A shadow minister is a member of the opposition party tasked with scrutinizing and challenging the policies and actions of their government counterpart. They play a crucial role in holding the ruling party accountable and developing alternative policies to present to voters. Discover how shadow ministers influence political debate and contribute to democratic governance in the full article.
Table of Comparison
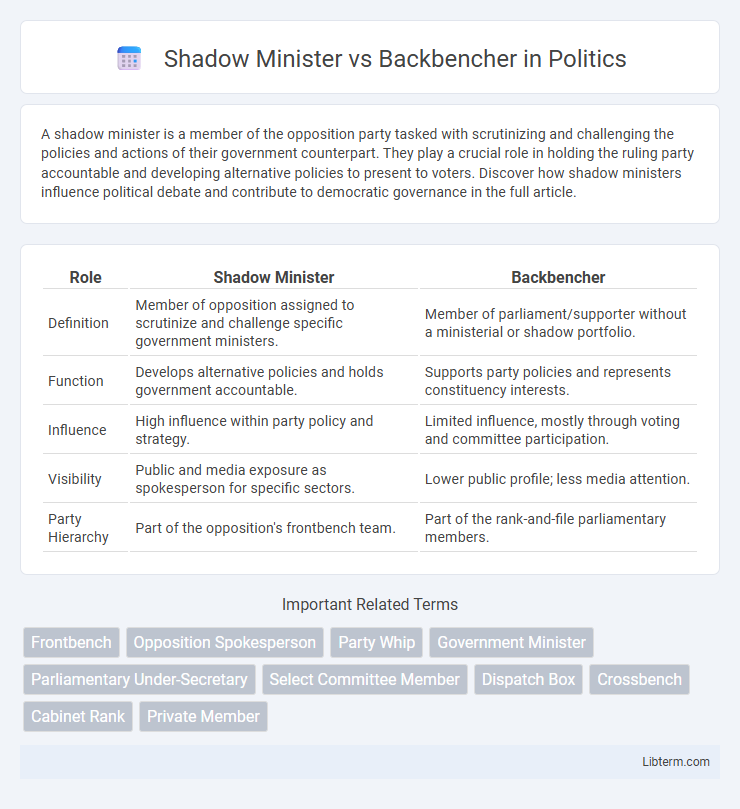
| Role | Shadow Minister | Backbencher |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Member of opposition assigned to scrutinize and challenge specific government ministers. | Member of parliament/supporter without a ministerial or shadow portfolio. |
| Function | Develops alternative policies and holds government accountable. | Supports party policies and represents constituency interests. |
| Influence | High influence within party policy and strategy. | Limited influence, mostly through voting and committee participation. |
| Visibility | Public and media exposure as spokesperson for specific sectors. | Lower public profile; less media attention. |
| Party Hierarchy | Part of the opposition's frontbench team. | Part of the rank-and-file parliamentary members. |
Introduction: Understanding Parliamentary Roles
The Shadow Minister plays a critical role in holding the government accountable by scrutinizing policies and offering alternative solutions, representing the opposition's stance in specific portfolios. Backbenchers, on the other hand, are legislators who do not hold ministerial or shadow ministerial positions, often focusing on constituency work and contributing to parliamentary debates from a less prominent platform. Understanding these roles highlights the balance of power and responsibility within parliamentary systems, emphasizing how governance and opposition interact to shape legislative processes.
Definition of a Shadow Minister
A Shadow Minister is a senior member of the opposition party assigned to scrutinize and challenge the policies and actions of a specific government minister. They develop alternative policies and hold the government accountable during parliamentary debates and committees. Unlike backbenchers, Shadow Ministers have formal roles within the opposition's shadow cabinet, contributing to strategic decision-making and public policy development.
Who is a Backbencher?
A backbencher is a Member of Parliament (MP) who does not hold a ministerial or shadow ministerial position and typically sits behind the frontbenchers in the parliamentary chamber. They play a crucial role in representing their constituents, participating in debates, and serving on committees without the responsibilities of shaping government or opposition policy directly. Unlike shadow ministers who scrutinize government actions and propose alternative policies, backbenchers influence legislation through voting and advocacy within their party and parliamentary framework.
Key Responsibilities of a Shadow Minister
Shadow Ministers hold defined portfolios within the opposition party, tasked with scrutinizing government policy and proposing alternatives in their specific area, such as health, education, or finance. Their key responsibilities include developing party policy, holding the corresponding government minister accountable through parliamentary debates and committees, and engaging with stakeholders to build informed critiques and effective policy responses. Backbenchers, by contrast, are typically members without ministerial or shadow ministerial roles, primarily supporting party positions and contributing to legislative discussions without direct policy portfolio management.
Daily Duties of a Backbencher
Backbenchers primarily focus on representing their constituents' interests, attending parliamentary debates, and voting on legislation, without holding ministerial responsibilities. They actively participate in committee work and contribute to policy discussions, providing support or opposition to government initiatives. Unlike Shadow Ministers, backbenchers have limited influence over party strategy and ministerial decisions but play a crucial role in holding the government accountable through questioning and scrutiny.
Influence on Policy: Shadow Ministers vs Backbenchers
Shadow Ministers hold significant influence on policy by scrutinizing government actions and shaping opposition strategies within their designated portfolios, often proposing alternative policies to challenge current legislation. Backbenchers, while less prominent, can impact policy through committee participation, raising constituency concerns, and influencing party debates, though their direct policy-making power remains limited compared to Shadow Ministers. The defined roles and access to party leadership grant Shadow Ministers a more strategic position in molding national policy than backbenchers.
Accountability and Public Profile
Shadow Ministers hold specific accountability by scrutinizing government policies and proposing alternatives within a defined portfolio, enhancing their public profile through media coverage and parliamentary debates. Backbenchers primarily focus on representing constituents and holding the government to account through committee work and private members' motions, maintaining a lower public profile due to less direct involvement in high-profile policy areas. The distinct roles impact their visibility and perceived responsibility, with Shadow Ministers often seen as future cabinet candidates, while Backbenchers provide essential grassroots oversight.
Pathways to Political Advancement
Shadow Ministers often gain political advancement through prominent roles in opposition parties, showcasing expertise by scrutinizing government policies and leading alternative proposals. Backbenchers progress by building constituency support, contributing to party strategy, and earning appointments to committees or junior ministerial positions. Both pathways require consistent party loyalty and effective parliamentary performance to secure higher leadership opportunities.
Impact on Legislation and Debates
Shadow Ministers play a critical role in shaping legislation and influencing parliamentary debates by scrutinizing government policies, proposing alternative solutions, and holding the ruling party accountable, thereby enhancing the quality and depth of legislative discussions. Backbenchers contribute to debates primarily by representing their constituents' interests, participating in committee work, and occasionally introducing private member's bills, which can impact legislation indirectly. While Shadow Ministers have a more direct and strategic influence on policy formulation and legislative agendas, Backbenchers provide essential grassroots perspectives and support democratic discourse within the parliament.
Conclusion: Comparing Shadow Ministers and Backbenchers
Shadow Ministers hold key roles in opposition parties, responsible for scrutinizing government policies and proposing alternatives, while Backbenchers primarily support party agendas without specific portfolios. The influence of Shadow Ministers is significantly greater due to their leadership responsibilities and media visibility, whereas Backbenchers contribute through committee work and constituency representation. Understanding these distinctions highlights the structured hierarchy and function within parliamentary systems.
Shadow Minister Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com