Objectivity ensures decisions and evaluations are based on unbiased facts rather than personal feelings or opinions. Maintaining objectivity enhances credibility and promotes fair assessments in any field. Explore the rest of the article to understand how you can apply objectivity effectively in your daily life.
Table of Comparison
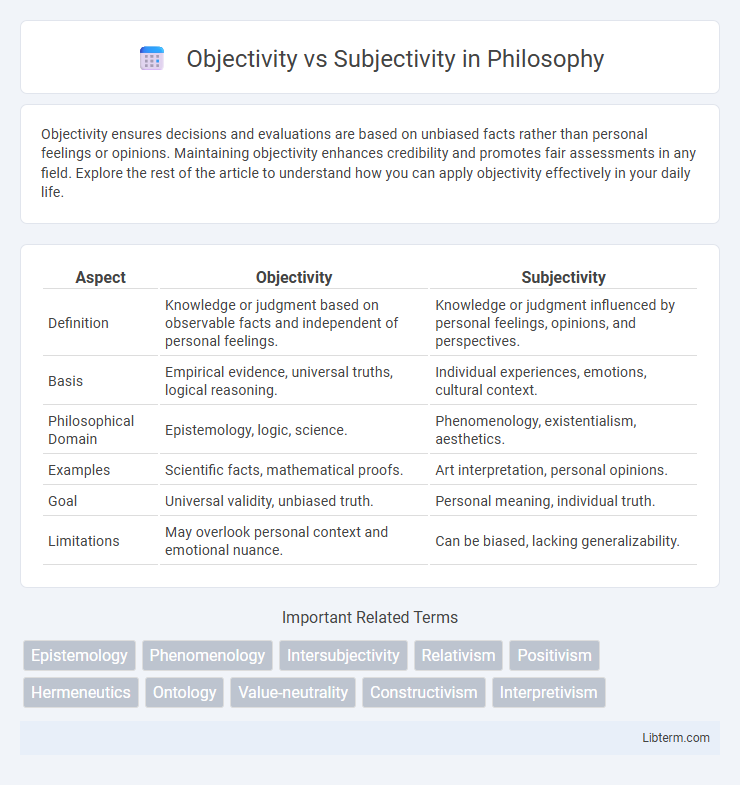
| Aspect | Objectivity | Subjectivity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Knowledge or judgment based on observable facts and independent of personal feelings. | Knowledge or judgment influenced by personal feelings, opinions, and perspectives. |
| Basis | Empirical evidence, universal truths, logical reasoning. | Individual experiences, emotions, cultural context. |
| Philosophical Domain | Epistemology, logic, science. | Phenomenology, existentialism, aesthetics. |
| Examples | Scientific facts, mathematical proofs. | Art interpretation, personal opinions. |
| Goal | Universal validity, unbiased truth. | Personal meaning, individual truth. |
| Limitations | May overlook personal context and emotional nuance. | Can be biased, lacking generalizability. |
Defining Objectivity and Subjectivity
Objectivity refers to the practice of relying on observable, measurable facts and evidence independent of personal feelings or biases, ensuring impartiality and universal validity. Subjectivity involves interpreting information through personal experiences, emotions, and perspectives, often resulting in varied and individual viewpoints. Defining objectivity emphasizes neutrality and consistency, while defining subjectivity highlights individual perception and emotional influence.
Historical Perspectives on Objectivity and Subjectivity
Historical perspectives on objectivity and subjectivity reveal shifting views across eras, with Enlightenment thinkers championing objectivity as essential for scientific progress while Romanticism emphasized individual experience and subjectivity. Philosophers such as Immanuel Kant bridged these concepts by proposing that objective knowledge arises through subjective cognitive structures. In modern discourse, objectivity remains central to empirical research, whereas subjectivity is acknowledged as crucial for understanding human consciousness and cultural contexts.
Key Differences Between Objective and Subjective Approaches
Objective approaches rely on observable, measurable facts and seek to eliminate personal bias, ensuring consistent and verifiable results. Subjective approaches prioritize individual perspectives, emotions, and interpretations, which can lead to diverse but less universally accepted outcomes. Key differences include objectivity's emphasis on impartiality and replicability versus subjectivity's focus on personal experience and context-driven analysis.
The Importance of Objectivity in Science and Research
Objectivity in science and research ensures that observations and conclusions are based on empirical evidence rather than personal biases or emotions, which enhances the reliability and validity of findings. Maintaining objectivity allows researchers to replicate studies and verify results, fostering scientific progress and trust in data interpretation. Emphasizing objective methodologies such as controlled experiments and peer review minimizes subjective influence, leading to more accurate and universally applicable knowledge.
Subjectivity in Art and Personal Expression
Subjectivity in art emphasizes the individual artist's unique perspective, emotions, and experiences, shaping personal expression through diverse styles and interpretations. Artistic subjectivity allows for emotional depth and nuance, enabling audiences to connect based on personal resonance rather than objective criteria. This focus on personal meaning fosters creativity and innovation, highlighting the fluid and dynamic nature of artistic expression.
Challenges of Maintaining Objectivity
Maintaining objectivity in research and decision-making processes faces challenges such as cognitive biases, emotional influences, and cultural perspectives that can skew judgment and interpretation of data. The difficulty in separating personal beliefs from factual evidence often leads to partiality, compromising the validity and reliability of outcomes. Consistent implementation of standardized methodologies and critical self-reflection are crucial to mitigating subjective distortions and preserving objectivity.
The Role of Bias in Shaping Perspectives
Bias fundamentally shapes perspectives by influencing the interpretation and evaluation of information through personal beliefs, experiences, and emotions. Objectivity seeks to minimize this bias by relying on facts, evidence, and impartial analysis, whereas subjectivity embraces individual viewpoints and emotions as integral to understanding. Understanding the role of bias is crucial for distinguishing between objective observations and subjective judgments in various contexts.
Balancing Objectivity and Subjectivity in Decision Making
Balancing objectivity and subjectivity in decision making involves integrating empirical data with personal judgment to achieve well-rounded outcomes. Objective analysis relies on factual evidence and measurable criteria, while subjective insights incorporate individual experience, intuition, and values. Effective decision making harnesses both approaches to address complex problems, ensuring rationality without neglecting human context and emotions.
Real-World Examples: Objectivity vs Subjectivity
Scientific research relies on objectivity to ensure findings are based on measurable evidence, such as clinical trials for new medications. In contrast, art critiques often embrace subjectivity, reflecting personal interpretations and emotional responses to works like Picasso's Guernica. Journalism aims for objectivity by reporting facts, but opinion columns intentionally incorporate subjectivity to express individual viewpoints.
Embracing Both Perspectives for Better Understanding
Embracing both objectivity and subjectivity fosters a deeper and more comprehensive understanding by balancing factual evidence with personal insights and experiences. Objective analysis provides unbiased data-driven conclusions, while subjective perspectives enrich interpretation through emotions and cultural context. This integration enhances decision-making, communication, and empathy across diverse disciplines and real-world scenarios.
Objectivity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com