State autonomy allows regions to govern themselves with minimal interference from central authorities, enabling tailored policies that reflect local needs and cultural identities. This independence supports efficient decision-making and fosters innovation at the local level. Explore the article to understand how state autonomy impacts governance and benefits your community.
Table of Comparison
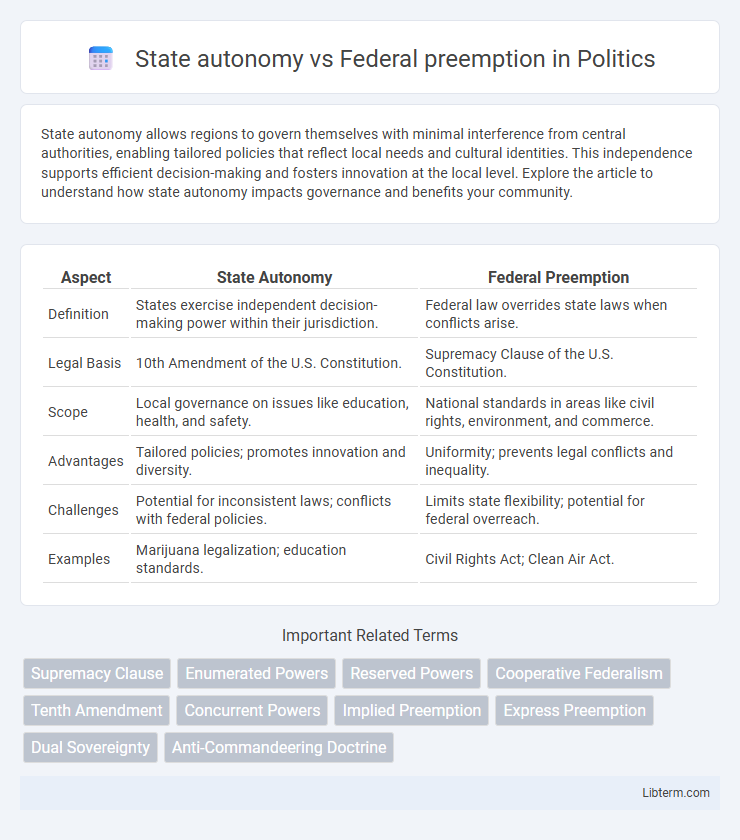
| Aspect | State Autonomy | Federal Preemption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | States exercise independent decision-making power within their jurisdiction. | Federal law overrides state laws when conflicts arise. |
| Legal Basis | 10th Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. | Supremacy Clause of the U.S. Constitution. |
| Scope | Local governance on issues like education, health, and safety. | National standards in areas like civil rights, environment, and commerce. |
| Advantages | Tailored policies; promotes innovation and diversity. | Uniformity; prevents legal conflicts and inequality. |
| Challenges | Potential for inconsistent laws; conflicts with federal policies. | Limits state flexibility; potential for federal overreach. |
| Examples | Marijuana legalization; education standards. | Civil Rights Act; Clean Air Act. |
Understanding State Autonomy: Definition and Importance
State autonomy refers to the authority of individual states to govern themselves without undue interference from the federal government, preserving their ability to enact laws and policies tailored to local needs. This autonomy is crucial for maintaining a balance of power within the federal system, allowing states to experiment with diverse regulatory frameworks and protect regional interests. Understanding state autonomy highlights the importance of decentralized governance in fostering innovation, responsiveness, and democratic participation at the state level.
Federal Preemption: Scope and Legal Foundations
Federal preemption derives from the Supremacy Clause of the U.S. Constitution, which establishes that federal law overrides conflicting state laws. The scope of federal preemption includes express preemption, where Congress explicitly states its intent to preempt state law, and implied preemption, which covers both field preemption, preventing states from regulating in areas dominated by federal interest, and conflict preemption, where state law conflicts with federal objectives. Judicial interpretations often hinge on Congressional intent and the balance between preserving state autonomy and ensuring uniform national regulation.
Historical Context: Evolution of Power Balance
The historical evolution of power balance between state autonomy and federal preemption reflects key moments such as the drafting of the U.S. Constitution, where the Supremacy Clause established federal law's primacy over conflicting state statutes. Landmark Supreme Court cases like McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) affirmed federal authority, while the New Deal era expanded federal regulatory powers, often overriding state discretion to address national economic crises. Over time, shifts in political ideology and federalism debates have continually redefined the tension between state sovereignty and federal preemption in American governance.
Key Legal Doctrines and Landmark Cases
State autonomy and federal preemption are governed by key legal doctrines including the Supremacy Clause of the U.S. Constitution, which establishes that federal law overrides conflicting state laws. Landmark cases such as McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) affirmed federal power over states by rejecting state interference with federal institutions, while Arizona v. United States (2012) clarified limits on state regulation when federal immigration laws occupy the field. These doctrines and rulings shape the balance between state sovereignty and federal authority in American constitutional law.
Areas of Frequent Conflict: Health, Environment, and Commerce
State autonomy often clashes with federal preemption in healthcare, environmental regulation, and commerce due to divergent policy priorities and regulatory standards. States may implement stricter health mandates or environmental protections that exceed federal requirements, leading to legal disputes over jurisdiction and enforcement authority. Commercial regulations, such as consumer protection and labor laws, frequently become battlegrounds where states seek to preserve local control while federal statutes aim for uniformity across the nation.
Impact on Policy Innovation and Local Governance
State autonomy fosters policy innovation by allowing states to experiment with diverse approaches tailored to their unique populations, which can lead to effective localized solutions not feasible under uniform federal mandates. Federal preemption restricts this flexibility, often imposing national standards that may stifle creative problem-solving and diminish the responsiveness of local governments to community-specific needs. The balance between state autonomy and federal preemption significantly shapes the capacity of policymakers to address complex social, economic, and environmental challenges through adaptive governance frameworks.
The Role of Courts in Resolving Jurisdictional Disputes
Courts play a pivotal role in resolving jurisdictional disputes between state autonomy and federal preemption by interpreting the Supremacy Clause of the U.S. Constitution. Judicial decisions often balance state interests against federal regulatory objectives, determining when federal laws override conflicting state statutes. Landmark cases like McCulloch v. Maryland and Arizona v. United States illustrate how courts delineate the boundaries of state sovereignty within the federal system.
Benefits and Drawbacks of State Autonomy
State autonomy allows individual states to tailor laws and policies to best fit their unique demographics, economic conditions, and cultural values, fostering innovation and responsiveness at the local level. This decentralized approach can lead to more effective governance and experimentation with diverse solutions to social and economic issues. However, state autonomy may result in inconsistencies across state lines, hindering national cohesion and creating challenges for businesses and citizens navigating varying regulations.
Federal Preemption: Arguments for Uniformity and Efficiency
Federal preemption ensures uniformity across states by establishing consistent regulations that prevent conflicting state laws, which streamlines compliance for businesses operating nationwide. It promotes efficiency by reducing regulatory fragmentation, lowering administrative costs, and enabling cohesive policy implementation in areas such as environmental standards and consumer protection. Uniform federal laws also enhance legal clarity and predictability, facilitating smoother interstate commerce and reducing litigation risks.
Future Trends and Implications for Federalism
Emerging trends indicate a nuanced balance between state autonomy and federal preemption, with states increasingly asserting their rights in areas like environmental regulation, healthcare, and data privacy while federal oversight expands in national security and interstate commerce. Legal battles and Supreme Court decisions continue to define the limits of state versus federal authority, influencing the evolving dynamic of American federalism. This tension shapes policy innovation at the state level and the uniformity of national standards, impacting governance and citizen rights across the United States.
State autonomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com