Latria is a term used in Christian theology to describe the highest form of worship and adoration, reserved exclusively for God. It involves recognizing God's supreme divinity and expressing profound reverence through prayer and devotion. Discover how understanding latria can deepen your spiritual practice by exploring the insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
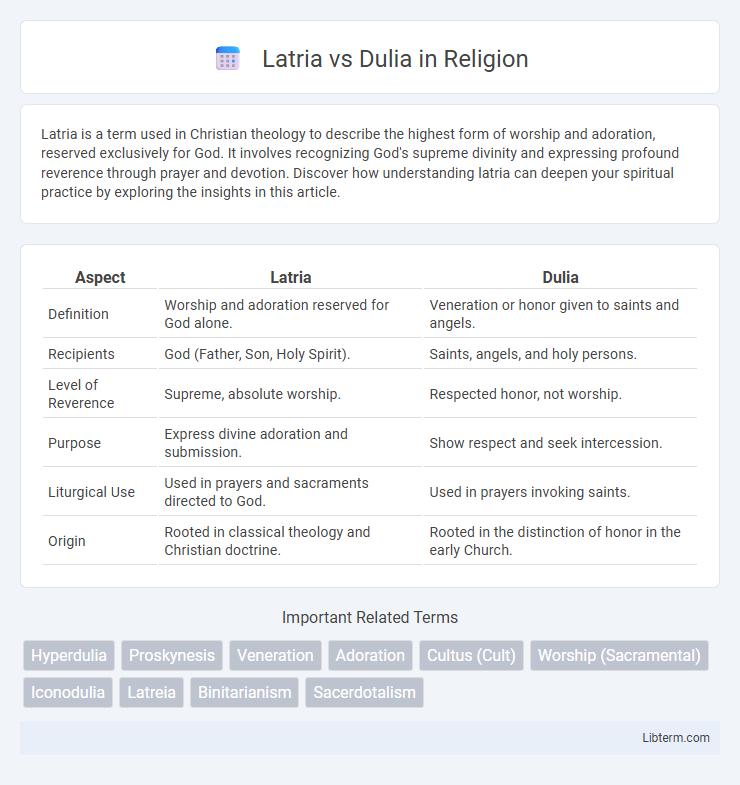
| Aspect | Latria | Dulia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Worship and adoration reserved for God alone. | Veneration or honor given to saints and angels. |
| Recipients | God (Father, Son, Holy Spirit). | Saints, angels, and holy persons. |
| Level of Reverence | Supreme, absolute worship. | Respected honor, not worship. |
| Purpose | Express divine adoration and submission. | Show respect and seek intercession. |
| Liturgical Use | Used in prayers and sacraments directed to God. | Used in prayers invoking saints. |
| Origin | Rooted in classical theology and Christian doctrine. | Rooted in the distinction of honor in the early Church. |
Introduction to Latria and Dulia
Latria and Dulia are terms used in Christian theology to describe different levels of veneration directed toward divine and holy figures. Latria refers to the highest form of worship and adoration reserved exclusively for God, highlighting His supreme divinity and sovereignty. Dulia denotes a reverence or veneration given to saints and angels, recognizing their holiness and role as intercessors without equating them to God's divine status.
Etymology and Origins of the Terms
Latria derives from the Greek word "latreia," meaning "worship" or "service," specifically denoting supreme worship reserved for God alone. Dulia originates from the Greek term "douleia," which means "servitude" or "service," signifying a lesser form of veneration given to saints and angels. Both terms emerged in early Christian theological debates to differentiate the levels of honor and worship appropriately given in religious practice.
Theological Definitions
Latria denotes the worship and adoration reserved exclusively for God, embodying the highest form of reverence in Christian theology. Dulia refers to the veneration given to saints and angels, recognizing their holy lives and intercessory roles without attributing divine status. The distinction between Latria and Dulia is essential for understanding the hierarchical nature of worship and honor within Catholic doctrine.
Key Differences Between Latria and Dulia
Latria refers to the worship and adoration given exclusively to God, emphasizing divine honor and supreme reverence. Dulia is the veneration shown to saints and angels, recognizing their holiness and role as intercessors without equating it to the worship of God. The key difference lies in Latria being reserved solely for the divine nature of God, while Dulia is a respectful honor directed toward holy beings.
Latria: Worship Reserved for God Alone
Latria represents the highest form of worship and adoration, reserved exclusively for God alone, emphasizing divine sovereignty and supreme reverence. This form of worship involves total submission, profound love, and absolute honor that acknowledges God's unique divinity. In contrast, dulia refers to veneration or honor given to saints and angels, distinct from the worship due only to God under latria.
Dulia: Veneration of Saints and Angels
Dulia refers to the veneration given to saints and angels, recognizing their holy and virtuous nature as intercessors between God and humanity. This form of honor respects their exemplary lives and spiritual closeness to God, distinct from Latria, which is worship due to God alone. In Christian theology, dulia expresses reverence without implying divinity, emphasizing support and guidance from saints and angels in the faith journey.
Hyperdulia: Special Honor to the Virgin Mary
Latria represents the highest form of worship, reserved exclusively for God, while Dulia is the veneration given to saints as a sign of respect. Hyperdulia is a unique category of veneration, elevated above Dulia, specifically honoring the Virgin Mary for her singular role in salvation history. This special honor acknowledges Mary's exceptional holiness and maternal intercession, distinguishing her devotion from that of other saints.
Scriptural Basis for Latria and Dulia
Latria, the worship due to God alone, finds scriptural basis in passages such as Exodus 20:3-5, which command exclusive devotion to God and prohibit idolatry, and Matthew 4:10, where Jesus affirms worshiping only the Lord. Dulia, the veneration given to saints and angels, is supported by biblical examples like Hebrews 1:6, showing angels as ministering spirits deserving reverence, and Luke 1:48, which highlights honoring Mary for her role in salvation history. This distinct scriptural foundation emphasizes the unique honor due to God (latria) versus the respectful honor paid to holy beings (dulia).
Practice and Application in Christian Traditions
Latria is the worship and adoration due to God alone, emphasizing ultimate reverence in Christian liturgy and prayer, while Dulia refers to the veneration given to saints and angels as honored servants of God. In practice, Latria involves the Eucharist and the Divine Office, expressing exclusive divine worship, whereas Dulia manifests through prayers asking saints for intercession and the veneration of relics and images without equating them to divine status. These distinctions uphold the monotheistic foundation of Christianity by clearly separating adoration reserved for God (Latria) from respect and honor given to holy persons (Dulia).
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
Latria is the worship reserved for God alone, recognizing His supreme divinity, while dulia refers to the veneration given to saints as honor, not worship. A common misconception is that dulia blurs the line with latria, but doctrinal teachings clarify that dulia is a respectful honor distinct from the adoration due only to God. Understanding this distinction is crucial for proper theological interpretation and avoiding confusion in Catholic devotional practices.
Latria Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com