Arbitrary governance undermines the rule of law by allowing leaders to make decisions based on personal whims rather than established rules or public interest. This form of governance often leads to unpredictability, decreased trust in institutions, and potential abuses of power. Discover how arbitrary governance impacts societies and what steps can be taken to promote fairness and accountability in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
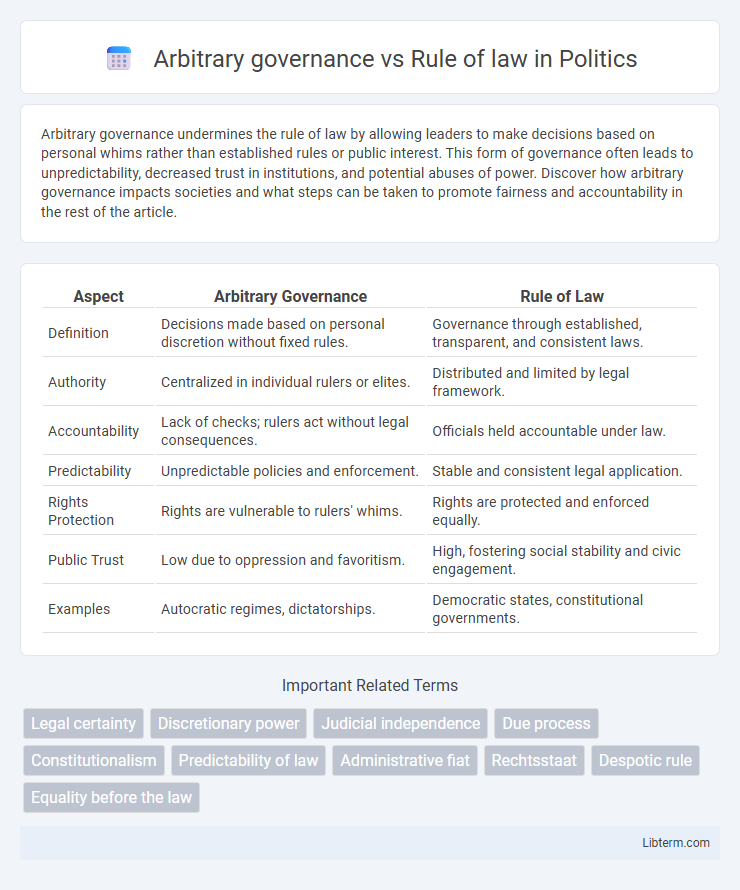
| Aspect | Arbitrary Governance | Rule of Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decisions made based on personal discretion without fixed rules. | Governance through established, transparent, and consistent laws. |
| Authority | Centralized in individual rulers or elites. | Distributed and limited by legal framework. |
| Accountability | Lack of checks; rulers act without legal consequences. | Officials held accountable under law. |
| Predictability | Unpredictable policies and enforcement. | Stable and consistent legal application. |
| Rights Protection | Rights are vulnerable to rulers' whims. | Rights are protected and enforced equally. |
| Public Trust | Low due to oppression and favoritism. | High, fostering social stability and civic engagement. |
| Examples | Autocratic regimes, dictatorships. | Democratic states, constitutional governments. |
Understanding Arbitrary Governance
Arbitrary governance occurs when decisions are made based on personal discretion rather than established laws, leading to unpredictable and often unjust outcomes. This form of governance undermines legal consistency, erodes public trust, and enables the abuse of power by officials who operate without accountability. Understanding arbitrary governance involves recognizing its detrimental effects on democratic institutions and the necessity for transparent, rule-based systems to ensure fairness and equality before the law.
Defining the Rule of Law
The Rule of Law is a fundamental principle ensuring that all individuals and institutions are subject to and accountable under laws that are publicly promulgated, equally enforced, and independently adjudicated. It contrasts sharply with arbitrary governance, where decisions are made based on the whims of rulers rather than established legal frameworks. Defining the Rule of Law emphasizes predictability, fairness, and the protection of fundamental rights, serving as a foundation for justice and democratic governance.
Key Differences Between Arbitrary Governance and Rule of Law
Arbitrary governance is characterized by decisions made at the discretion of rulers without consistent legal frameworks, resulting in unpredictable enforcement and potential abuse of power. Rule of law ensures that laws are transparent, stable, and applied equally to all individuals, limiting governmental authority and protecting fundamental rights. Key differences include accountability mechanisms, legal consistency, and protection against arbitrary decision-making, which are foundational to the rule of law but absent in arbitrary governance.
Historical Examples of Arbitrary Rule
Historical examples of arbitrary rule include the reign of King Louis XIV of France, whose absolute monarchy allowed unchecked decisions without legal constraints, leading to widespread inequality and resentment. The Soviet Union under Joseph Stalin exemplified arbitrary governance through purges and policies enforced without rule-based accountability, resulting in mass repression and human rights abuses. These instances highlight the dangers of governance lacking a structured legal framework, where power is centralized and subject to the ruler's whims rather than codified laws.
Benefits of the Rule of Law in Modern Societies
The Rule of Law ensures accountability by subjecting all individuals and institutions to transparent legal standards, preventing arbitrary governance and abuse of power. It provides legal certainty and stability, fostering economic growth and protecting human rights through consistent enforcement of laws. By maintaining an independent judiciary, the Rule of Law upholds fairness and equality, enhancing public trust and social cohesion in modern societies.
Consequences of Arbitrary Governance
Arbitrary governance undermines the rule of law by allowing power to be exercised without legal constraints, leading to unpredictability and injustice. This type of governance fosters corruption, erodes public trust, and stifles economic growth due to the lack of consistent legal protections. In contrast, the rule of law ensures accountability, fairness, and stability by adhering to established legal frameworks and principles.
The Role of Institutions in Upholding the Law
Institutions play a crucial role in upholding the rule of law by ensuring that laws are applied consistently and fairly, preventing arbitrary governance where decisions are made based on personal or political preferences. Independent courts, transparent legal frameworks, and accountable enforcement agencies maintain checks and balances that protect individual rights and promote legal certainty. Strong institutions foster trust in legal systems and support the stability and predictability essential for social and economic development.
Safeguards Against Arbitrary Power
Safeguards against arbitrary power include clear legal frameworks that restrict the actions of government officials and ensure accountability through independent judicial review. Rule of law enforces consistent application of laws, preventing arbitrary decisions by establishing transparent procedures and protections for individual rights. Mechanisms such as checks and balances, separation of powers, and codified human rights standards bolster protection against governance based on unchecked discretion.
Case Studies: Rule of Law Success Stories
Singapore exemplifies the rule of law through its robust legal framework, transparent governance, and strong anti-corruption measures, resulting in sustained economic growth and high public trust. In contrast, countries with arbitrary governance like Zimbabwe have faced economic instability and widespread corruption due to weak legal institutions and unchecked executive power. South Korea's transition from authoritarian rule to a democratic system underscores the critical role of rule of law in promoting political stability, human rights, and economic development.
Strengthening the Rule of Law for the Future
Strengthening the rule of law ensures that governance operates within a framework of established laws, protecting individual rights and promoting fairness, unlike arbitrary governance which depends on unpredictable decisions by rulers. Investing in transparent legal institutions and consistent enforcement mechanisms cultivates accountability and prevents abuses of power, fostering sustainable development and social stability. Future-focused reforms prioritizing judicial independence, legal education, and public participation reinforce the rule of law as the backbone of democratic governance.
Arbitrary governance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com