Diwali, the Festival of Lights, symbolizes the triumph of light over darkness and good over evil through vibrant decorations, fireworks, and traditional rituals. This celebrated Hindu festival includes lighting oil lamps, sharing sweets, and participating in family prayers to invoke prosperity and happiness. Discover the rich cultural significance and unique customs behind Diwali in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
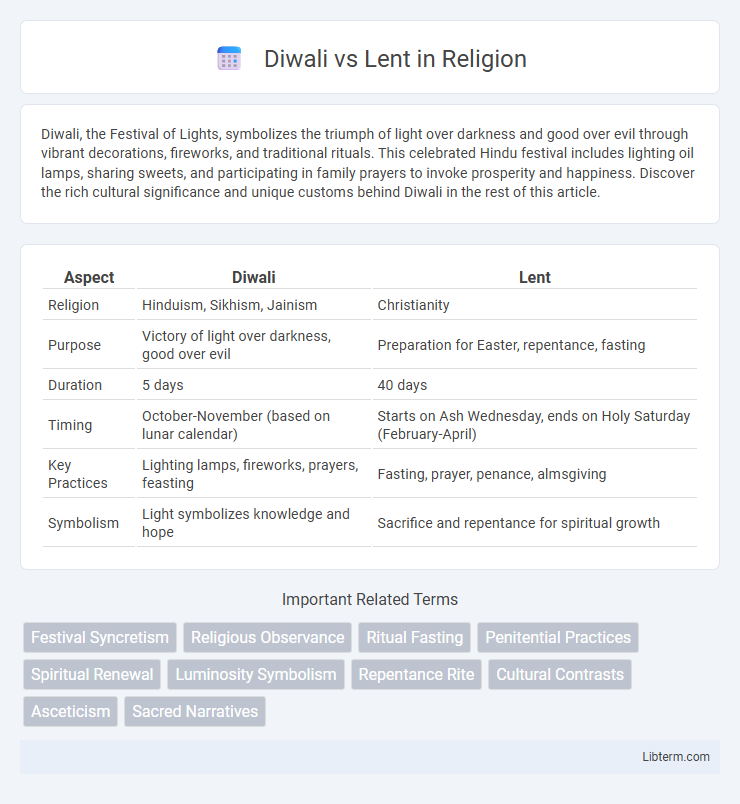
| Aspect | Diwali | Lent |
|---|---|---|
| Religion | Hinduism, Sikhism, Jainism | Christianity |
| Purpose | Victory of light over darkness, good over evil | Preparation for Easter, repentance, fasting |
| Duration | 5 days | 40 days |
| Timing | October-November (based on lunar calendar) | Starts on Ash Wednesday, ends on Holy Saturday (February-April) |
| Key Practices | Lighting lamps, fireworks, prayers, feasting | Fasting, prayer, penance, almsgiving |
| Symbolism | Light symbolizes knowledge and hope | Sacrifice and repentance for spiritual growth |
Introduction: Understanding Diwali and Lent
Diwali, known as the Festival of Lights, is a significant Hindu celebration symbolizing the victory of light over darkness and good over evil, observed with lighting lamps, fireworks, and feasts. Lent, a solemn Christian observance lasting 40 days before Easter, involves fasting, prayer, and penance to prepare spiritually for the resurrection of Jesus Christ. Both Diwali and Lent hold profound cultural and religious importance, marking periods of reflection, renewal, and communal participation.
Historical Origins and Significance
Diwali, originating from ancient Hindu traditions around 2,500 years ago, celebrates the victory of light over darkness and good over evil, marking the return of Lord Rama to Ayodhya. Lent, rooted in early Christian practices dating back to the 4th century CE, is a 40-day period of fasting and repentance commemorating Jesus Christ's 40 days of fasting in the desert. Both festivals hold deep spiritual significance, with Diwali emphasizing renewal and prosperity and Lent focusing on penance and preparation for Easter.
Key Beliefs and Spiritual Themes
Diwali celebrates the triumph of light over darkness and good over evil, emphasizing themes of renewal, prosperity, and the victory of righteousness through rituals and prayers to deities like Lakshmi and Rama. Lent centers on introspection, repentance, and spiritual discipline, marking 40 days of fasting, prayer, and sacrifice in preparation for Easter, reflecting Jesus Christ's sacrifice and resurrection. Both observances emphasize spiritual growth, but Diwali highlights joyful celebration and divine blessings, while Lent focuses on penitence and self-denial.
Rituals and Practices Compared
Diwali, the Hindu festival of lights, involves lighting oil lamps, decorating homes with rangoli, and performing Lakshmi Puja to invoke prosperity and happiness. Lent, observed in Christianity, emphasizes fasting, prayer, and penance over 40 days, symbolizing Jesus Christ's sacrifice and preparation for Easter. Both rituals foster spiritual reflection, but Diwali celebrates renewal and triumph of light, while Lent focuses on repentance and self-discipline.
Symbolic Foods and Fasting Customs
Diwali features symbolic foods like sweets such as ladoos, barfis, and festive snacks that represent prosperity and joy, while Lent involves fasting customs emphasizing abstaining from rich foods and sometimes meat to signify penance and spiritual discipline. Diwali celebrations include feasting with diverse offerings that highlight abundance, whereas Lent fasting practices vary from complete fasts to partial restrictions like avoiding dairy or flour. Both traditions use food rituals to convey deeper spiritual meanings, with Diwali's foods symbolizing light and positivity, and Lent's fasting underscoring sacrifice and reflection.
Family and Community Celebrations
Diwali, celebrated by millions of Hindus, Sikhs, and Jains worldwide, emphasizes vibrant family gatherings, communal prayers, and festive lighting to symbolize the victory of light over darkness. Lent, observed by Christians during 40 days preceding Easter, centers around reflective family rituals and community worship aimed at spiritual renewal and sacrifice. Both celebrations foster strong family bonds and community unity through shared traditions and collective participation.
Decorations, Symbols, and Visual Elements
Diwali decorations prominently feature vibrant rangoli patterns, oil lamps called diyas, and strings of colorful lights that symbolize the triumph of light over darkness. Lent visuals center around simplicity and reflection, often using purple drapes in churches and symbols like the cross and ashes to represent penance and renewal. While Diwali emphasizes bright, festive ornaments highlighting joy and prosperity, Lent employs subdued, minimalistic visuals to evoke solemnity and spiritual discipline.
Duration and Main Dates Observed
Diwali typically spans five days, with the main celebrations occurring on the third day, which falls between October and November based on the Hindu lunar calendar. Lent lasts for 40 days, beginning on Ash Wednesday and ending on Holy Saturday, leading up to Easter Sunday, usually observed in March or April according to the Christian liturgical calendar. These distinct durations and dates highlight the cultural and religious significance unique to each observance.
Impact on Modern Society and Cultural Influence
Diwali, the Hindu festival of lights, significantly impacts modern society by promoting values of hope, prosperity, and the victory of good over evil, influencing contemporary cultural practices through vibrant celebrations and community bonding. Lent, observed primarily by Christians, encourages reflection, sacrifice, and spiritual renewal, shaping cultural behaviors around fasting and charitable acts during its 40-day period. Both festivals deeply influence social cohesion and cultural identity, fostering traditions that resonate in modern multicultural societies worldwide.
Conclusion: Common Values and Differences
Diwali and Lent both emphasize themes of self-discipline, spiritual renewal, and the triumph of light over darkness, reflecting common values of inner purification and devotion. Diwali celebrates prosperity and the victory of good through vibrant festivities, while Lent involves solemn reflection and fasting in preparation for Easter. These differences highlight unique cultural expressions of faith alongside their shared goal of personal and spiritual growth.
Diwali Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com