Incremental policy focuses on making small, gradual adjustments to existing policies rather than implementing large-scale changes all at once, which helps minimize risks and unforeseen consequences. This approach leverages feedback and real-world results to continuously refine and improve policy outcomes. Discover how incremental policy can enhance your decision-making process by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
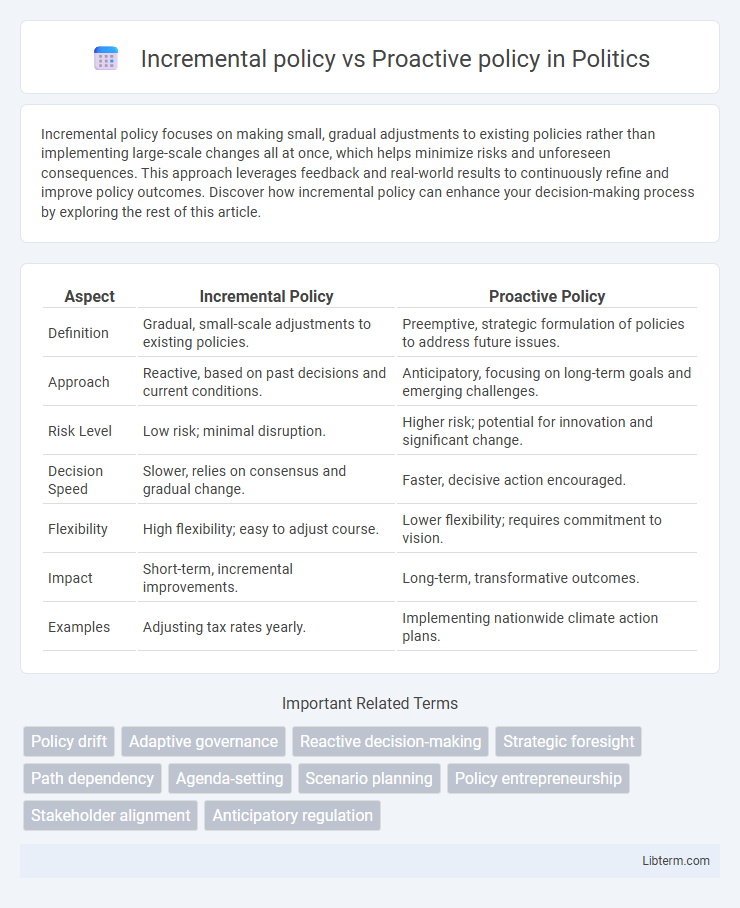
| Aspect | Incremental Policy | Proactive Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual, small-scale adjustments to existing policies. | Preemptive, strategic formulation of policies to address future issues. |
| Approach | Reactive, based on past decisions and current conditions. | Anticipatory, focusing on long-term goals and emerging challenges. |
| Risk Level | Low risk; minimal disruption. | Higher risk; potential for innovation and significant change. |
| Decision Speed | Slower, relies on consensus and gradual change. | Faster, decisive action encouraged. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; easy to adjust course. | Lower flexibility; requires commitment to vision. |
| Impact | Short-term, incremental improvements. | Long-term, transformative outcomes. |
| Examples | Adjusting tax rates yearly. | Implementing nationwide climate action plans. |
Understanding Incremental Policy: Definition and Principles
Incremental policy refers to a method of public policymaking that involves small, gradual adjustments to existing policies rather than sweeping reforms, emphasizing feasibility and risk reduction. This approach relies on continuous evaluation and minor modifications informed by experience, practical feedback, and evolving circumstances. Core principles include limited changeability, bounded rationality, and consensus-building among stakeholders to ensure stability and adaptability in policy implementation.
Proactive Policy Explained: Key Attributes
Proactive policy prioritizes anticipatory actions and risk mitigation before issues arise, emphasizing continuous monitoring and early intervention. It integrates data analytics and predictive modeling to enhance decision-making and resource allocation, ensuring optimal outcomes. Key attributes include forward-looking strategies, adaptive frameworks, and strong stakeholder engagement to preempt challenges effectively.
Major Differences Between Incremental and Proactive Policies
Incremental policies involve small, gradual changes to existing frameworks, focusing on short-term adjustments and minimizing risks, while proactive policies emphasize forward-looking, strategic planning aimed at long-term goals and prevention of future issues. Incremental approaches rely heavily on past experiences and incremental learning, whereas proactive policies anticipate challenges and innovate solutions to address systemic problems before they escalate. The major difference lies in reactive adaptation versus strategic anticipation, with incremental policies being more flexible but slower to effect change compared to the comprehensive, goal-oriented nature of proactive policies.
Advantages of Incremental Policy Approaches
Incremental policy approaches offer the advantage of flexibility by allowing gradual adjustments based on real-time feedback and evolving circumstances, reducing the risk of large-scale failures. They facilitate stakeholder engagement and consensus-building through continuous, manageable changes, enhancing policy acceptance and effectiveness. Incrementalism also enables better allocation of resources by focusing on immediate issues and prioritizing incremental improvements over comprehensive reforms.
Benefits of Proactive Policy Strategies
Proactive policy strategies enable organizations to anticipate challenges and implement solutions before issues escalate, improving long-term operational efficiency and risk management. These policies foster innovation by encouraging continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving market conditions. Early intervention through proactive measures reduces costs associated with crisis management and regulatory compliance failures.
Drawbacks of Incremental Policymaking
Incremental policymaking often suffers from slow adaptation to rapidly changing environments due to its focus on small, gradual adjustments rather than comprehensive reform. This approach can perpetuate existing inefficiencies and fail to address underlying systemic problems, leading to fragmented and inconsistent policy outcomes. Limited scope and short-term focus hinder the ability to respond effectively to complex, long-term challenges such as climate change or economic crises.
Challenges of Proactive Policymaking
Proactive policymaking faces significant challenges such as anticipating future trends amid uncertain data and rapidly changing socio-economic conditions, which can lead to misaligned policy outcomes. The complexity of integrating diverse stakeholder interests and predicting long-term impacts often results in resource-intensive processes that may delay implementation. Furthermore, the reliance on advanced data analytics and forecasting models increases vulnerability to errors and biases, complicating effective decision-making.
Real-World Examples: Incremental vs Proactive Policies
Incremental policies focus on small, gradual changes as seen in the UK's National Health Service reforms, which evolved through minor adjustments over decades. Proactive policies, exemplified by Singapore's water conservation strategy, anticipate future challenges and implement comprehensive measures like rainwater harvesting and wastewater recycling early on. Real-world outcomes demonstrate incremental policies often adapt to immediate feedback, while proactive policies drive long-term sustainability and innovation.
Impact on Organizational Decision-Making
Incremental policy encourages gradual decision-making through small, reversible steps, allowing organizations to adapt and learn from intermediate outcomes, reducing the risk of large-scale failures. Proactive policy emphasizes foresight and strategic planning, enabling organizations to anticipate challenges and shape outcomes, which can lead to more decisive and transformative decisions. The impact on organizational decision-making is that incremental policy fosters flexibility and continuous improvement, while proactive policy drives innovation and long-term vision alignment.
Choosing the Right Policy Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right policy approach involves evaluating the urgency and scope of the issue, where incremental policy suits gradual, low-risk changes, and proactive policy addresses complex problems requiring immediate, comprehensive action. Consider stakeholder involvement, resource availability, and potential long-term impacts to determine whether small adjustments or forward-thinking strategies better achieve desired outcomes. Policymakers must balance flexibility with foresight to optimize effectiveness and sustainability in decision-making.
Incremental policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com