Dialectical contradiction refers to the dynamic tension between opposing forces or ideas that drive change and development in various contexts, such as philosophy, society, or personal growth. This concept highlights how conflicting elements can coexist and interact, leading to transformation and progress through their resolution or synthesis. Explore the rest of the article to understand how dialectical contradiction shapes your perspectives and influences real-world scenarios.
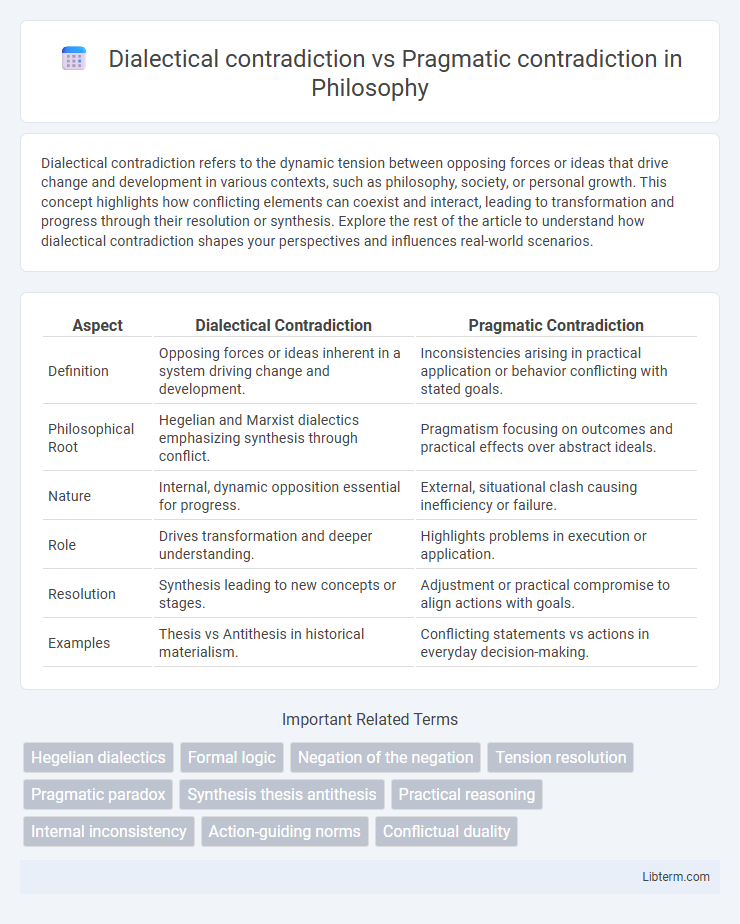
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dialectical Contradiction | Pragmatic Contradiction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Opposing forces or ideas inherent in a system driving change and development. | Inconsistencies arising in practical application or behavior conflicting with stated goals. |
| Philosophical Root | Hegelian and Marxist dialectics emphasizing synthesis through conflict. | Pragmatism focusing on outcomes and practical effects over abstract ideals. |
| Nature | Internal, dynamic opposition essential for progress. | External, situational clash causing inefficiency or failure. |
| Role | Drives transformation and deeper understanding. | Highlights problems in execution or application. |
| Resolution | Synthesis leading to new concepts or stages. | Adjustment or practical compromise to align actions with goals. |
| Examples | Thesis vs Antithesis in historical materialism. | Conflicting statements vs actions in everyday decision-making. |
Introduction to Contradictions in Philosophy
Dialectical contradiction in philosophy involves the clash of opposing forces or ideas that drive change and development within a system, rooted in Hegelian and Marxist thought. Pragmatic contradiction occurs when actions or beliefs produce conflicting consequences in practical contexts, highlighting inconsistencies in behavior or reasoning. Understanding these contradictions helps clarify the dynamics of philosophical inquiry and the relationship between theory and practice.
Defining Dialectical Contradiction
Dialectical contradiction refers to the fundamental opposition between two interconnected and interdependent forces or ideas that drive change and development within a system, often characterized by conflict and unity simultaneously. It is rooted in dialectical materialism, where contradictions are seen as inherent and necessary for progress through synthesis. Pragmatic contradiction, by contrast, involves practical inconsistencies in beliefs or actions that create tension without necessarily generating transformative change.
Understanding Pragmatic Contradiction
Pragmatic contradiction arises when language users encounter statements that conflict in practical context, causing confusion or communication breakdown. Understanding pragmatic contradiction involves analyzing the speaker's intent, contextual cues, and the interaction between literal and implied meanings. Unlike dialectical contradictions, which stem from logical opposites within theory, pragmatic contradictions highlight real-world inconsistencies in language use and social interaction.
Historical Roots of Both Concepts
Dialectical contradiction originates from Hegelian dialectics, where conflict between opposing forces drives historical change and development. Pragmatic contradiction, rooted in American pragmatism, particularly the work of Charles Sanders Peirce and William James, emphasizes the practical consequences and usefulness of contradictory beliefs or statements in real-world contexts. Both concepts reflect differing historical approaches to understanding conflict: dialectical contradiction centers on dynamic synthesis in philosophy and social theory, while pragmatic contradiction focuses on experiential validation and problem-solving in epistemology.
Key Differences Between Dialectical and Pragmatic Contradiction
Dialectical contradiction involves opposing forces or ideas that coexist and drive change through their resolution, often seen in philosophy and social theory. Pragmatic contradiction, on the other hand, arises from conflicting practical outcomes or actions that hinder achieving specific goals, commonly addressed in communication and problem-solving contexts. The key difference lies in dialectical contradiction fostering dynamic development, while pragmatic contradiction emphasizes real-world conflicts impacting decision-making and behavior.
Dialectical Contradiction in Practice
Dialectical contradiction in practice refers to the dynamic interplay between opposing forces or ideas within a system, driving change and development through their resolution. This form of contradiction is inherent in social, political, and philosophical contexts, where conflicting interests or concepts clash and interact, leading to progress or transformation. Unlike pragmatic contradiction, which centers on practical inconsistencies in actions or decisions, dialectical contradiction emphasizes the synthesis that emerges from the tension between opposing elements.
Pragmatic Contradiction in Everyday Reasoning
Pragmatic contradiction in everyday reasoning occurs when actions or statements clash with practical goals or social norms, highlighting inconsistencies in real-world behavior rather than abstract principles. Unlike dialectical contradiction, which centers on opposing ideas within a theoretical framework, pragmatic contradiction emphasizes the tension between intent and outcome in daily interactions. This form of contradiction reveals flaws in decision-making and communication by exposing how practical constraints and context influence understanding and problem-solving.
Examples Illustrating Each Contradiction Type
Dialectical contradiction is exemplified in the conflict between the bourgeoisie and proletariat in Marxist theory, where opposing social classes drive historical change through tension and resolution. Pragmatic contradiction appears in everyday decision-making, such as a manager advocating for teamwork while privately undermining collaborative efforts, revealing inconsistency between stated intentions and actual behavior. These examples highlight how dialectical contradictions involve structural oppositions shaping systems, whereas pragmatic contradictions arise from practical conflicts in communication and actions.
Implications for Critical Thinking and Debate
Dialectical contradictions arise from opposing ideas that reflect real-world dynamics and drive intellectual progress, while pragmatic contradictions emerge from practical inconsistencies in action or reasoning. Understanding dialectical contradictions enhances critical thinking by encouraging deeper analysis of underlying tensions and dialectical synthesis, fostering more nuanced debates. Differentiating pragmatic contradictions sharpens debate skills by highlighting flaws in arguments or strategies, promoting clearer communication and more effective problem-solving.
Conclusion: Navigating Contradictions in Theory and Practice
Dialectical contradiction involves inherent opposing forces within a system driving change and development, while pragmatic contradiction centers on conflicts arising from practical challenges and real-world applications. Understanding these distinctions enhances decision-making by balancing theoretical perspectives and practical exigencies in complex scenarios. Navigating contradictions requires integrating dialectical analysis with pragmatic flexibility to foster innovative solutions and sustainable progress.
Dialectical contradiction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com