Faith empowers your inner strength, providing hope and resilience in challenging times. It offers a sense of purpose and connection beyond the tangible world, guiding decisions and actions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how faith can transform your life and mindset.
Table of Comparison
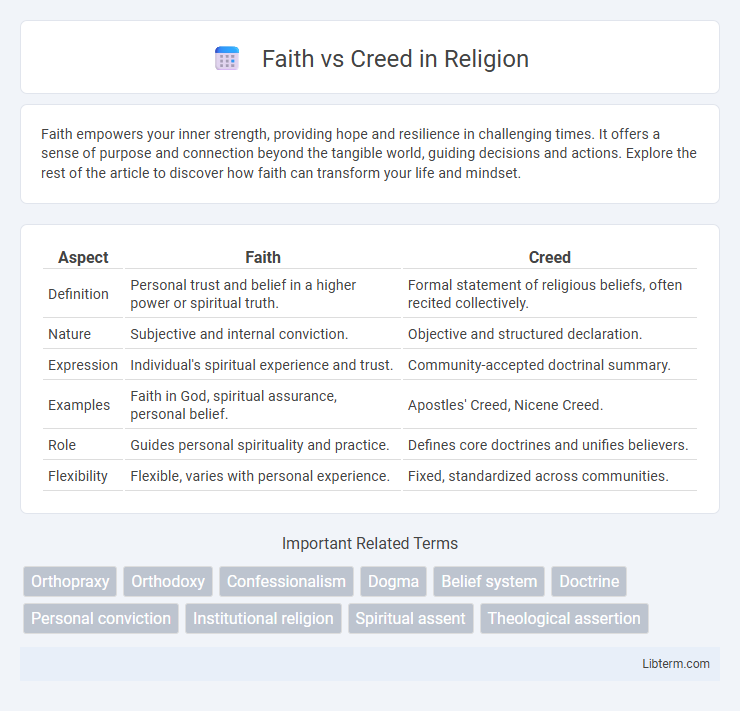
| Aspect | Faith | Creed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal trust and belief in a higher power or spiritual truth. | Formal statement of religious beliefs, often recited collectively. |
| Nature | Subjective and internal conviction. | Objective and structured declaration. |
| Expression | Individual's spiritual experience and trust. | Community-accepted doctrinal summary. |
| Examples | Faith in God, spiritual assurance, personal belief. | Apostles' Creed, Nicene Creed. |
| Role | Guides personal spirituality and practice. | Defines core doctrines and unifies believers. |
| Flexibility | Flexible, varies with personal experience. | Fixed, standardized across communities. |
Understanding Faith: Definitions and Perspectives
Faith encompasses a deeply personal belief in the unseen and spiritual trust often rooted in individual experience, while creed refers to a formalized set of doctrines authored by religious institutions. Understanding faith involves exploring diverse perspectives, including psychological, theological, and cultural dimensions that highlight its role in shaping values and guiding behavior. Studies reveal that faith functions as an intrinsic motivator, fostering resilience and a sense of purpose beyond codified creeds.
Unpacking Creed: Historical and Religious Contexts
Creed refers to a formalized set of beliefs or doctrines historically rooted in religious traditions, serving as authoritative declarations within faith communities such as Christianity's Nicene Creed or Islam's Shahada. These creeds function as concise summaries of core theological principles, establishing communal identity and guiding religious practices across generations. Understanding creeds involves examining their development in historical councils, their role in doctrinal disputes, and their enduring influence on religious orthodoxy.
Key Differences Between Faith and Creed
Faith represents a personal, internal belief system centered on trust and spiritual conviction, often without formal requirements or institutional boundaries. Creed refers to an established set of doctrinal statements or formalized beliefs endorsed by religious organizations, serving as a guide for communal worship and practice. Key differences include faith's emphasis on individual experience and trust, whereas creed emphasizes collective agreement and systematic theology.
The Role of Faith in Personal Belief Systems
Faith serves as the foundational element in personal belief systems, providing individuals with intrinsic conviction beyond empirical evidence. Unlike creed, which outlines formalized doctrines, faith embodies a dynamic and personal trust in spiritual or moral truths that shape identity and behavior. This internalized commitment fosters resilience and guides ethical decision-making in diverse life experiences.
How Creeds Shape Religious Communities
Creeds define core beliefs that unify religious communities by providing a shared framework for faith and practice, fostering collective identity and cohesion. Structured statements like the Nicene Creed articulate essential doctrines that guide worship, moral values, and community rituals. These creeds serve as doctrinal benchmarks, clarifying theological boundaries and strengthening communal bonds among adherents.
Faith vs Creed: Impacts on Spiritual Practice
Faith shapes spiritual practice through personal belief and trust in the divine, fostering an individual's connection and experience of spirituality. Creed provides a structured set of doctrines that guide communal worship and unify practitioners under shared theological principles. The dynamic between faith and creed influences how spirituality is expressed, balancing personal conviction with collective religious identity.
Faith Beyond Doctrine: Individual Experience
Faith beyond doctrine emphasizes personal spiritual encounters and individual conviction over rigid adherence to established creeds, allowing for a more intimate and evolving relationship with the divine. This approach values subjective experience and inner transformation as central to belief, highlighting the diversity within religious faiths. By prioritizing personal insight, faith transcends institutional boundaries and fosters a deeper, more authentic connection with spirituality.
Creeds as Collective Identity: Unity or Division?
Creeds serve as formal statements of shared beliefs that solidify collective identity within religious communities, fostering unity by providing a common doctrinal foundation. However, rigid adherence to creeds can also lead to division, as differing interpretations or exclusion of variant beliefs create boundaries between groups. The role of creeds in shaping group cohesion highlights the tension between maintaining doctrinal purity and embracing diverse expressions of faith.
When Faith Challenges Established Creeds
Faith challenges established creeds by emphasizing personal spiritual experience over rigid doctrinal adherence, often leading to dynamic interpretations of religious beliefs. This tension fosters theological debates that question traditional authority and promote individual conviction as a source of legitimacy. Conflicts arise when faith-inspired insights contradict orthodox creeds, prompting reformations or new movements within religious communities.
The Future of Faith and Creed in Modern Religion
Faith and creed continue to shape modern religion by influencing spiritual identity and communal practices in evolving cultural contexts. Advances in technology and increased interfaith dialogue are driving shifts toward more personalized expressions of faith, while traditional creeds provide foundational doctrines that maintain religious continuity and unity. The future sees a dynamic interplay where faith adapts to contemporary existential questions and creeds evolve to remain relevant in a pluralistic society.
Faith Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com