Doubt can often hinder decision-making and cloud your confidence, limiting personal growth and success. Understanding the roots of doubt and learning strategies to overcome it empowers you to take decisive action with clarity. Explore the article to discover effective techniques to manage doubt and boost your self-assurance.
Table of Comparison
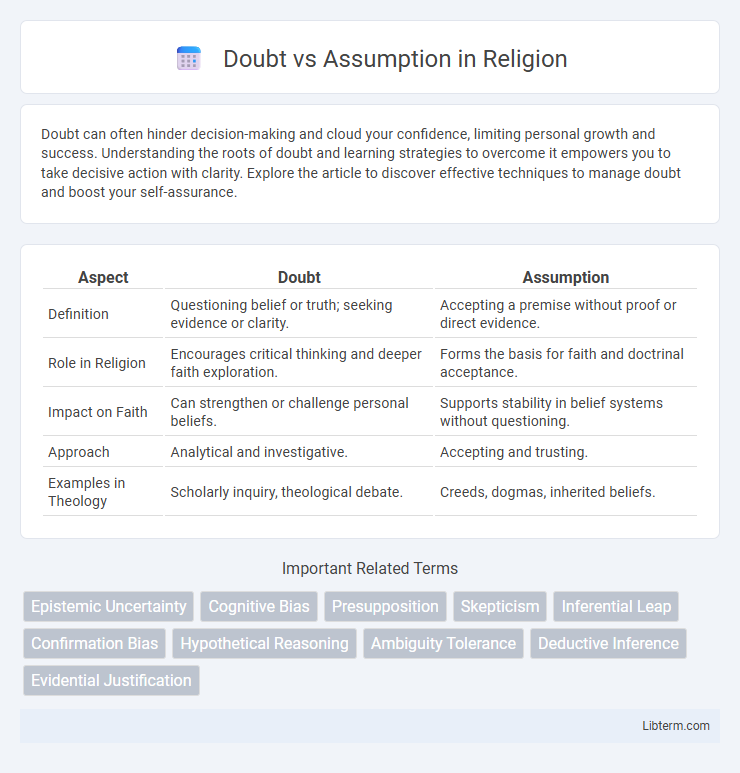
| Aspect | Doubt | Assumption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Questioning belief or truth; seeking evidence or clarity. | Accepting a premise without proof or direct evidence. |
| Role in Religion | Encourages critical thinking and deeper faith exploration. | Forms the basis for faith and doctrinal acceptance. |
| Impact on Faith | Can strengthen or challenge personal beliefs. | Supports stability in belief systems without questioning. |
| Approach | Analytical and investigative. | Accepting and trusting. |
| Examples in Theology | Scholarly inquiry, theological debate. | Creeds, dogmas, inherited beliefs. |
Understanding Doubt: Definition and Nature
Doubt is a cognitive state characterized by uncertainty and questioning, arising when evidence or information is insufficient or contradictory. It functions as a critical thinking tool, prompting individuals to seek clarity, verify facts, and avoid premature conclusions. Unlike assumptions, which are accepted without verification, doubt drives a deeper investigation into the validity of beliefs and claims.
What is Assumption? Meaning and Implications
Assumption is the acceptance of something as true without concrete evidence or proof, often serving as a foundational belief that influences decision-making and reasoning. It implies a degree of uncertainty, as assumptions can lead to errors if the underlying premise is incorrect or incomplete. Understanding assumptions is crucial for critical thinking, as it allows individuals to identify potential biases and question the validity of unverified information.
The Psychological Roots of Doubt and Assumption
Doubt originates from cognitive processes involving uncertainty and critical evaluation, rooted in the brain's prefrontal cortex where judgment and decision-making occur. Assumption arises from heuristic shortcuts, driven by the brain's tendency to fill gaps in knowledge based on prior experiences or biases stored in the hippocampus and amygdala. These psychological mechanisms influence how individuals interpret information, shaping behavior and thought patterns through either skepticism or premature conclusions.
Key Differences: Doubt vs Assumption
Doubt involves questioning the truth or validity of information, while assumption accepts something as true without proof. Doubt prompts critical thinking and verification, whereas assumption relies on presuppositions that may lead to incorrect conclusions. Understanding these differences enhances decision-making clarity and reduces cognitive biases.
How Doubt Influences Decision-Making
Doubt triggers a critical evaluation process by prompting individuals to question available information, leading to more deliberate and cautious decision-making. It encourages the consideration of alternative perspectives and potential risks, which can prevent impulsive choices and enhance problem-solving accuracy. In contrast to assumptions, which often rely on unverified beliefs, doubt fosters a mindset of inquiry that improves decision outcomes through increased analytical rigor.
The Role of Assumptions in Everyday Life
Assumptions serve as cognitive shortcuts that streamline decision-making by filling gaps in incomplete information, allowing individuals to function efficiently in daily life. While assumptions enable quick judgments, they can also introduce errors if not regularly questioned or verified against facts. Understanding the balance between doubt and assumption helps improve critical thinking and reduces the risk of misinformation influencing behavior.
Positive and Negative Impacts of Doubt and Assumption
Doubt can foster critical thinking and cautious decision-making, promoting deeper understanding and reducing errors in judgment, but excessive doubt may lead to indecisiveness and anxiety. Assumption enables swift decision-making and simplifies complex information, aiding efficiency and confidence, yet it risks inaccuracies and misunderstandings when based on incomplete or incorrect information. Balancing doubt and assumption is crucial for effective problem-solving and maintaining intellectual openness without compromising decisiveness.
Overcoming the Pitfalls of Assumptive Thinking
Overcoming the pitfalls of assumptive thinking requires cultivating critical questioning skills and seeking evidence before drawing conclusions. Assumptions often lead to misunderstandings, miscommunication, and flawed decision-making, making it essential to replace guesswork with verified facts. Emphasizing curiosity and open-mindedness enhances cognitive accuracy and fosters more effective problem-solving.
Balancing Doubt and Assumption for Better Outcomes
Balancing doubt and assumption enhances decision-making by fostering critical thinking while maintaining forward momentum. Incorporating measured skepticism prevents premature conclusions, enabling thorough evaluation of evidence and reducing cognitive biases. Calibrating assumptions based on verified information promotes confidence in actions, ultimately leading to more accurate predictions and optimized outcomes in complex scenarios.
Practical Tips to Cultivate Healthy Skepticism and Reduce Bias
Doubt encourages critical thinking by prompting individuals to question information and verify facts, which helps reduce cognitive bias in decision-making processes. Cultivating healthy skepticism involves actively seeking diverse perspectives, asking targeted questions, and relying on evidence-based sources to evaluate claims objectively. Practicing mindfulness techniques and pausing before accepting information as true further strengthens the ability to differentiate between valid assumptions and unfounded beliefs.
Doubt Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com