effect of change. | Represents possibility or cause for change. |
| Example | A seed grown into a tree (actual tree). | A seed with the capacity to grow into a tree. |
| Philosophers | Aristotle, Thomas Aquinas | Aristotle, Thomas Aquinas |
Understanding Action and Potentiality
Understanding action involves recognizing its realization of potentiality, where potentiality refers to the inherent capacity or possibility for change or development. In philosophical terms, action signifies the actualization of latent qualities within an entity, distinguishing what is actively occurring from what merely could occur. This distinction forms the basis for analyzing processes of transformation, causality, and agency in metaphysics and epistemology.
Defining Action: What It Means to Act
Action signifies the realization of potentiality through deliberate movement or decision that transforms possibilities into concrete outcomes. In philosophy, acting involves the exercise of agency where intention aligns with execution, distinguishing mere capability from actual behavior. This dynamic interplay underscores action as the pivotal manifestation of human will and practical engagement with the world.
Unpacking Potentiality: The Power of Possibility
Unpacking potentiality reveals the intrinsic power of possibility as the foundation for change and development inherent in all entities. It represents unrealized capacities that drive innovation, growth, and transformation by bridging the gap between what is and what could be. This dynamic interplay between potentiality and action fuels progress, enabling the actualization of latent abilities into tangible outcomes.
Key Differences Between Action and Potentiality
Action represents the actualization of a capability, where potentiality transitions into reality through performance or execution. Potentiality refers to the inherent capacity or possibility within an entity that has not yet been realized or manifested in concrete form. The key difference lies in action being the fulfillment or expression of what potentiality inherently contains but has not yet actualized.
The Relationship Between Action and Potentiality
The relationship between action and potentiality is rooted in the transformation of possibilities into actualities, where potentiality represents the capacity or power to perform or become something, while action is the realization or fulfillment of that capacity. In Aristotelian philosophy, this dynamic serves as a fundamental principle explaining change and development in both nature and human behavior. Understanding the interplay between action and potentiality provides insight into how latent abilities or conditions manifest through concrete activities and outcomes.
Philosophical Perspectives on Action and Potentiality
Aristotle's metaphysical framework distinguishes action (energeia) as the actualization of an entity's potentiality (dunamis), emphasizing that potentiality represents inherent capabilities awaiting realization. Philosophical perspectives explore how potentiality grounds the possibility of change while action embodies the fulfillment and expression of that possibility in concrete existence. Contemporary debates analyze this dynamic to address questions of causality, free will, and the nature of being in both classical and process metaphysics.
Action’s Role in Achieving Potential
Action plays a pivotal role in transforming potentiality into reality by initiating the process of actualization. Without deliberate and sustained action, inherent capabilities remain dormant, preventing growth and achievement. Consistent effort bridges the gap between latent possibilities and tangible outcomes, emphasizing action as the catalyst in realizing potential.
Barriers That Inhibit Action from Potential
Barriers that inhibit action from potential often stem from fear of failure, lack of motivation, and insufficient resources or support. Cognitive distortions such as procrastination and perfectionism create psychological blocks, preventing individuals from translating their capabilities into tangible outcomes. Structural obstacles, including limited access to information or opportunities, also impede the transition from potential to actualized performance.
Real-Life Examples: Action vs Potentiality
Action manifests when an individual actively engages in a task, such as a student writing an exam or an athlete running a race, transforming potential energy into tangible outcomes. Potentiality resides in latent abilities or resources, like a piano left unplayed or an untrained employee, representing possibilities yet to be actualized. Real-life examples emphasize that progress depends on converting potentiality into deliberate action to achieve measurable success.
Cultivating Action to Fulfill Potential
Cultivating action harnesses intrinsic potential by transforming latent capabilities into tangible outcomes through deliberate practice and consistent effort. Neuroscientific studies reveal that repeated intentional actions strengthen neural pathways, enabling sustained performance and growth. Emphasizing goal-oriented behaviors accelerates the realization of potential, bridging the gap between possibility and achievement.
Action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com