Pragmatism emphasizes practical consequences and real-world applications as essential components of meaning and truth. This philosophy guides decision-making by focusing on results rather than abstract principles, making it highly relevant to everyday problem-solving. Explore the rest of the article to understand how pragmatism can enhance Your critical thinking and approach to challenges.
Table of Comparison
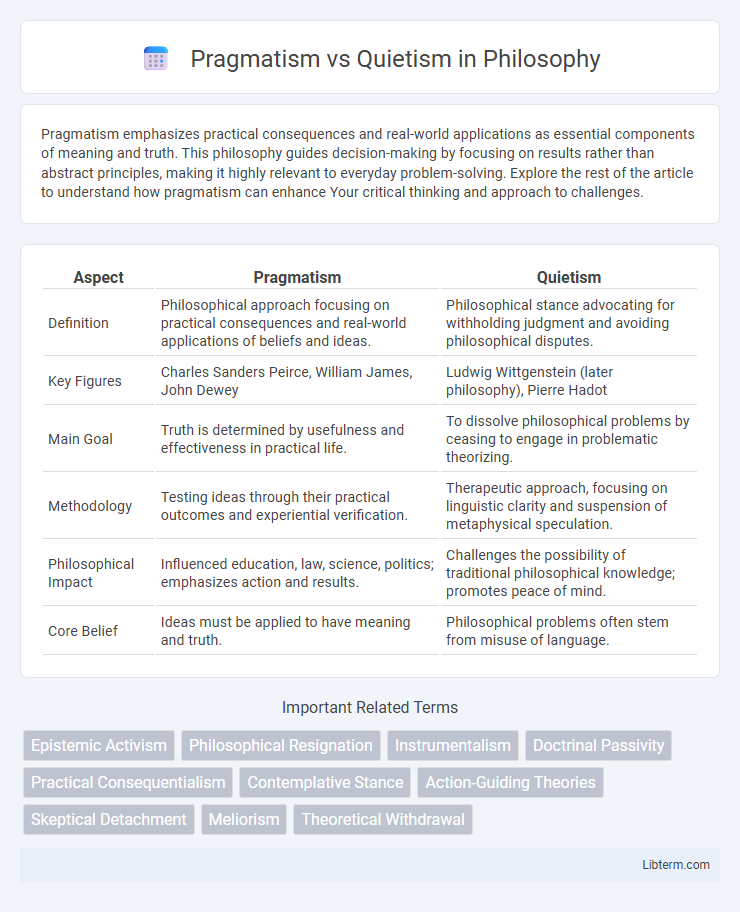
| Aspect | Pragmatism | Quietism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical approach focusing on practical consequences and real-world applications of beliefs and ideas. | Philosophical stance advocating for withholding judgment and avoiding philosophical disputes. |
| Key Figures | Charles Sanders Peirce, William James, John Dewey | Ludwig Wittgenstein (later philosophy), Pierre Hadot |
| Main Goal | Truth is determined by usefulness and effectiveness in practical life. | To dissolve philosophical problems by ceasing to engage in problematic theorizing. |
| Methodology | Testing ideas through their practical outcomes and experiential verification. | Therapeutic approach, focusing on linguistic clarity and suspension of metaphysical speculation. |
| Philosophical Impact | Influenced education, law, science, politics; emphasizes action and results. | Challenges the possibility of traditional philosophical knowledge; promotes peace of mind. |
| Core Belief | Ideas must be applied to have meaning and truth. | Philosophical problems often stem from misuse of language. |
Defining Pragmatism and Quietism
Pragmatism is a philosophical approach that emphasizes practical consequences and real-world applications as the primary criteria for meaning and truth, often associated with thinkers like Charles Sanders Peirce and William James. Quietism, by contrast, advocates for a withdrawal from metaphysical speculation and philosophical theorizing, promoting a stance of acceptance and passive awareness rather than active engagement or intervention. Defining pragmatism involves highlighting its commitment to actionable beliefs and problem-solving, while quietism centers on minimizing disturbance in intellectual and existential matters.
Historical Roots of Pragmatism
Pragmatism originated in the late 19th century with philosophers like Charles Sanders Peirce and William James, emphasizing practical consequences and experiential outcomes as criteria for meaning and truth. This philosophical approach emerged as a response to abstract metaphysics, promoting a method where ideas are validated through their utility in real-world applications. Its historical roots reveal a commitment to adaptive reasoning, contrasting sharply with Quietism's focus on quiet acceptance and suspension of judgment.
Origins and Philosophy of Quietism
Quietism, rooted in 17th-century Catholic mysticism with figures like Miguel de Molinos, emphasizes inner passivity and spiritual surrender to achieve union with the divine. Unlike Pragmatism, which prioritizes practical consequences and empirical outcomes, Quietism advocates for detachment from active interventions and worldly affairs to cultivate inner tranquility. This philosophy centers on the belief that true spiritual progress arises from complete self-abandonment and silence rather than intellectual or pragmatic action.
Key Philosophers in Pragmatism
Pragmatism centers around key philosophers such as Charles Sanders Peirce, who coined the pragmatic maxim emphasizing meaning through practical effects, William James, known for his focus on belief and truth as tools for effective action, and John Dewey, who advanced pragmatism in education and democracy by prioritizing experience and experimental inquiry. These thinkers positioned pragmatism as a dynamic method to solve problems through action and results rather than detached contemplation. Their work contrasts with quietism, which advocates acceptance and passivity, rejecting active intervention as a path to truth or meaning.
Major Proponents of Quietism
Major proponents of Quietism include seventeenth-century philosophers like Miguel de Molinos, who emphasized spiritual passivity and inner stillness as a path to divine union. Edward Stillingfleet and later Pierre Poiret contributed to Quietist thought by advocating a withdrawal from worldly concerns and intellectual efforts to achieve tranquility. Quietism contrasts with Pragmatism by rejecting active problem-solving in favor of contemplative surrender and acceptance.
Pragmatic Approaches to Knowledge and Truth
Pragmatic approaches to knowledge and truth emphasize practical consequences and usefulness as criteria for validating beliefs and theories, arguing that truth is what works effectively in real-world applications. This philosophy prioritizes experience, experimentation, and the adaptability of ideas to evolving contexts, contrasting with Quietism's emphasis on refraining from theoretical disputes. Pragmatism, as championed by thinkers like Charles Sanders Peirce and William James, focuses on the operational outcomes and problem-solving capacities of knowledge over abstract or metaphysical certainty.
Quietist Attitudes towards Belief and Action
Quietism emphasizes a passive stance towards belief, advocating for refraining from metaphysical speculation and normative commitments. It promotes a skeptical attitude that suspends judgment, encouraging individuals to avoid dogmatic assertions and pursue tranquility through intellectual detachment. This approach prioritizes acceptance and non-intervention over active engagement, contrasting with pragmatic philosophies that emphasize practical consequences and belief-driven action.
Practical Implications: Pragmatism in Daily Life
Pragmatism emphasizes actionable solutions and adapting beliefs based on their practical outcomes, leading to decision-making grounded in real-world effectiveness. Quietism advocates for disengagement from active intervention, promoting acceptance and inner tranquility rather than external problem-solving. In daily life, pragmatism encourages proactive behavior and iterative learning, shaping habits and choices to achieve tangible improvements in personal and professional contexts.
Quietism’s Role in Modern Thought
Quietism in modern thought emphasizes acceptance and mindfulness as tools for navigating uncertainty and existential dilemmas. Unlike Pragmatism, which prioritizes practical outcomes and adaptive problem-solving, Quietism advocates for a contemplative detachment that fosters inner peace and reduces cognitive dissonance. This philosophical stance influences contemporary approaches to mental health, spirituality, and ethics by promoting calm reflection over active intervention.
Comparative Analysis: Pragmatism vs Quietism
Pragmatism emphasizes practical consequences and actionable beliefs, prioritizing results and adaptability in knowledge application, while Quietism advocates for intellectual humility and refraining from theoretical speculation, focusing on inner tranquility and epistemic restraint. Pragmatism values epistemic progress through experimentation and revision, whereas Quietism seeks to dissolve philosophical problems by clarifying language and avoiding metaphysical commitments. The contrast lies in pragmatism's active engagement with reality versus quietism's minimalist approach to philosophical inquiry.
Pragmatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com