Bhakti represents a profound devotional practice rooted in love and surrender to a personal deity, fostering a deep spiritual connection. This path emphasizes emotional devotion, encouraging Your heartfelt expression through prayer, song, and rituals that cultivate inner peace and divine intimacy. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Bhakti can transform Your spiritual journey and enrich Your daily life.
Table of Comparison
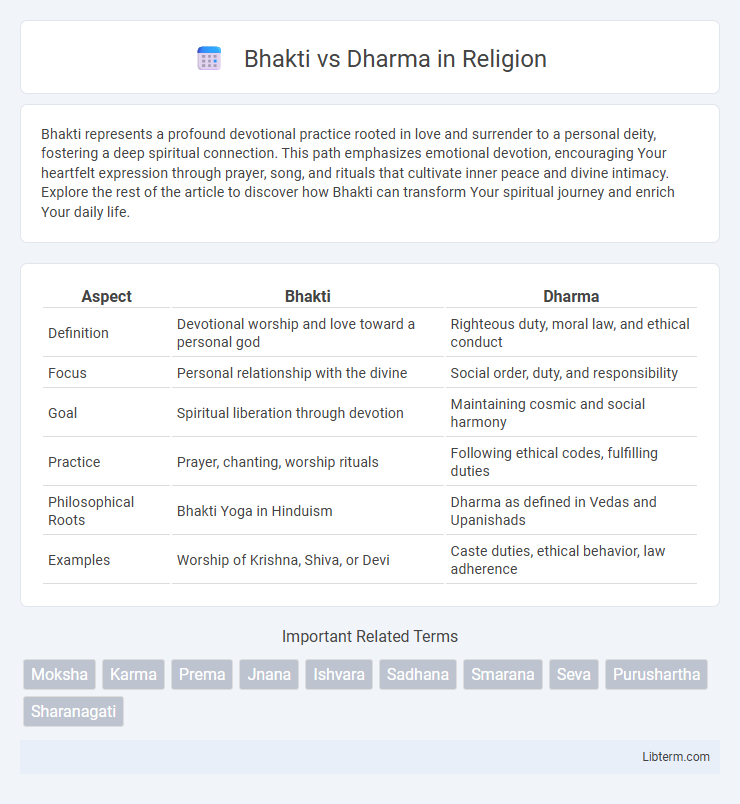
| Aspect | Bhakti | Dharma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Devotional worship and love toward a personal god | Righteous duty, moral law, and ethical conduct |
| Focus | Personal relationship with the divine | Social order, duty, and responsibility |
| Goal | Spiritual liberation through devotion | Maintaining cosmic and social harmony |
| Practice | Prayer, chanting, worship rituals | Following ethical codes, fulfilling duties |
| Philosophical Roots | Bhakti Yoga in Hinduism | Dharma as defined in Vedas and Upanishads |
| Examples | Worship of Krishna, Shiva, or Devi | Caste duties, ethical behavior, law adherence |
Introduction: Understanding Bhakti and Dharma
Bhakti is a profound devotional practice centered on intense love and surrender to a personal deity, emphasizing emotional connection and spiritual devotion. Dharma refers to the ethical and moral duties that govern individual behavior and societal order, rooted in righteousness and duty. Understanding Bhakti and Dharma involves recognizing their complementary roles in guiding spiritual growth and ethical living within Hindu philosophy.
Defining Bhakti: The Path of Devotion
Bhakti represents a profound spiritual practice centered on unwavering devotion and love toward a personal deity, emphasizing emotional connection and surrender. It contrasts with Dharma, which involves adherence to moral duties, social responsibilities, and ethical living as prescribed by scriptures like the Bhagavad Gita. Bhakti cultivates a direct, heartfelt bond with the divine, making it a path accessible to all regardless of caste or background.
Understanding Dharma: The Path of Duty and Righteousness
Dharma represents the fundamental path of duty and righteousness guiding ethical behavior in Hindu philosophy. It encompasses moral obligations tailored to one's caste, stage of life, and personal circumstances, ensuring societal harmony and spiritual growth. Understanding dharma requires recognizing its fluid nature, balancing individual duties with universal principles to maintain cosmic order.
Philosophical Roots of Bhakti and Dharma
Bhakti, rooted in devotion and personal surrender to a deity, emerges from the Bhakti movement emphasizing emotional connection and individual spirituality within Hinduism. Dharma, grounded in ancient Vedic and Dharmashastra texts, refers to the moral, ethical, and social duties prescribed to maintain cosmic order and societal harmony. Both concepts coexist as complementary paths in Indian philosophy, with Bhakti focusing on devotional love and Dharma on righteous conduct.
Bhakti in Major Indian Religions
Bhakti, emphasizing devotional love and personal connection to a deity, plays a central role in Hinduism, Sikhism, and certain traditions of Jainism and Buddhism. In Hinduism, Bhakti manifests through practices like chanting, temple worship, and festivals dedicated to gods such as Krishna, Shiva, and Vishnu, fostering emotional engagement and spiritual liberation (moksha). Sikhism integrates Bhakti into its core teachings with devotion to Waheguru expressed through hymn singing (Kirtan) and meditation, highlighting love and submission over ritualistic observance.
Dharma in Hindu Texts and Traditions
Dharma in Hindu texts and traditions represents the fundamental moral and ethical duties that uphold cosmic order and individual righteousness, as outlined in scriptures like the Manusmriti and the Bhagavad Gita. It encompasses duties specific to one's class (varna) and stage of life (ashrama), guiding behavior to sustain societal harmony and spiritual progress. Unlike Bhakti, which emphasizes devotional love towards a personal deity, Dharma serves as the practical framework for living a balanced and principled life according to Vedic law.
Bhakti vs Dharma: Key Differences
Bhakti emphasizes personal devotion and emotional connection to a deity, fostering love and surrender as the path to spiritual liberation, while Dharma centers on duty, moral law, and righteous living according to societal and cosmic order. Bhakti is characterized by practices such as chanting, worship, and prayer aiming for union with the divine, whereas Dharma involves fulfilling ethical responsibilities, social roles, and adherence to scriptures. The key difference lies in Bhakti's focus on heartfelt devotion as the means to salvation, contrasting with Dharma's emphasis on duty and moral conduct as the foundation for spiritual progress.
The Interplay between Bhakti and Dharma
The interplay between Bhakti and Dharma highlights a dynamic balance where Bhakti, the path of devotion and love towards the divine, enriches Dharma by infusing it with heartfelt surrender and ethical commitment. Dharma, representing cosmic law and righteous duty, provides a structured framework for Bhakti to be practiced with discipline and moral clarity. Together, Bhakti and Dharma create a holistic spiritual approach that integrates emotional devotion with responsible living.
Modern Interpretations of Bhakti and Dharma
Modern interpretations of Bhakti emphasize personal devotion and emotional connection to the divine, often seen in contemporary spiritual movements and individual practices. Contemporary Dharma is increasingly understood as a dynamic ethical framework guiding responsibilities and moral duties in everyday life, adaptable to changing social contexts. Both Bhakti and Dharma today intersect to promote a balanced approach combining heartfelt spirituality with practical ethical living.
Conclusion: Integrating Bhakti and Dharma in Daily Life
Integrating Bhakti and Dharma in daily life fosters holistic spiritual growth by balancing devotion with righteous action, enhancing moral clarity and emotional fulfillment. Bhakti infuses practices with heartfelt devotion, while Dharma grounds behavior in ethical duties, creating a dynamic synergy that nurtures both inner peace and social harmony. This integration encourages consistent self-improvement and compassionate living, essential for achieving spiritual liberation and societal well-being.
Bhakti Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com