Party loyalists demonstrate unwavering support for their chosen political party, often prioritizing party goals over personal beliefs or external opinions. Their dedication reinforces party unity and drives collective action during elections and policymaking. Discover how party loyalty shapes political dynamics and influences your voting decisions in the full article.
Table of Comparison
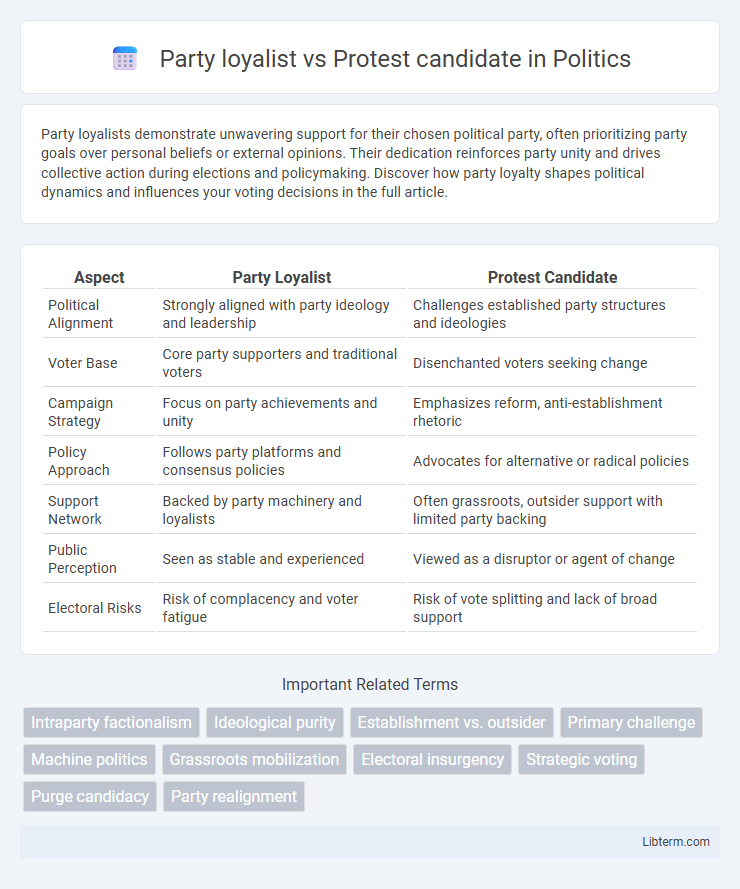
| Aspect | Party Loyalist | Protest Candidate |
|---|---|---|
| Political Alignment | Strongly aligned with party ideology and leadership | Challenges established party structures and ideologies |
| Voter Base | Core party supporters and traditional voters | Disenchanted voters seeking change |
| Campaign Strategy | Focus on party achievements and unity | Emphasizes reform, anti-establishment rhetoric |
| Policy Approach | Follows party platforms and consensus policies | Advocates for alternative or radical policies |
| Support Network | Backed by party machinery and loyalists | Often grassroots, outsider support with limited party backing |
| Public Perception | Seen as stable and experienced | Viewed as a disruptor or agent of change |
| Electoral Risks | Risk of complacency and voter fatigue | Risk of vote splitting and lack of broad support |
Understanding Party Loyalists and Protest Candidates
Party loyalists are committed supporters who consistently back their political party's platform and candidates, often prioritizing party unity and long-term goals. Protest candidates emerge as challengers within or outside established parties, representing voter dissatisfaction and calling for significant political change or reform. Understanding these dynamics clarifies voter behavior patterns and electoral outcomes, highlighting the tension between maintaining party cohesion and addressing grassroots demands for innovation.
Historical Context: Party Loyalty in Politics
Party loyalty in politics has historically shaped the loyalty-driven electoral system, where candidates loyal to established party lines secure consistent voter bases and party resources. Protest candidates often emerge during periods of political dissatisfaction, challenging traditional party structures by mobilizing support around specific issues or anti-establishment sentiments. Historical examples such as the rise of third-party candidates during the Progressive Era or recent populist movements illustrate the tension between entrenched party loyalists and insurgent protest candidates reshaping political landscapes.
Defining the Protest Candidate Phenomenon
The protest candidate phenomenon emerges when voters reject traditional party loyalists, seeking representatives who directly challenge the political establishment. These candidates often capitalize on widespread dissatisfaction by emphasizing outsider status, reformist agendas, and grassroots support. Their rise signals a shift toward issue-driven campaigns and reflects deepening polarization within the electorate.
Motivations Behind Party Loyalty
Party loyalists are motivated by ideological alignment, long-term policy consistency, and trust in the party's leadership to achieve collective goals. They often prioritize party unity and institutional stability, believing that supporting their party strengthens democratic processes and governance. Protest candidates attract voters driven by dissatisfaction with the status quo, aiming to challenge entrenched power structures and advocate for rapid, systemic change.
Voter Appeal: Why Protest Candidates Surge
Protest candidates surge because they tap into widespread voter dissatisfaction with established party loyalists, presenting themselves as fresh alternatives to the political status quo. Their appeal often lies in addressing unaddressed grievances, offering radical policy proposals, and mobilizing disenfranchised or apathetic voters. By emphasizing authenticity and grassroots support, protest candidates can rapidly gain traction, especially in polarized or crisis-hit electorates.
Media Influence on Party Loyalists vs Protest Candidates
Media influence strongly shapes voter perceptions by reinforcing party loyalists' existing beliefs through targeted messaging and echo chambers, increasing their attachment to traditional platforms. Conversely, protest candidates gain visibility and public support by leveraging alternative media channels and social networks that challenge mainstream narratives. The contrast in media strategies affects election dynamics, with loyalists relying on established outlets while protest candidates harness digital platforms to mobilize disenfranchised voters.
Impacts on Party Unity and Stability
Party loyalists often enhance party unity by aligning closely with established policies and leadership, fostering cohesion during elections and legislative processes. Protest candidates challenge this stability by introducing divergent viewpoints that can energize voter bases but also risk internal divisions and fragmented messaging. The dynamic between loyalists and protest candidates shapes party resilience, influencing its ability to adapt while maintaining a unified front in political contests.
Electoral Outcomes: Case Studies and Trends
Party loyalists often secure electoral victories due to established voter bases and robust party machinery, as evidenced in cases like the 2020 U.S. House elections where incumbents predominantly retained seats. Protest candidates, driven by anti-establishment sentiments, gain traction during periods of political dissatisfaction, illustrated by France's 2017 presidential race with Emmanuel Macron's insurgent movement disrupting traditional party dominance. Trends reveal that while party loyalists benefit from institutional support, protest candidates can catalyze significant political shifts when electorate trust in mainstream parties declines.
Challenges Facing Protest Candidates
Protest candidates face significant challenges including limited access to party resources, lower media coverage, and difficulty building broad-based electoral coalitions compared to party loyalists. Their campaign structure often lacks established funding networks and grassroots mobilization, hindering visibility and voter outreach. Overcoming institutional barriers and voter skepticism about electability remains a critical hurdle for protest candidates.
The Future of Party Loyalty in Modern Politics
The Future of Party Loyalty in Modern Politics is increasingly shaped by the tension between party loyalists and protest candidates who challenge traditional party structures. Party loyalists maintain electoral stability by supporting established platforms and reinforcing long-standing voter bases, while protest candidates capitalize on public dissatisfaction, often driving political realignment through grassroots mobilization and social media influence. This dynamic underscores a growing fragmentation in voter identity, suggesting that future political landscapes will prioritize issue-based coalitions over strict party allegiance.
Party loyalist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com