National identity shapes the cultural values and traditions that define a country's uniqueness and influence its citizens' daily lives. Understanding the impact of national policies and social dynamics on your community can deepen your sense of belonging and responsibility. Explore the rest of the article to learn how national factors shape society and affect your world.
Table of Comparison
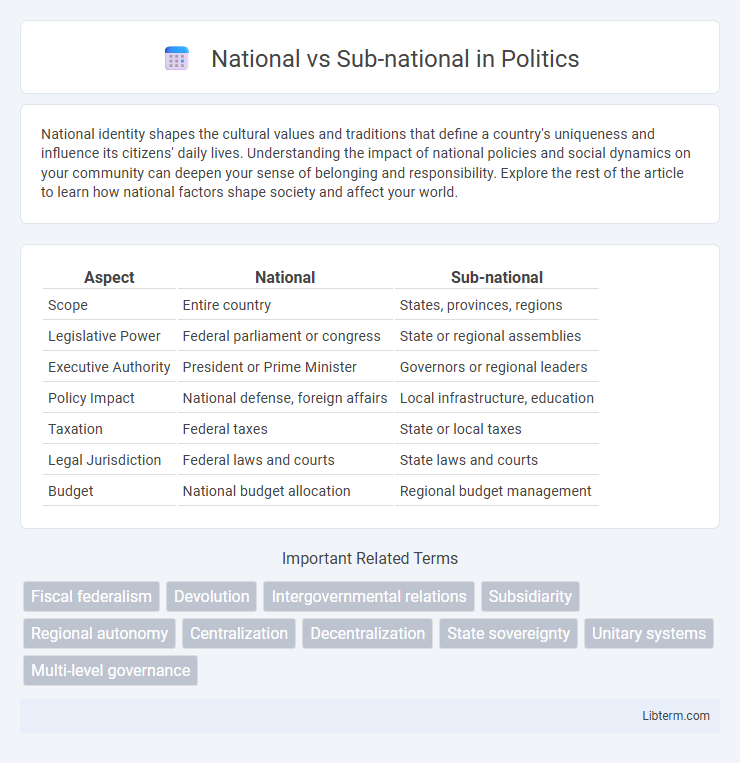
| Aspect | National | Sub-national |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Entire country | States, provinces, regions |
| Legislative Power | Federal parliament or congress | State or regional assemblies |
| Executive Authority | President or Prime Minister | Governors or regional leaders |
| Policy Impact | National defense, foreign affairs | Local infrastructure, education |
| Taxation | Federal taxes | State or local taxes |
| Legal Jurisdiction | Federal laws and courts | State laws and courts |
| Budget | National budget allocation | Regional budget management |
Understanding National and Sub-national Levels
National levels represent the highest administrative divisions within a country, governing policies that impact the entire nation, while sub-national levels include states, provinces, or regions handling localized governance tailored to specific areas. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for grasping how power and responsibilities are distributed, enabling effective policy implementation and resource allocation. Sub-national governments often address regional needs more efficiently by creating targeted regulations reflecting cultural, economic, and geographic diversity.
Key Differences Between National and Sub-national Governance
National governance involves centralized decision-making at the country level, managing policies that affect the entire nation's population and territory. Sub-national governance operates within smaller administrative divisions such as states, provinces, or municipalities, focusing on localized issues, resource allocation, and implementation of national laws tailored to regional needs. Key differences include the scope of authority, with national governments handling foreign affairs, defense, and national legislation, while sub-national entities manage local infrastructure, education, and public services.
Roles and Responsibilities: National vs Sub-national Authorities
National authorities establish overarching policies, regulations, and frameworks that guide the country's governance, security, and economic strategies. Sub-national authorities focus on localized implementation, service delivery, and addressing community-specific needs while ensuring compliance with national standards. Coordination between national and sub-national levels is essential for effective policy execution, resource allocation, and crisis management.
Policy Implementation at National and Sub-national Scales
Policy implementation at national scales ensures uniformity across regions by establishing broad regulatory frameworks and standards that guide sub-national entities. Sub-national implementation allows for tailored adaptation of national policies to local contexts, addressing specific socio-economic and cultural variations. Effective coordination between national and sub-national governments enhances policy coherence, resource allocation, and monitoring, improving overall governance outcomes.
Financial Management: Comparing National and Sub-national Budgets
National budgets encompass comprehensive fiscal policies and large-scale revenue sources such as federal taxes and international trade duties, allocating funds across diverse sectors including defense, infrastructure, and social welfare. Sub-national budgets, managed by states or provinces, focus on region-specific priorities funded primarily through local taxes, intergovernmental transfers, and targeted grants, emphasizing sectors like education, public safety, and transportation. Effective financial management at both levels requires coordination to optimize resource allocation, maintain fiscal discipline, and address economic disparities within the broader framework of national economic goals.
Intergovernmental Relations and Collaboration
Intergovernmental relations between national and sub-national governments are essential for effective policy implementation and resource allocation across different administrative levels. Collaboration mechanisms such as joint committees, fiscal transfers, and shared service agreements optimize governance by enhancing coordination, reducing overlaps, and addressing regional disparities. Strong cooperative frameworks foster transparency, accountability, and mutual support, enabling efficient management of public services and socio-economic development initiatives.
Decentralization: Benefits and Challenges
Decentralization enhances governance by distributing authority from national to sub-national governments, improving local responsiveness and tailored policy implementation. Benefits of decentralization include increased citizen participation, improved public service delivery, and enhanced accountability at regional and local levels. Challenges involve disparities in resource allocation, coordinating policies across levels, and maintaining national unity while empowering sub-national entities.
Impact on Public Services Delivery
National governments set overarching policies and allocate funding that shapes the framework for public services delivery across the entire country. Sub-national entities, such as states or municipalities, tailor these policies to local needs, improving responsiveness and efficiency in healthcare, education, and infrastructure services. Decentralization often enhances accountability and resource allocation, leading to more effective public service outcomes at the community level.
Case Studies: National vs Sub-national Success Stories
Case studies highlight that national initiatives like Germany's Energiewende showcase large-scale renewable energy integration, while sub-national efforts such as California's aggressive emissions reductions demonstrate localized policy impact. National programs benefit from coordinated funding and uniform regulations, whereas sub-national successes often arise from tailored strategies addressing regional priorities and stakeholder engagement. These examples illustrate that combining national frameworks with sub-national innovation fosters comprehensive and adaptive climate solutions.
Future Trends in National and Sub-national Dynamics
National and sub-national dynamics are expected to become increasingly intertwined, with decentralization trends empowering regional governments to address local needs more effectively. Technological advancements like AI and big data will drive smarter policy-making at both levels, enhancing governance efficiency and citizen engagement. Shifts in economic power and demographic changes will further compel collaboration between national and sub-national entities to ensure sustainable development and social equity.
National Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com