Screening plays a crucial role in early detection of diseases, improving treatment outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. Various screening methods are tailored to identify specific conditions, helping to catch health issues before symptoms appear. Explore the rest of the article to understand how screening can benefit your health and well-being.
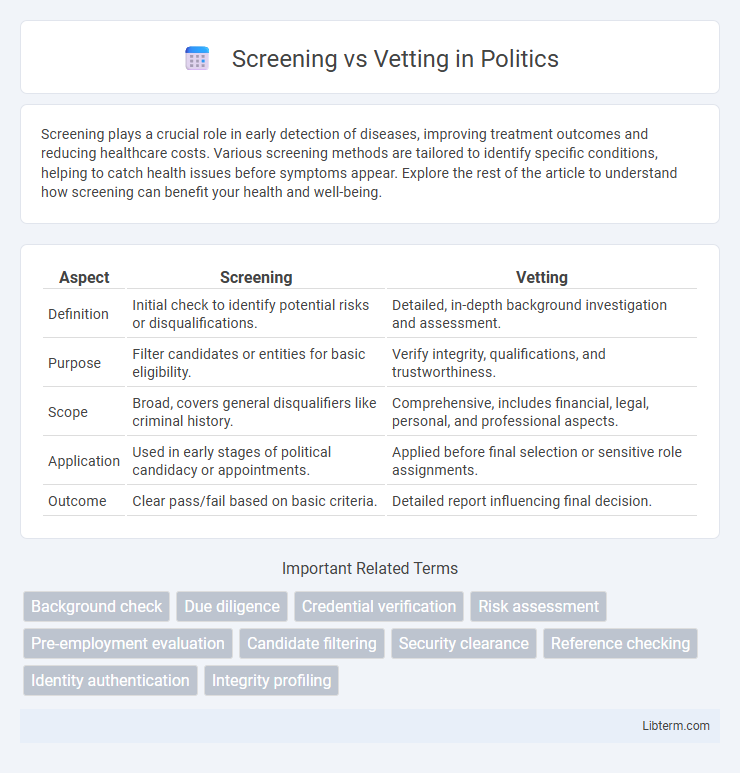
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Screening | Vetting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initial check to identify potential risks or disqualifications. | Detailed, in-depth background investigation and assessment. |
| Purpose | Filter candidates or entities for basic eligibility. | Verify integrity, qualifications, and trustworthiness. |
| Scope | Broad, covers general disqualifiers like criminal history. | Comprehensive, includes financial, legal, personal, and professional aspects. |
| Application | Used in early stages of political candidacy or appointments. | Applied before final selection or sensitive role assignments. |
| Outcome | Clear pass/fail based on basic criteria. | Detailed report influencing final decision. |
Introduction to Screening and Vetting
Screening involves a preliminary process of checking basic information to identify potential risks or disqualifications, often using databases, background checks, and identity verification tools. Vetting is a more thorough and detailed evaluation that assesses credentials, reputation, and suitability for a specific role or responsibility. Both processes are essential in ensuring security, compliance, and quality in hiring, security clearances, or vendor selection.
Defining Screening: Purpose and Process
Screening involves the initial review of candidates or entities to identify those who meet basic eligibility criteria, serving as a preliminary filter in recruitment, compliance, or security contexts. The purpose of screening is to quickly eliminate unsuitable options through standardized assessments such as background checks, identity verification, or qualifications matching. This process ensures efficiency by focusing detailed evaluation resources only on potentially suitable candidates or entities.
Understanding Vetting: Purpose and Process
Vetting is a comprehensive evaluation process designed to assess an individual's background, qualifications, and trustworthiness beyond basic screening methods. It involves detailed verification of credentials, references, criminal records, and sometimes financial status to ensure suitability for sensitive roles or responsibilities. The purpose of vetting is to mitigate risks, protect organizational integrity, and assure compliance with regulatory standards.
Key Differences Between Screening and Vetting
Screening involves a preliminary review of candidates or information to identify potential risks or qualifications, often using automated tools or background checks. Vetting is a more in-depth process, including thorough investigation and verification of credentials, references, and personal history to ensure full compliance and reliability. The key differences lie in the depth and scope, with screening being broader and quicker, while vetting is detailed and comprehensive.
Common Methods Used in Screening
Common methods used in screening include background checks, identity verification, and reference verification to ensure the candidate's qualifications and history align with job requirements. Automated software often scans resumes and applications for keyword relevance and red flags such as criminal records or employment gaps. Biometric and drug testing are also employed to assess physical and health-related eligibility.
Essential Steps in the Vetting Process
Vetting involves a detailed verification process including identity confirmation, background checks, and credential validation to ensure trustworthiness and compliance. Essential steps in vetting consist of collecting personal information, conducting criminal and financial history reviews, and assessing professional qualifications. This rigorous approach distinguishes vetting from screening by prioritizing in-depth evaluation for higher-risk or sensitive positions.
Advantages of Screening in Recruitment
Screening in recruitment offers the advantage of efficiently filtering large candidate pools through automated tools and predefined criteria, ensuring a faster selection process. It enhances the identification of candidates who meet basic qualifications and reduces time-to-hire by minimizing manual review efforts. This initial vetting stage improves overall recruitment efficiency, enabling recruiters to focus on high-potential candidates for detailed evaluation.
Benefits of Thorough Vetting for Organizations
Thorough vetting enhances organizational security by uncovering detailed background information, reducing risks associated with fraud, insider threats, and non-compliance. It ensures candidates or partners meet specific qualifications and cultural fit, leading to higher retention rates and stronger team dynamics. Comprehensive vetting also supports regulatory adherence, mitigating legal liabilities and fostering trust with stakeholders.
Challenges and Limitations of Screening and Vetting
Screening often faces challenges such as incomplete data sources and reliance on automated algorithms that may produce false positives or miss nuanced risks, limiting its effectiveness in identifying complex threats. Vetting, while more thorough, is constrained by time-consuming processes, the need for expert analysis, and difficulties accessing comprehensive, up-to-date information, which can delay decision-making and increase costs. Both practices encounter limitations in detecting sophisticated fraud or security risks due to evolving tactics and the global variability of data accuracy and availability.
Best Practices for Effective Screening and Vetting
Effective screening and vetting processes rely on thorough background checks, verification of credentials, and consistent criteria tailored to the specific role or context. Integrating advanced data analytics and automated tools enhances accuracy and reduces human error during candidate evaluation. Establishing clear protocols for data privacy and compliance ensures ethical management of sensitive information throughout the screening and vetting stages.
Screening Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com