A breach of privilege occurs when a person's legal protections, such as parliamentary or attorney-client privileges, are violated, compromising confidentiality or immunity. Such breaches can result in serious legal consequences and undermine the integrity of institutional processes. Discover how breaches of privilege impact your rights and what measures safeguard your interests in the full article.
Table of Comparison
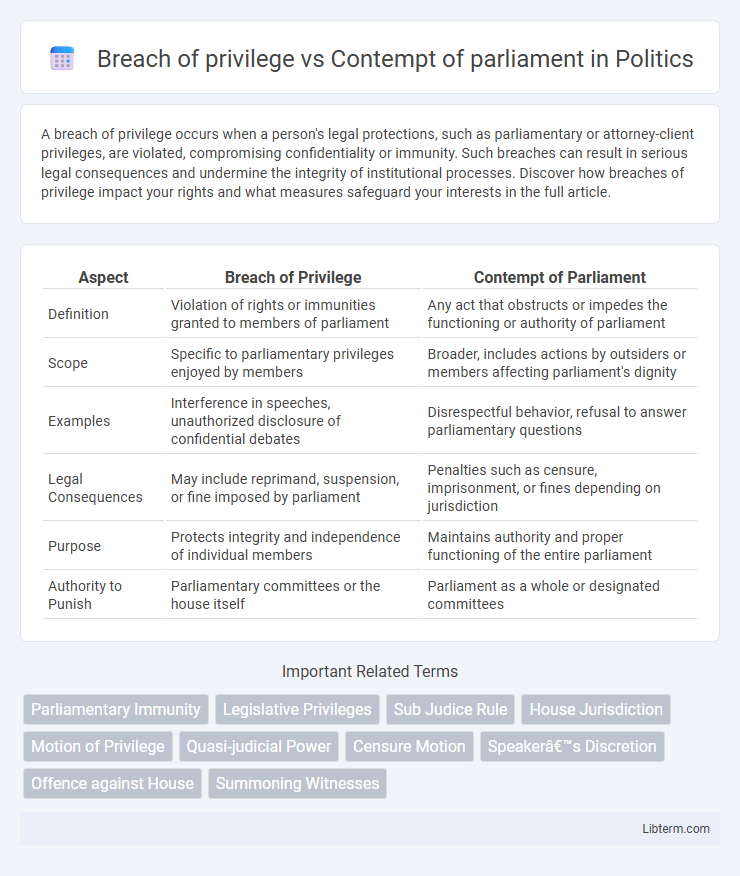
| Aspect | Breach of Privilege | Contempt of Parliament |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Violation of rights or immunities granted to members of parliament | Any act that obstructs or impedes the functioning or authority of parliament |
| Scope | Specific to parliamentary privileges enjoyed by members | Broader, includes actions by outsiders or members affecting parliament's dignity |
| Examples | Interference in speeches, unauthorized disclosure of confidential debates | Disrespectful behavior, refusal to answer parliamentary questions |
| Legal Consequences | May include reprimand, suspension, or fine imposed by parliament | Penalties such as censure, imprisonment, or fines depending on jurisdiction |
| Purpose | Protects integrity and independence of individual members | Maintains authority and proper functioning of the entire parliament |
| Authority to Punish | Parliamentary committees or the house itself | Parliament as a whole or designated committees |
Understanding Parliamentary Privilege
Breach of privilege refers to the violation of the rights and immunities granted to members of parliament to perform their legislative functions without external interference. Contempt of parliament encompasses actions that obstruct or hinder the authority and dignity of the legislative body, including breaches of privilege and other misconducts that undermine parliamentary proceedings. Understanding parliamentary privilege involves recognizing these protections that ensure free debate, freedom from arrest in certain cases, and non-interference in legislative activities, critical for maintaining parliamentary sovereignty and effective governance.
Defining Breach of Privilege
Breach of privilege refers to any act that obstructs or impedes a legislator in the performance of their official duties, violating the special rights and immunities granted to members of parliament. It protects parliamentary functions by ensuring members can conduct business without external interference or intimidation. This concept differs from contempt of parliament, which broadly covers behavior that disrespects or disobeys the authority of the legislative body itself.
What Constitutes Contempt of Parliament?
Contempt of Parliament constitutes any act that obstructs or impedes the functioning or authority of a parliamentary body, including disobedience to its orders, disruption of proceedings, or refusal to testify when summoned. It encompasses behaviors such as lying to Parliament, withholding evidence, or revealing confidential information without authorization. Breach of privilege, a subset of contempt, specifically involves violation of the special rights or immunities granted to members or institutions of Parliament.
Key Differences: Breach of Privilege vs Contempt of Parliament
Breach of privilege involves actions that impede the rights or immunities of members of parliament, whereas contempt of parliament covers any behavior that obstructs the legislature's authority or dignity. Breach of privilege specifically protects parliamentary functions and its members, while contempt includes a broader range of conduct disrespecting the institution or its orders. Enforcement of breach of privilege often entails specific parliamentary privileges, whereas contempt proceedings address general misconduct affecting parliamentary proceedings.
Historical Cases of Breach of Privilege
Historical cases of breach of privilege in parliamentary systems reveal instances where members or outsiders have attempted to obstruct or insult the functioning of the legislature, such as the 1629 incident with the English MPs challenging King Charles I's authority. Breach of privilege involves violations of parliamentary immunities or powers, preserving legislative independence, whereas contempt of parliament broadly covers acts that obstruct or disrespect the legislature without necessarily infringing on its core privileges. The 19th-century case of John Wilkes exemplifies breach of privilege, highlighting tensions between individual rights and parliamentary authority in safeguarding legislative integrity.
Notable Examples of Contempt of Parliament
Notable examples of Contempt of Parliament include the refusal of witnesses to comply with parliamentary subpoenas, such as the 2018 case in the UK where a former Brexit minister was held in contempt for not providing documents. In India, the 2016 incident involving the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) was significant when it was found guilty of contempt for ignoring parliamentary directives. These instances underscore the serious consequences faced when individuals or bodies obstruct the legislative process, distinguishing Contempt of Parliament from Breach of Privilege, which typically involves direct interference with the rights and immunities of the members of parliament.
Legal Provisions and Constitutional Basis
Breach of privilege in parliamentary law refers to the violation of rights and immunities essential for the legislature's functioning, grounded in Article 105 and 194 of the Indian Constitution, which empower legislatures to punish breaches to ensure independence and authority. Contempt of Parliament involves acts that obstruct or undermine parliamentary proceedings, drawing authority from the same constitutional provisions alongside Parliament's inherent powers to safeguard dignity and discipline. Both concepts maintain legislative supremacy but differ as breach of privilege is a specific infraction against members or the institution, whereas contempt addresses broader disruptions to parliamentary operations.
Investigative Procedures and Powers
Breach of privilege involves the violation of legislative members' rights or the institution's privileges, prompting parliamentary committees to exercise powers like summoning witnesses, examining documents, and demanding testimony under oath. Contempt of parliament encompasses actions that obstruct or disrespect parliamentary proceedings, leading to investigative procedures such as inquiries, hearings, and sanctions authorized by parliamentary rules. Both offenses empower legislatures to deploy coercive measures including fines, imprisonment, or suspension to uphold authority and ensure compliance during investigations.
Punishments and Consequences
Breach of privilege typically results in sanctions such as suspension, fines, or reprimands specific to parliamentary members, aiming to uphold legislative integrity. Contempt of Parliament often carries more severe penalties, including imprisonment, fines, or even arrest, reflecting the offense's impact on the authority and functioning of the legislature. Both punishments serve to reinforce the principle of parliamentary sovereignty and ensure compliance with parliamentary rules and decorum.
Safeguarding Democratic Accountability
Breach of privilege involves actions that violate the rights or immunities of parliamentary members, directly challenging the institution's authority. Contempt of Parliament encompasses conduct that obstructs or undermines parliamentary proceedings, threatening the integrity of legislative functions. Both offenses are crucial for safeguarding democratic accountability by ensuring members and external parties respect parliamentary sovereignty and maintain transparency in governance.
Breach of privilege Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com