Sanmukh represents a profound spiritual concept symbolizing direct divine presence and spiritual enlightenment. Exploring its significance can transform your understanding of inner peace and higher consciousness. Discover more about Sanmukh and its impact on your spiritual journey in the full article.
Table of Comparison
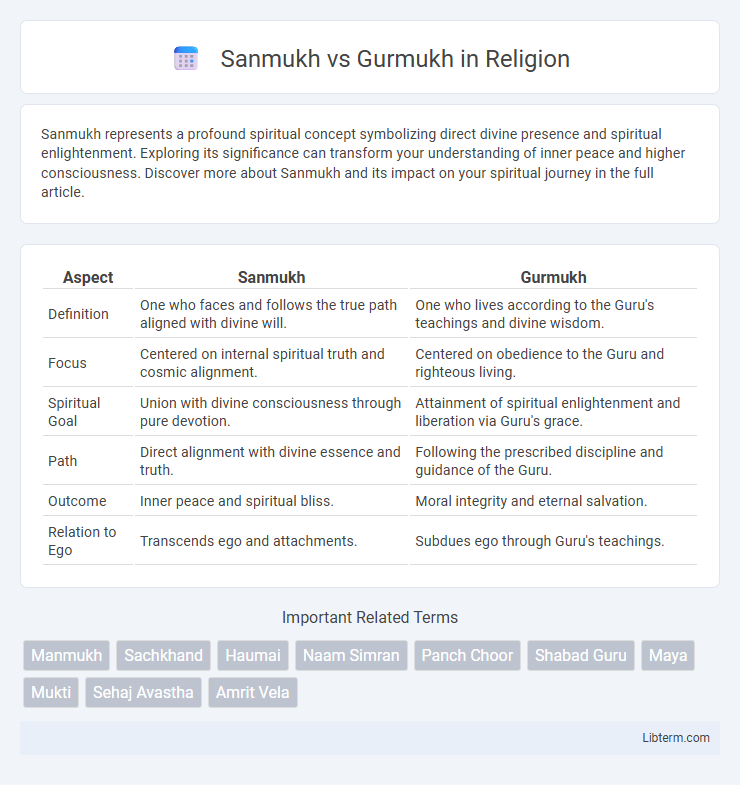
| Aspect | Sanmukh | Gurmukh |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One who faces and follows the true path aligned with divine will. | One who lives according to the Guru's teachings and divine wisdom. |
| Focus | Centered on internal spiritual truth and cosmic alignment. | Centered on obedience to the Guru and righteous living. |
| Spiritual Goal | Union with divine consciousness through pure devotion. | Attainment of spiritual enlightenment and liberation via Guru's grace. |
| Path | Direct alignment with divine essence and truth. | Following the prescribed discipline and guidance of the Guru. |
| Outcome | Inner peace and spiritual bliss. | Moral integrity and eternal salvation. |
| Relation to Ego | Transcends ego and attachments. | Subdues ego through Guru's teachings. |
Introduction to Sanmukh and Gurmukh
Sanmukh and Gurmukh are key terms in Sikh spirituality, representing inward and outward orientations of the self. Sanmukh refers to being "facing the self," emphasizing ego-driven, worldly attachments and external influences, whereas Gurmukh means "facing the Guru," symbolizing alignment with divine wisdom and inner spiritual guidance. Understanding these concepts aids in discerning the path of self-centeredness versus the path of devotion and enlightenment in Sikh teachings.
Etymology and Linguistic Roots
Sanmukh and Gurmukh originate from Punjabi and Sanskrit linguistic roots, where Sanmukh combines "san" (good) and "mukh" (face or presence) to imply being 'positively oriented'; Gurmukh merges "gur" (guru or teacher) with "mukh" (face), denoting one who is 'guru-centered' or spiritually guided. The etymology reflects core Sikh philosophical ideals, with Sanmukh emphasizing correct knowledge or viewpoint and Gurmukh representing alignment with divine wisdom imparted by the guru. These terms linguistically underscore an individual's orientation either towards righteous consciousness (Sanmukh) or guru's teachings (Gurmukh), foundational in Sikh spiritual discourse.
Philosophical Foundations
Sanmukh and Gurmukh represent two divergent philosophical orientations in Sikh thought, where Sanmukh refers to one whose focus is self-centered and ego-driven, rooted in materialism and attachment to worldly desires. Gurmukh, by contrast, aligns with the divine wisdom of the Guru, embodying spiritual enlightenment, selflessness, and adherence to the path of righteousness (Dharma) as prescribed in the Guru Granth Sahib. This dichotomy underscores the Sikh emphasis on transcending the ego (Haumai) through meditative devotion (Simran) and living a life guided by Guru's teachings for ultimate liberation (Mukti).
Sanmukh: Characteristics and Traits
Sanmukh refers to a person who is self-centered, egoistic, and driven by worldly desires, often prioritizing personal gain over spiritual growth. This mindset is characterized by attachment to materialism, arrogance, and a lack of humility, which obstructs inner peace and enlightenment. Unlike Gurmukh, who follows the Guru's teachings, Sanmukh remains trapped in ego, resulting in ignorance and disharmony.
Gurmukh: Characteristics and Traits
Gurmukh embodies qualities of selflessness, spiritual devotion, and alignment with divine will, emphasizing inner purity and compassion in daily life. This individual prioritizes collective well-being, consistently practicing mindfulness, humility, and ethical conduct according to Sikh teachings. Gurmukh represents the ideal of living a life centered on Gurmat principles, contrasting with Sanmukh's focus on ego and materialism.
Sanmukh vs Gurmukh: Core Differences
Sanmukh and Gurmukh represent distinct spiritual orientations within Sikhism, where Sanmukh refers to being self-centered and ego-driven, while Gurmukh denotes being God-centered and aligned with the Guru's teachings. The core difference lies in their focus: Sanmukh individuals prioritize personal desires and worldly attachments, whereas Gurmukh individuals embody humility, devotion, and adherence to divine guidance. This fundamental contrast influences behavior, mindset, and spiritual progress in the Sikh path.
Spiritual Significance in Sikhism
Sanmukh and Gurmukh represent two opposing spiritual orientations in Sikhism, with Gurmukh symbolizing a soul aligned with divine will and spiritual wisdom as taught by the Guru. Gurmukh individuals prioritize living according to Gurbani and the teachings of the Sikh Gurus, embodying virtues like humility, compassion, and devotion, which leads to liberation (mukti). On the contrary, Sanmukh denotes a self-centered focus driven by ego and material attachments, hindering spiritual progress and distancing one from the path of Naam Simran and divine truth.
Role in Daily Life and Practice
Sanmukh and Gurmukh represent contrasting orientations in daily life and spiritual practice within Sikh philosophy. Sanmukh refers to a self-centered individual driven by ego and material desires, often leading to attachment and ignorance in everyday actions. Gurmukh, on the other hand, embodies alignment with divine wisdom and values, guiding daily conduct through humility, selflessness, and meditation on Gurbani, fostering inner peace and ethical living.
Teachings from Sikh Scriptures
Sanmukh and Gurmukh represent contrasting spiritual orientations in Sikh philosophy, with Sanmukh indicating a self-centered ego-driven life and Gurmukh signifying a God-centered, spiritually enlightened path. Sikh scriptures, particularly the Guru Granth Sahib, emphasize living as a Gurmukh by embodying virtues like humility, selflessness, and devotion to Waheguru, reflecting teachings that promote inner transformation and alignment with divine will. The Gurbani explains that Sanmukh leads to suffering and ignorance, while Gurmukh attains liberation (mukti) through meditation, truthful living, and loving remembrance of God's name (Naam Simran).
Path to Becoming a Gurmukh
Becoming a Gurmukh involves aligning one's actions, thoughts, and intentions with the divine will as described in Sikh teachings, contrasting with the Sanmukh path, which centers on self-driven desires and ego. The Gurmukh path emphasizes living according to Gurbani, embracing humility, devotion, and selfless service, which leads to spiritual awakening and union with Waheguru. This journey entails consistent meditation on God's name (Naam Simran), adherence to the teachings of the Guru, and overcoming the five vices--lust, anger, greed, attachment, and ego.
Sanmukh Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com