Rule-following ensures consistent outcomes by adhering to established guidelines and standards. It helps maintain order, enhances safety, and fosters trust in various environments, from workplaces to communities. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering rule-following can benefit your personal and professional life.
Table of Comparison
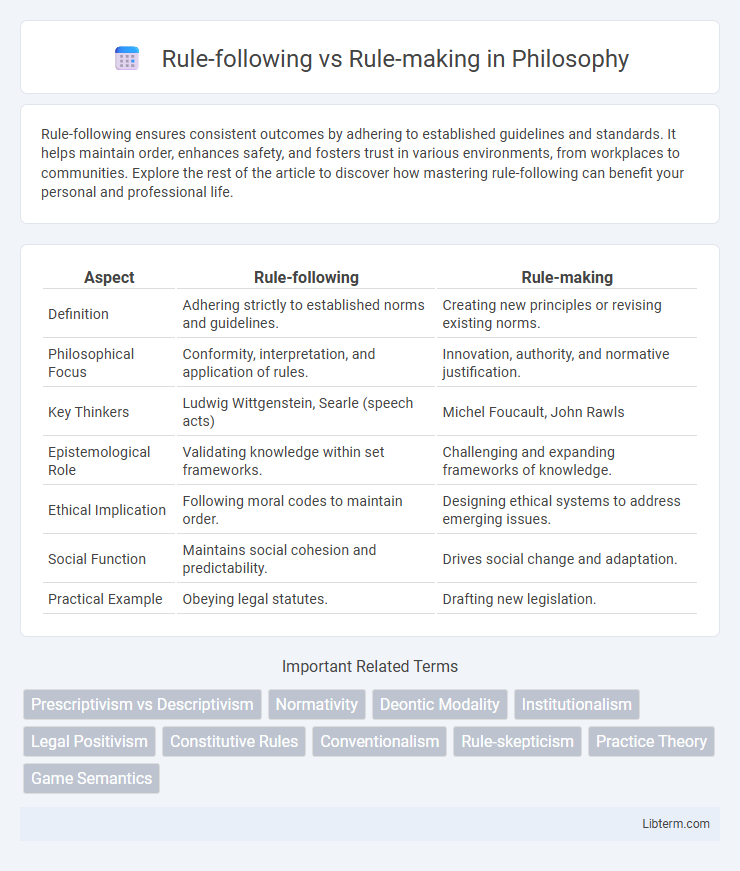
| Aspect | Rule-following | Rule-making |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adhering strictly to established norms and guidelines. | Creating new principles or revising existing norms. |
| Philosophical Focus | Conformity, interpretation, and application of rules. | Innovation, authority, and normative justification. |
| Key Thinkers | Ludwig Wittgenstein, Searle (speech acts) | Michel Foucault, John Rawls |
| Epistemological Role | Validating knowledge within set frameworks. | Challenging and expanding frameworks of knowledge. |
| Ethical Implication | Following moral codes to maintain order. | Designing ethical systems to address emerging issues. |
| Social Function | Maintains social cohesion and predictability. | Drives social change and adaptation. |
| Practical Example | Obeying legal statutes. | Drafting new legislation. |
Understanding Rule-Following and Rule-Making
Understanding rule-following involves recognizing the importance of compliance with established guidelines to maintain order, consistency, and predictability in social and organizational contexts. Rule-making, on the other hand, requires critical thinking and creativity to develop effective, fair, and adaptable standards that address emerging needs and challenges. Mastery in both areas enhances decision-making processes and fosters a balanced environment where innovation aligns with structure.
The Psychology Behind Following Rules
The psychology behind following rules reveals that individuals comply due to cognitive mechanisms like social conformity and fear of punishment, which activate the brain's reward system when rules are adhered to. Internalized norms and perceived legitimacy of authority significantly enhance rule-following behavior by fostering trust and a sense of obligation. Research in behavioral economics and social psychology highlights that clear, consistent rules coupled with transparent enforcement increase compliance and cooperation in groups.
The Motivation for Making Rules
The motivation for making rules often stems from the need to establish order, promote fairness, and address gaps in existing regulations. Rule-making empowers individuals or institutions to shape behavior and outcomes by setting standards that reflect shared values or practical necessities. This proactive creation of rules enables control over complex systems and anticipates future challenges, differentiating it from passive rule-following.
Cultural Influences on Rule Adherence
Cultural influences significantly shape how individuals approach rule-following versus rule-making, with collectivist societies often emphasizing adherence to established norms to maintain social harmony. In contrast, individualistic cultures tend to encourage rule-making and innovation, valuing personal autonomy and challenge to authority. Understanding these cultural dimensions is crucial for designing effective policies and organizational practices that align with local values and behavioral expectations.
Benefits of Being a Rule Follower
Being a rule follower promotes consistency and reliability, which enhances trustworthiness in professional and social environments. Compliance with established guidelines reduces risks and errors, ensuring smoother operations and increased safety. Adhering to rules also fosters discipline and accountability, contributing to long-term success and stability.
Advantages of Being a Rule Maker
Being a rule maker allows individuals to shape organizational culture and influence decision-making processes, enhancing leadership effectiveness and strategic impact. Rule makers can establish standards that foster innovation, efficiency, and fairness, thereby driving long-term success and stability. This position also grants greater control over resource allocation and priority setting, empowering one to align policies with overarching goals and values.
Challenges in Balancing Rule-Making and Rule-Following
Balancing rule-making and rule-following poses significant challenges in maintaining organizational agility while ensuring compliance and consistency. Rule-makers must anticipate diverse scenarios and embed flexibility to adapt to evolving contexts, yet overly rigid rules constrain innovation and responsiveness. Effective governance requires a dynamic interplay where clear guidelines coexist with discretion, empowering individuals to interpret and apply rules without compromising overall objectives.
Rule Dynamics in Organizations and Leadership
Rule-following in organizations ensures consistency, compliance, and operational stability by guiding employee behavior within established frameworks. Rule-making, driven by leadership, enables adaptation and innovation by creating or modifying guidelines aligned with strategic goals and evolving environmental demands. The dynamic interplay between rule-following and rule-making fosters organizational agility, balancing control with flexibility to achieve sustained performance and competitive advantage.
Creative Innovation: Breaking vs. Setting Rules
Creative innovation thrives on the dynamic tension between rule-following and rule-making, where breaking conventional rules sparks original thinking and novel solutions. Rule-breaking challenges established norms, fostering disruptive ideas that can transform industries and cultural paradigms. Conversely, setting new rules through strategic frameworks institutionalizes innovation, enabling sustainable growth and long-term competitive advantage.
Finding Personal Balance: When to Follow, When to Create
Finding personal balance between rule-following and rule-making involves understanding the context and recognizing when established guidelines enhance efficiency versus when innovation demands new frameworks. Effective individuals discern situations requiring adherence to existing norms to maintain order and those calling for creative rule formulation to address evolving challenges. Developing this skill fosters adaptability, empowering one to contribute constructively within systems while shaping progress through thoughtful rule creation.
Rule-following Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com