Travel bans restrict movement between countries or regions to control the spread of diseases, protect national security, or respond to political conflicts. These measures can significantly impact global mobility, tourism, and international business operations, affecting both travelers and economies. Discover the full implications of travel bans and how they might influence Your future journeys in the rest of this article.
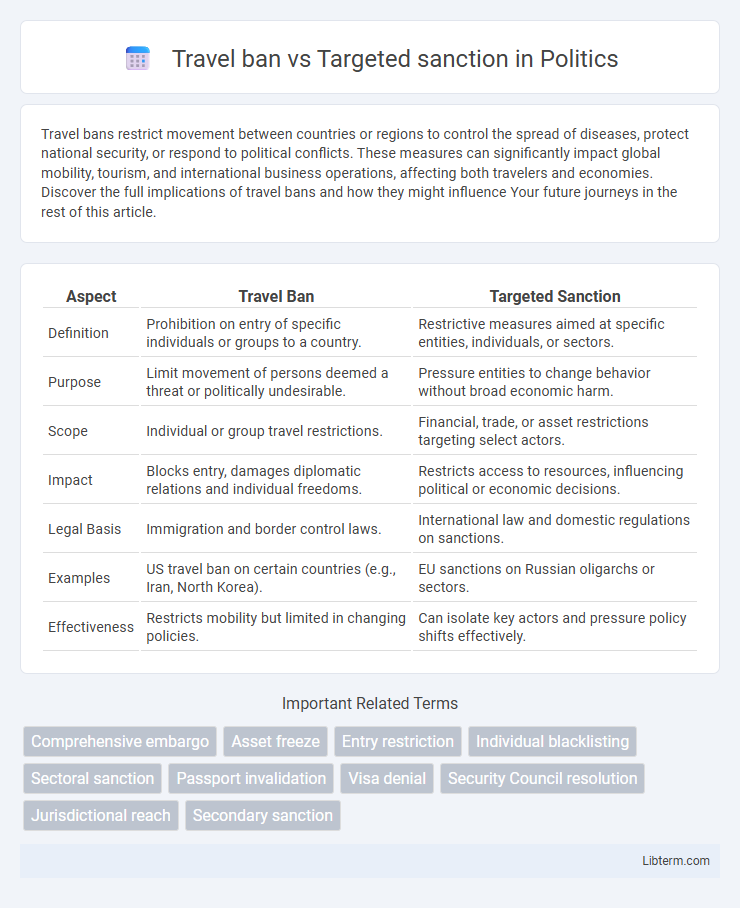
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Travel Ban | Targeted Sanction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prohibition on entry of specific individuals or groups to a country. | Restrictive measures aimed at specific entities, individuals, or sectors. |
| Purpose | Limit movement of persons deemed a threat or politically undesirable. | Pressure entities to change behavior without broad economic harm. |
| Scope | Individual or group travel restrictions. | Financial, trade, or asset restrictions targeting select actors. |
| Impact | Blocks entry, damages diplomatic relations and individual freedoms. | Restricts access to resources, influencing political or economic decisions. |
| Legal Basis | Immigration and border control laws. | International law and domestic regulations on sanctions. |
| Examples | US travel ban on certain countries (e.g., Iran, North Korea). | EU sanctions on Russian oligarchs or sectors. |
| Effectiveness | Restricts mobility but limited in changing policies. | Can isolate key actors and pressure policy shifts effectively. |
Understanding Travel Bans and Targeted Sanctions
Travel bans restrict specific individuals or groups from entering or transiting through certain countries, aiming to limit personal mobility based on political, security, or human rights concerns. Targeted sanctions focus on freezing assets, restricting financial transactions, or imposing trade limitations on designated entities to influence behavior without widespread economic impact. Both measures are strategic tools in international diplomacy aimed at enforcing compliance while minimizing collateral effects on broader populations.
Key Differences Between Travel Bans and Targeted Sanctions
Travel bans restrict the entry of specific individuals or groups into a country, primarily focusing on immigration control and security measures. Targeted sanctions impose financial and economic restrictions on particular entities or sectors to limit their operational capabilities and influence. While travel bans primarily affect movement and access, targeted sanctions aim to disrupt economic activities and pressure governments or organizations to change behavior.
Historical Context: The Evolution of Sanctions
Travel bans and targeted sanctions have evolved as strategic tools in international diplomacy since the Cold War, shifting from broad economic embargoes to precise measures addressing specific individuals or entities. Initially, comprehensive sanctions aimed to exert maximum pressure on entire nations, often causing widespread humanitarian impacts. Over time, the international community developed targeted sanctions that focus on restricting travel and freezing assets of key political figures, enhancing effectiveness while minimizing collateral damage.
Legal Frameworks Governing Travel Bans and Sanctions
Travel bans and targeted sanctions operate under distinct legal frameworks established by international bodies such as the United Nations Security Council and regional organizations like the European Union. Travel bans are typically enforced through national immigration laws complemented by international agreements, aiming to restrict entry or transit of specified individuals based on security or diplomatic grounds. Targeted sanctions involve precise measures, including asset freezes and trade restrictions, codified in resolutions or legal statutes to limit the financial and operational capacities of designated entities without broadly impacting civilian populations.
Impact on Individuals and Entities
Travel bans restrict the movement of specific individuals, limiting their ability to attend international events, conduct business, or engage in diplomatic activities, thereby directly affecting their personal and professional lives. Targeted sanctions freeze assets and impose financial restrictions on designated entities or persons, crippling their economic activities and limiting access to global financial systems. Both measures create significant barriers, but travel bans primarily disrupt individual mobility, while targeted sanctions exert broader economic pressure on entities and networks.
Effectiveness in Achieving Policy Objectives
Travel bans restrict individuals' movement to limit influence and signal condemnation but often face challenges in enforcement and can harm diplomatic relations. Targeted sanctions focus on specific entities or sectors, offering precision and adaptability to weaken financial networks while minimizing broader economic impact. Studies show that targeted sanctions generally achieve policy objectives more effectively by combining economic pressure with clear, measurable outcomes.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Enforcement
Travel bans often face challenges related to identifying and verifying individuals across borders, leading to enforcement discrepancies and potential human rights concerns. Targeted sanctions present difficulties in accurately pinpointing entities or persons responsible for illicit activities, raising debates over due process and collateral impacts on innocent parties. Both measures generate controversies around transparency, legal jurisdiction, and effectiveness in achieving political or security objectives.
Case Studies: Notable Examples and Outcomes
Travel bans and targeted sanctions have been employed in high-profile cases such as the sanctions against Russia following the annexation of Crimea in 2014 and the travel bans imposed on North Korean officials due to nuclear proliferation activities. The European Union's restrictive measures against Venezuelan government figures aimed to pressure political change while sparing the broader economy, demonstrating targeted sanctions' precision. Outcomes reveal mixed effectiveness; Russia has faced economic strain and political isolation, while North Korea's nuclear ambitions persist despite travel restrictions, highlighting the complexity of enforcing international policy tools.
International Perspectives and Reactions
Travel bans and targeted sanctions serve distinct roles in international diplomacy, with travel bans restricting the movement of specific individuals or groups, while targeted sanctions impose economic or financial penalties to influence behavior. International perspectives vary, as travel bans are often seen as symbolic measures aiming to isolate leaders responsible for human rights abuses, whereas targeted sanctions are viewed as strategic tools designed to exert economic pressure without harming civilian populations. Reactions from global actors depend on geopolitical interests and humanitarian concerns, with some countries advocating for comprehensive sanctions regimes to enforce compliance, while others criticize their potential to exacerbate conflicts or undermine diplomatic dialogue.
Future Trends in Global Sanction Strategies
Travel bans restrict the movement of specific individuals across borders, limiting their access to international hubs, while targeted sanctions focus on financial restrictions and asset freezes to disrupt illicit activities. Emerging global sanction strategies increasingly integrate digital monitoring and AI to enhance enforcement precision, targeting key actors in transnational networks without broad economic fallout. Future trends emphasize multilateral coordination and adaptive frameworks to address evolving geopolitical challenges and ensure sanctions remain effective and flexible.
Travel ban Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com