Political appointees hold key government positions determined by the current administration, influencing policy implementation and administrative priorities. Their roles often reflect the president's agenda, affecting how public services and regulations are executed. Explore the rest of the article to understand the impact of political appointees on your government and daily life.
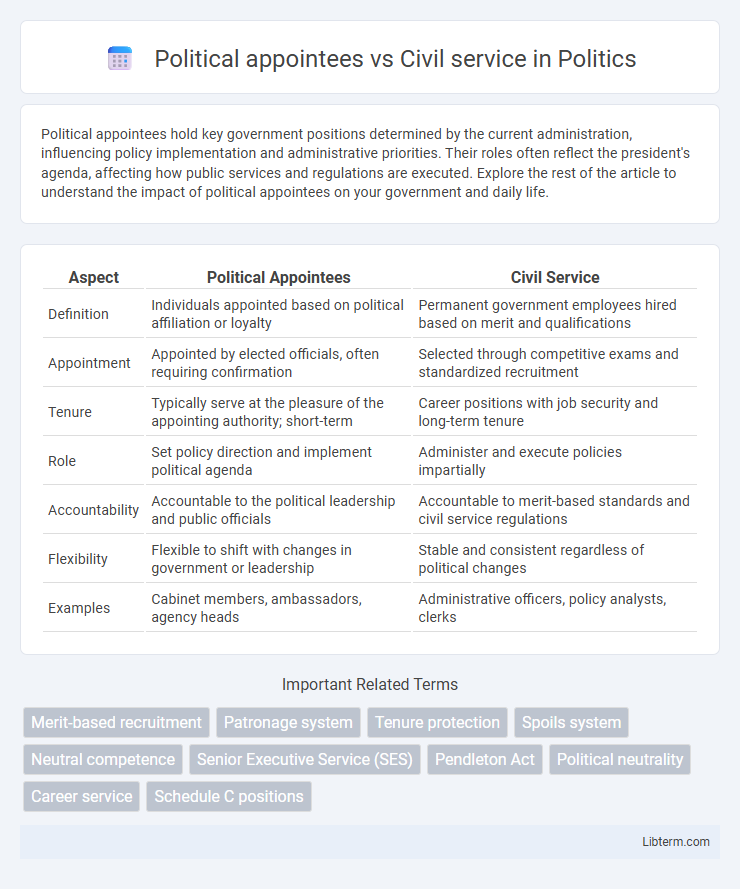
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Political Appointees | Civil Service |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individuals appointed based on political affiliation or loyalty | Permanent government employees hired based on merit and qualifications |
| Appointment | Appointed by elected officials, often requiring confirmation | Selected through competitive exams and standardized recruitment |
| Tenure | Typically serve at the pleasure of the appointing authority; short-term | Career positions with job security and long-term tenure |
| Role | Set policy direction and implement political agenda | Administer and execute policies impartially |
| Accountability | Accountable to the political leadership and public officials | Accountable to merit-based standards and civil service regulations |
| Flexibility | Flexible to shift with changes in government or leadership | Stable and consistent regardless of political changes |
| Examples | Cabinet members, ambassadors, agency heads | Administrative officers, policy analysts, clerks |
Introduction to Political Appointees and Civil Service
Political appointees are individuals selected by elected officials to fill key policy-making positions, often serving at the pleasure of the appointing authority. Civil service employees, in contrast, are career government workers hired based on merit through competitive exams and protected by regulations ensuring job stability and neutrality. The distinction ensures political leadership can implement their agenda while maintaining a professional, impartial bureaucracy.
Defining Political Appointees: Roles and Responsibilities
Political appointees are individuals appointed by elected officials to serve in key government positions, typically for a limited term aligning with the appointing authority's tenure. Their roles often include shaping policy, advising on strategic decisions, and implementing the political agenda of the administration. Responsibilities vary widely, encompassing leadership in departments, diplomatic assignments, and senior advisory roles, with a strong emphasis on political loyalty and policy alignment.
Understanding the Civil Service System
The Civil Service System ensures merit-based recruitment and job security for government employees, distinguishing them from political appointees who serve at the discretion of elected officials. Civil servants maintain continuity and expertise in public administration, operating independently from political pressures to implement policies effectively. This system promotes stability within government operations by protecting positions from partisan changes and emphasizing professional qualifications.
Key Differences Between Political Appointees and Civil Servants
Political appointees are selected by elected officials to serve at the pleasure of the administration, often holding leadership or advisory roles that align with current policy priorities. Civil servants, in contrast, are career professionals hired based on merit through competitive exams, ensuring continuity and expertise within government operations regardless of political changes. Key differences include appointment methods, job security, and primary focus, with political appointees being inherently temporary and policy-driven, while civil servants maintain nonpartisan stability and administrative functions.
Appointment Processes Explained
Political appointees are selected directly by elected officials, often requiring confirmation by legislative bodies depending on the position, with appointments typically reflecting the current administration's policy priorities. Civil service employees undergo competitive examinations and meet merit-based qualifications, ensuring a professional, nonpartisan workforce insulated from political influence. This dual system balances political control of key offices with a stable, skilled bureaucracy managing day-to-day government operations.
Duration and Terms of Service
Political appointees typically serve at the pleasure of the appointing authority, often with terms linked to the tenure of the administration, resulting in shorter and less predictable durations. Civil service employees usually enjoy longer, more stable careers with defined terms and protections that emphasize merit-based retention and continuity. This distinction ensures political appointees align with current policy goals while civil servants maintain institutional knowledge and operational stability.
Influence on Policy and Governance
Political appointees shape policy and governance by directly implementing the elected administration's agenda, often driving swift changes aligned with current political priorities. Civil service employees provide continuity and institutional knowledge, ensuring stability and expertise in policy execution regardless of political turnover. This balance between political direction and bureaucratic consistency influences the effectiveness and durability of government programs.
Accountability and Oversight Mechanisms
Political appointees are subject to direct accountability through executive oversight, legislative review, and often public scrutiny due to their alignment with the administration's policy agenda, resulting in a higher level of political accountability. Civil service employees operate under merit-based systems with protections that ensure continuity and impartiality, but their oversight primarily involves internal audits, performance evaluations, and adherence to administrative rules, which limit political influence. These distinct accountability frameworks balance responsiveness and stability, where political appointees face greater external oversight while career civil servants benefit from structured, rule-bound supervision.
Impacts on Public Administration Efficiency
Political appointees bring strategic direction aligned with elected leadership but may lack specialized administrative expertise, potentially causing disruptions in public administration efficiency. Civil service employees provide stability and institutional knowledge, ensuring consistent policy implementation and operational continuity. Balancing the dynamic leadership of appointees with the technical skills of career civil servants enhances overall government performance and responsiveness.
Future Trends and Challenges in Public Sector Staffing
Future trends in public sector staffing indicate increasing reliance on political appointees to drive rapid policy changes, while civil service professionals ensure continuity and operational stability. Challenges include balancing merit-based hiring in civil services with the growing demand for political loyalty and agility in decision-making roles. Technology integration and evolving public expectations will also require adaptive recruitment strategies to attract diverse talent capable of navigating complex governance landscapes.
Political appointees Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com