Reality shapes our perceptions and influences every decision we make, grounding us in the tangible and the observable. Understanding the nuances of reality can enhance your awareness and improve how you interact with the world around you. Explore the rest of this article to unlock deeper insights into the nature of reality.
Table of Comparison
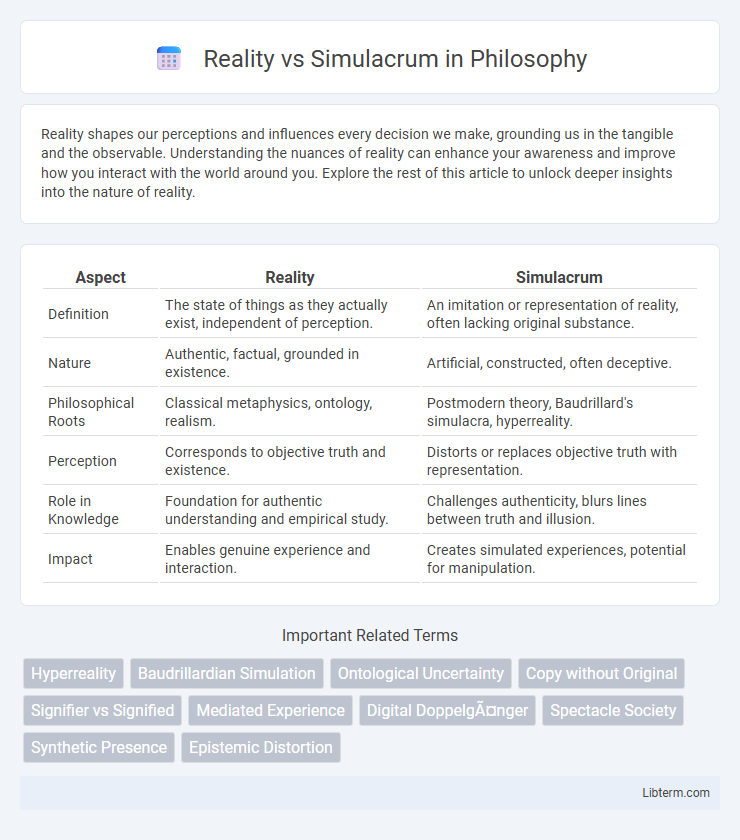
| Aspect | Reality | Simulacrum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The state of things as they actually exist, independent of perception. | An imitation or representation of reality, often lacking original substance. |
| Nature | Authentic, factual, grounded in existence. | Artificial, constructed, often deceptive. |
| Philosophical Roots | Classical metaphysics, ontology, realism. | Postmodern theory, Baudrillard's simulacra, hyperreality. |
| Perception | Corresponds to objective truth and existence. | Distorts or replaces objective truth with representation. |
| Role in Knowledge | Foundation for authentic understanding and empirical study. | Challenges authenticity, blurs lines between truth and illusion. |
| Impact | Enables genuine experience and interaction. | Creates simulated experiences, potential for manipulation. |
Understanding Reality and Simulacrum
Understanding reality involves recognizing the existence of an objective world independent of perception, while simulacrum refers to a representation or imitation that replaces or distorts that reality. Jean Baudrillard's theory highlights how simulacra can create hyperreality, where distinctions between the real and the artificial blur, leading to a simulated experience that feels more authentic than reality itself. This challenges traditional notions of truth, perception, and authenticity in contemporary society.
Historical Origins of the Simulacrum Concept
The concept of the simulacrum traces back to Plato's philosophy, where it was viewed as an imitation or distortion of reality, often linked to his theory of Forms. In the Renaissance, the idea evolved as artists and thinkers explored representations that challenged perceptions of truth and reality. The 20th century saw Jean Baudrillard redefine the simulacrum as a copy without an original, a notion central to postmodern critiques of media, culture, and reality.
Philosophical Foundations: Plato to Baudrillard
Plato's Allegory of the Cave introduces the philosophical foundation of reality versus simulacrum by depicting shadows as mere reflections of the true forms, emphasizing the distinction between appearance and essence. Building on this, Jean Baudrillard argues that postmodern society is dominated by simulacra--copies without originals--where symbols and signs replace reality, leading to hyperreality. This evolution from Platonic ideals to Baudrillardian hyperreality reframes the understanding of truth, representation, and existence in contemporary philosophy.
Differentiating Reality from Representation
Reality consists of tangible, objective existence grounded in physical and empirical evidence, whereas simulacrum represents a copy or imitation that lacks original authenticity. Differentiating reality from representation involves assessing the fidelity, context, and function of the simulacrum to determine whether it reflects or distorts the original. The distinction is crucial in fields like philosophy, media studies, and virtual reality, where understanding the boundaries between genuine experience and constructed images shapes perception and truth.
The Rise of Hyperreality in Modern Society
The rise of hyperreality in modern society blurs the distinction between reality and simulacrum, where simulated experiences often feel more authentic than actual ones. Media saturation, digital environments, and consumer culture contribute to creating hyperreal spaces where representations replace genuine human interactions. This phenomenon reshapes perceptions, influencing identity, social behavior, and collective consciousness.
Media, Technology, and Simulation
The concept of Reality vs Simulacrum in media explores how technological advancements create hyperreal representations that blur the line between authentic experiences and fabricated simulations. Media platforms generate simulated realities through algorithms and virtual environments, influencing perception and challenging the distinction between the real and the constructed. Simulation technologies such as augmented reality and deepfakes exemplify this shift by producing immersive, manipulated content that reshapes cultural and social understanding of reality.
Everyday Life: Navigating the Simulacrum
Everyday life increasingly blurs the lines between reality and simulacrum as digital media and virtual experiences shape perceptions and interactions. Consumers navigate hyperreal environments where representations often replace or distort authentic experiences, creating a simulated reality that influences identity and social behavior. This immersion challenges traditional notions of truth and presence, demanding critical awareness of the mediated landscapes shaping modern existence.
Impacts on Identity and Perception
The interplay between reality and simulacrum profoundly influences identity by blurring the boundaries between authentic experiences and constructed representations, leading individuals to question the authenticity of their self-perception. Simulacra, as hyperreal copies devoid of an original, distort sensory and cognitive frameworks, causing shifts in how reality is perceived and internalized. This shift fosters a fluid, often fragmented sense of identity shaped more by mediated images and narratives than by direct, unmediated experiences.
Reality vs Simulacrum in Art and Culture
Reality vs. simulacrum in art and culture explores the tension between authentic representation and fabricated images that mimic reality without original reference. Artists and cultural theorists analyze how simulacra challenge perceptions by creating hyperreal experiences that blur boundaries between truth and illusion. This dynamic shifts interpretive frameworks, influencing contemporary visual arts, media, and consumer culture through mediated realities and symbolic duplications.
The Future of Reality in a Simulated World
The future of reality in a simulated world hinges on the increasing sophistication of virtual environments and AI-driven experiences that blur the boundaries between physical and digital existence. Advances in neural interfaces and immersive technologies will redefine human perception, making simulated realities indistinguishable from the tangible world. As these simulations evolve, ethical considerations and the nature of consciousness within digital realms will become critical areas of philosophical and technological inquiry.
Reality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com