Democracy empowers citizens to participate in decision-making through elections and representative institutions, ensuring accountability and protection of individual rights. It fosters transparency and inclusivity, allowing diverse voices to shape policies that impact society. Explore how democracy shapes your community and the global landscape in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
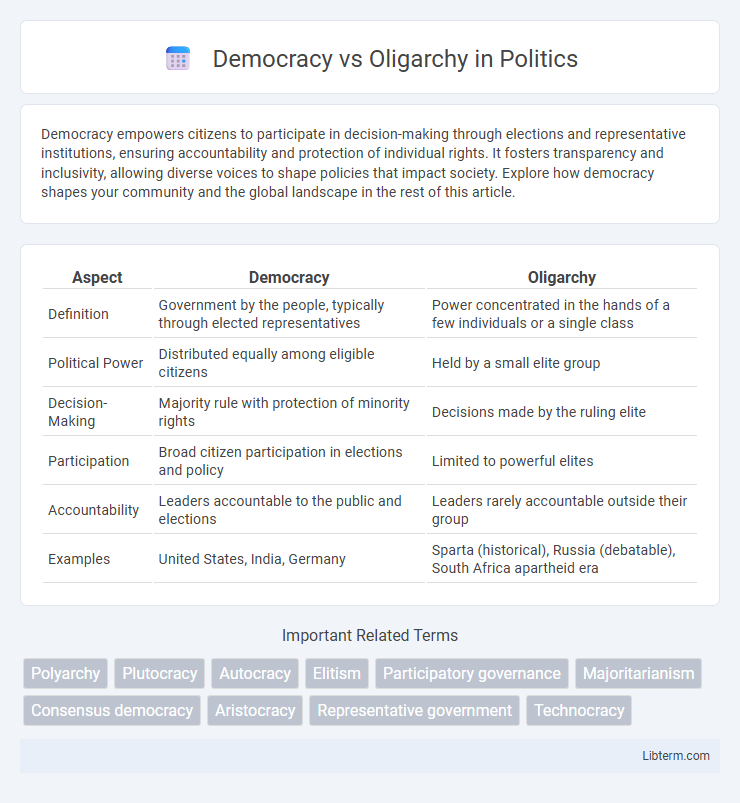
| Aspect | Democracy | Oligarchy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government by the people, typically through elected representatives | Power concentrated in the hands of a few individuals or a single class |
| Political Power | Distributed equally among eligible citizens | Held by a small elite group |
| Decision-Making | Majority rule with protection of minority rights | Decisions made by the ruling elite |
| Participation | Broad citizen participation in elections and policy | Limited to powerful elites |
| Accountability | Leaders accountable to the public and elections | Leaders rarely accountable outside their group |
| Examples | United States, India, Germany | Sparta (historical), Russia (debatable), South Africa apartheid era |
Defining Democracy: Principles and Practice
Democracy is a political system grounded in the principles of political equality, popular sovereignty, and majority rule, ensuring that citizens have the power to participate in decision-making processes through free and fair elections. Its practice involves institutional mechanisms such as representative assemblies, constitutional protections of individual rights, and transparent governance that holds leaders accountable to the public. The core objective of democracy is to promote inclusive participation and safeguard civil liberties while preventing the concentration of power characteristic of oligarchic regimes.
Understanding Oligarchy: Core Characteristics
Oligarchy is a political system where power is concentrated in the hands of a small, elite group, often based on wealth, family ties, or military control. This concentration restricts broader public participation in governance, leading to decisions that primarily serve the interests of the ruling minority. The lack of political competition and limited accountability often result in policies that exacerbate social inequalities and undermine democratic principles.
Historical Origins of Democracy and Oligarchy
Democracy originated in ancient Athens around the 5th century BCE, where citizens participated directly in decision-making processes, marking a shift from monarchic or aristocratic rule. Oligarchy, conversely, has roots in various ancient civilizations like Sparta, where power was concentrated in the hands of a small elite class based on wealth or military strength. These contrasting governance systems reflect differing approaches to political power and citizen inclusion in early human societies.
Key Differences Between Democracy and Oligarchy
Democracy is a political system where power is vested in the hands of the majority of citizens through free and fair elections, promoting equal participation and representation. Oligarchy concentrates power in the hands of a small, elite group that controls decision-making and resources, limiting political influence to a select few. The key differences between democracy and oligarchy revolve around the distribution of power, citizen participation, and the mechanisms for accountability and governance.
Citizen Participation: Democracy vs Oligarchy
Democracy maximizes citizen participation by allowing individuals to vote, run for office, and influence policy decisions through direct or representative means. In contrast, oligarchy limits participation to a small, privileged group, restricting the broader population's ability to affect governance. This disparity in involvement often leads to more inclusive and accountable decision-making processes in democracies compared to the concentration of power in oligarchies.
Power Distribution in Both Systems
Democracy ensures power distribution through elected representatives, allowing citizens to participate in decision-making processes and promoting political equality. In contrast, oligarchy concentrates power in the hands of a small group or elite, limiting broader public influence and centralizing control. This stark difference in power allocation impacts governance, accountability, and civil liberties in each system.
Pros and Cons of Democracy
Democracy ensures political participation and accountability by allowing citizens to elect representatives and influence decisions directly or indirectly, fostering equality and protection of individual rights. However, it can result in slower decision-making processes due to the need for consensus and may be vulnerable to populism or misinformation influencing voter behavior. Despite these challenges, democracies typically promote transparency and adaptability compared to oligarchies, where power is concentrated among a few, often limiting public input and risking authoritarianism.
Pros and Cons of Oligarchy
Oligarchy, a system where power is concentrated in the hands of a few, offers efficient decision-making and political stability due to centralized control. However, it often leads to reduced political participation, limited representation, and increased risk of corruption and inequality. The lack of accountability in oligarchic systems can suppress individual freedoms and hinder social mobility.
Modern Examples of Democracy and Oligarchy
Modern democracy is exemplified by nations like the United States, Germany, and India, where power is vested in elected representatives and citizens participate in free and fair elections. Contemporary oligarchies include Russia and Saudi Arabia, where political power is concentrated in the hands of a few elite individuals or families, limiting broad public influence. The contrast between these systems is reflected in governance transparency, citizen engagement, and the distribution of political authority.
Which System Fosters Better Governance?
Democracy fosters better governance by promoting inclusive decision-making and accountability through regular elections where citizens exercise their voting rights, ensuring leaders represent the public interest. Oligarchy, dominated by a small group of elites, often leads to governance that prioritizes their interests, reducing transparency and increasing the risk of corruption. Empirical studies indicate democracies tend to achieve higher levels of development, political stability, and social welfare compared to oligarchic regimes.
Democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com