Recess plays a crucial role in children's development by promoting physical activity, social skills, and cognitive growth. Regular breaks during the school day help improve focus and reduce stress, making learning more effective. Discover how recess benefits Your child's overall well-being and academic success in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
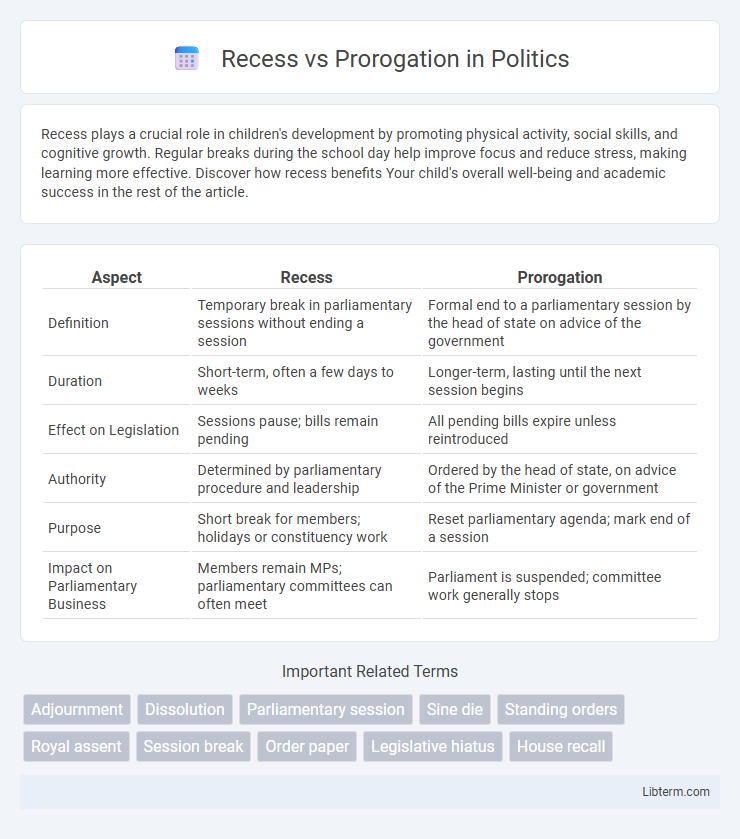
| Aspect | Recess | Prorogation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary break in parliamentary sessions without ending a session | Formal end to a parliamentary session by the head of state on advice of the government |
| Duration | Short-term, often a few days to weeks | Longer-term, lasting until the next session begins |
| Effect on Legislation | Sessions pause; bills remain pending | All pending bills expire unless reintroduced |
| Authority | Determined by parliamentary procedure and leadership | Ordered by the head of state, on advice of the Prime Minister or government |
| Purpose | Short break for members; holidays or constituency work | Reset parliamentary agenda; mark end of a session |
| Impact on Parliamentary Business | Members remain MPs; parliamentary committees can often meet | Parliament is suspended; committee work generally stops |
Introduction: Understanding Parliamentary Breaks
Recess and prorogation are key parliamentary breaks with distinct purposes and impacts on legislative processes. Recess refers to short-term pauses allowing members to address constituency duties and personal affairs without dissolving the session. Prorogation ends a parliamentary session, suspending all business until the next session convenes, often used strategically by governments.
Defining Recess and Prorogation
Recess refers to a temporary break within a legislative session, allowing members to pause proceedings without ending the session itself. Prorogation is the formal end of a legislative session, suspending all parliamentary activities until a new session is summoned. Both mechanisms control the timing and flow of legislative work but differ in duration and procedural implications.
Key Differences Between Recess and Prorogation
Recess refers to a temporary break in a legislative session during which the parliament or congress pauses its proceedings but retains its authority to resume without formal closure. Prorogation, by contrast, marks the formal ending of a parliamentary session, suspending all legislative business until the next session begins, effectively clearing all pending bills unless reintroduced. Key differences include duration, with recess being shorter and intended for breaks like holidays, while prorogation is a formal closure impacting legislative continuity and procedural resets.
Legal Basis for Recess and Prorogation
Recess and prorogation both represent pauses in legislative sessions but differ in their legal foundations. Recess is typically mandated by a legislature's internal rules or statutes, allowing temporary breaks without dissolving the session, while prorogation is a formal executive act, often by the head of state or government, that formally ends a legislative session and pauses all parliamentary business. The legal basis for prorogation usually stems from constitutional or statutory provisions granting executive authority to conclude a session, contrasting with recess, which arises from procedural rules within the legislature.
Procedural Processes: How Recess and Prorogation Occur
Recess occurs when a legislative body temporarily suspends its sessions without formally ending a legislative term, typically decided by the house leadership or presiding officer and can last from days to weeks. Prorogation is a formal procedure where the head of state, often on the advice of the executive, ends a legislative session entirely, pausing all parliamentary activities until a new session begins. During recess, committees and offices may still operate, while prorogation dissolves all parliamentary business, requiring new orders to restart legislative functions.
Impact on Legislative Business
Recess suspends legislative business temporarily, allowing lawmakers to pause and resume deliberations without losing continuity on pending bills. Prorogation terminates a legislative session, leading to the clearance of all unfinished business, which must be reintroduced in the next session. This distinction significantly impacts the legislative workflow, with prorogation disrupting the progress of legislative agendas more severely than recess.
Historical Examples of Recess and Prorogation
Throughout U.S. history, recess has been utilized strategically, such as President Dwight D. Eisenhower's 1954 recess appointments during Senate inaction, while prorogation, though rare at the federal level, is commonly used in parliamentary systems like the U.K., exemplified by Prime Minister Boris Johnson's controversial 2019 prorogation attempt to limit parliamentary debate on Brexit. Historical recesses have often allowed presidents to bypass Senate confirmation delays by appointing officials temporarily. Prorogation in the British context serves to formally end a parliamentary session, with historical instances like the 1948 prorogation under Clement Attlee aligning with legislative scheduling and political strategy.
Political Implications and Public Perception
Recess allows legislators temporary breaks without dissolving parliamentary sessions, preserving ongoing political agendas, while prorogation suspends parliamentary activity and can halt legislative processes, often perceived as executive overreach. Public perception of recess is generally neutral or positive, seen as necessary downtime, whereas prorogation frequently invites criticism for undermining democratic transparency and accountability. Political implications of recess maintain legislative continuity, but prorogation can disrupt party strategies and provoke political crises or public protests.
Recess vs Prorogation: Advantages and Disadvantages
Recess allows legislative bodies to temporarily pause sessions, facilitating breaks without dissolving the assembly, which maintains continuity and enables quick resumption of work; however, it may delay urgent decision-making and reduce legislative productivity. Prorogation formally ends a parliamentary session, resetting the agenda and often promoting government efficiency by clearing pending business, but it can hinder legislative scrutiny and limit opposition debate. Both mechanisms balance operational needs and political strategy, with recess favoring legislative continuity and prorogation emphasizing procedural closure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Appropriate Parliamentary Break
Selecting between recess and prorogation depends on the legislative agenda's status and political strategy; recess serves as a temporary pause allowing parliamentarians to regroup without halting ongoing business. Prorogation formally ends a parliamentary session, clearing all pending matters and signaling a shift toward a new legislative phase. Accurate timing of these breaks ensures efficient parliamentary workflow and aligns with constitutional procedures for governance continuity.
Recess Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com