An inquiry is a systematic process of seeking information or clarification about a specific topic or issue, often used in research, investigations, or customer service. It involves asking questions, gathering relevant data, and analyzing findings to arrive at a clear understanding or decision. Discover how inquiries can improve Your knowledge and problem-solving skills throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
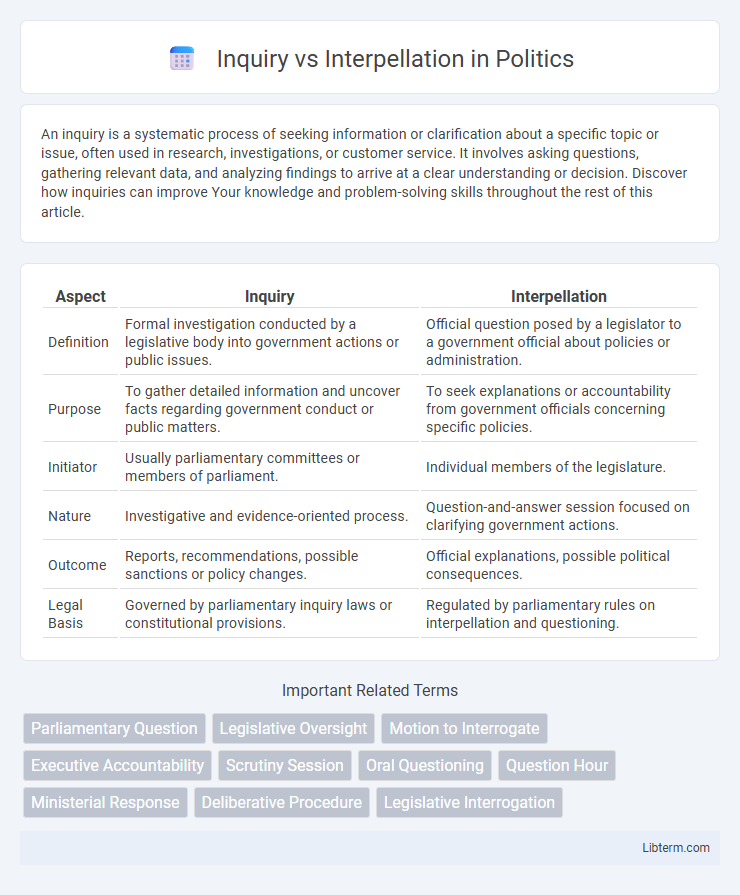
| Aspect | Inquiry | Interpellation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal investigation conducted by a legislative body into government actions or public issues. | Official question posed by a legislator to a government official about policies or administration. |
| Purpose | To gather detailed information and uncover facts regarding government conduct or public matters. | To seek explanations or accountability from government officials concerning specific policies. |
| Initiator | Usually parliamentary committees or members of parliament. | Individual members of the legislature. |
| Nature | Investigative and evidence-oriented process. | Question-and-answer session focused on clarifying government actions. |
| Outcome | Reports, recommendations, possible sanctions or policy changes. | Official explanations, possible political consequences. |
| Legal Basis | Governed by parliamentary inquiry laws or constitutional provisions. | Regulated by parliamentary rules on interpellation and questioning. |
Understanding the Concepts: Inquiry and Interpellation
Inquiry involves a formal process of questioning or investigating a subject to gain information or clarify facts, commonly used in legislative or academic contexts. Interpellation is a specific form of political questioning where a member of a legislative body formally demands explanations from the government or officials about policies or actions. Both concepts focus on obtaining detailed responses, but inquiry broadly encompasses fact-finding, whereas interpellation centers on accountability and political oversight.
Defining Inquiry: Purpose and Process
Inquiry serves as a systematic process aimed at gathering detailed information, examining issues, and clarifying facts to support informed decision-making in legislative or institutional contexts. The purpose of inquiry is to investigate specific matters thoroughly, often through hearings, evidence collection, and expert testimonies, ensuring transparency and accountability. This process is designed to uncover the root causes of problems, evaluate policies, and recommend actions without directly challenging individual responsibilities.
What is Interpellation? Key Characteristics
Interpellation is a political process where legislators formally question government officials to hold them accountable, often related to policy decisions and administrative actions. Key characteristics include its role as a tool of parliamentary oversight, the necessity for the questioned official to provide detailed explanations, and its formal procedure defined by legislative rules. This mechanism promotes transparency and ensures executive responsibility within a democratic framework.
Historical Context: Evolution of Inquiry and Interpellation
Inquiry and interpellation evolved through different historical trajectories, with inquiry rooted in the development of parliamentary systems emphasizing accountability and transparency since the 19th century. Interpellation originated in European parliamentary practices, particularly in France and Belgium, as a formal mechanism for legislators to question government officials, gaining prominence in the early 20th century. Both processes reflect the evolution of democratic governance and the institutionalization of checks and balances within legislative bodies.
Legal Frameworks: When Are Inquiries and Interpellations Used?
In legal frameworks, inquiries are typically formal investigations initiated to examine specific issues or allegations within government or organizational structures, often led by appointed committees or investigators with the authority to gather evidence and summon witnesses. Interpellations, on the other hand, are procedural tools used primarily in parliamentary systems, allowing legislators to question government officials or ministers directly to obtain explanations on policies, actions, or decisions. Inquiries are used when detailed fact-finding is necessary to hold entities accountable, while interpellations serve as a means for legislative oversight and immediate governmental accountability during sessions.
Main Differences: Inquiry vs Interpellation
Inquiry is a formal process of seeking information or clarification, typically through structured questioning to gather facts or understand issues, often used in administrative or legislative contexts. Interpellation specifically refers to the act where members of a legislative body question government officials or the executive to hold them accountable for policies or actions. The main difference lies in Inquiry's broader scope of information-gathering versus Interpellation's targeted political oversight within parliamentary systems.
Functions in Government and Legislation
Inquiry serves as a formal mechanism for gathering information and clarifying facts within government institutions, primarily aiming to ensure transparency and accountability in public administration. Interpellation functions as a constitutional tool allowing legislators to question executive officers or government officials directly, compelling them to explain policies or decisions and facilitating legislative oversight. Both mechanisms strengthen democratic governance by promoting checks and balances through systematic scrutiny of government actions and legislative processes.
Impact on Accountability and Transparency
Inquiry and interpellation significantly enhance accountability and transparency by allowing legislative bodies to question government officials and demand explanations regarding public policies and actions. Inquiry provides a structured mechanism for in-depth investigation and gathering evidence, promoting thorough oversight and exposure of irregularities. Interpellation, often used for immediate clarification, pressures executives to respond publicly, increasing transparency and deterring misconduct.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Inquiry in government typically involves formal investigations to gather facts and evidence about specific public issues, as seen in the UK's Chilcot Inquiry into the Iraq War, which examined decisions and outcomes without holding individuals politically accountable. Interpellation, often practiced in parliamentary systems like France and India, requires government officials to respond directly to questions posed by legislators, exemplified by India's frequent interpellations during parliamentary sessions addressing policy or administrative concerns. Case studies demonstrate that while inquiries provide comprehensive reports and recommendations, interpellations foster immediate political accountability and dialogue within legislative bodies.
Choosing the Right Mechanism: Inquiry or Interpellation
Choosing the right mechanism between inquiry and interpellation depends on the objective and context of parliamentary oversight. Inquiry is a comprehensive tool suited for gathering detailed information and investigating broader issues, often involving committees and extensive documentation. Interpellation serves as a direct and immediate question posed to government officials, ideal for seeking clarification and holding them accountable during sessions.
Inquiry Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com