Christian faith emphasizes love, compassion, and forgiveness as core principles shaping personal and communal life. Understanding the teachings of Jesus Christ can inspire Your spiritual growth and ethical decisions daily. Explore the article to deepen Your knowledge of Christianity's impact on culture and individual well-being.
Table of Comparison
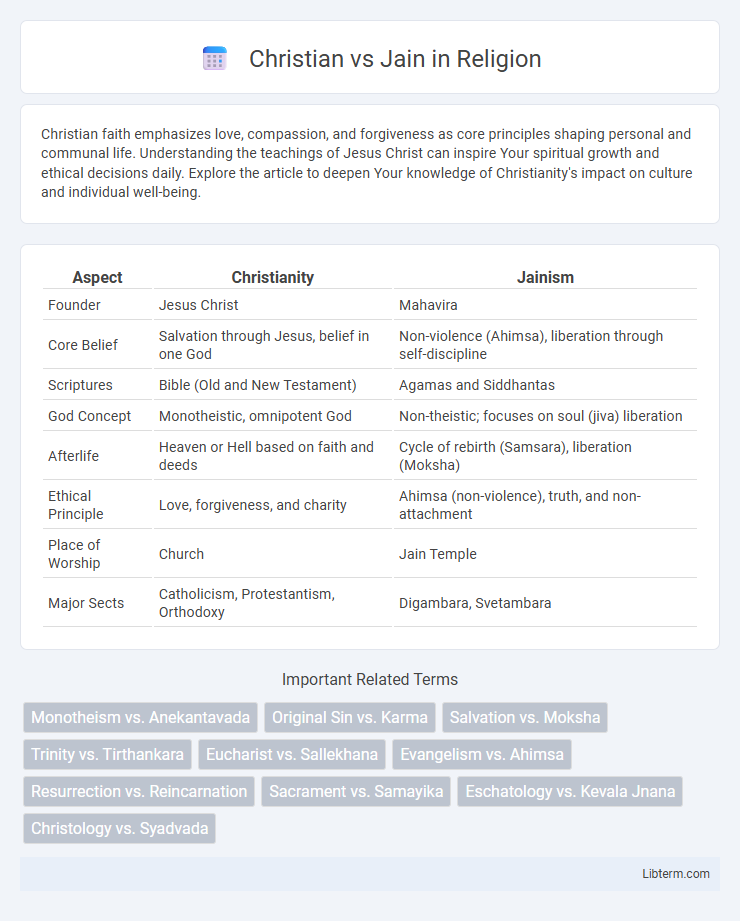
| Aspect | Christianity | Jainism |
|---|---|---|
| Founder | Jesus Christ | Mahavira |
| Core Belief | Salvation through Jesus, belief in one God | Non-violence (Ahimsa), liberation through self-discipline |
| Scriptures | Bible (Old and New Testament) | Agamas and Siddhantas |
| God Concept | Monotheistic, omnipotent God | Non-theistic; focuses on soul (jiva) liberation |
| Afterlife | Heaven or Hell based on faith and deeds | Cycle of rebirth (Samsara), liberation (Moksha) |
| Ethical Principle | Love, forgiveness, and charity | Ahimsa (non-violence), truth, and non-attachment |
| Place of Worship | Church | Jain Temple |
| Major Sects | Catholicism, Protestantism, Orthodoxy | Digambara, Svetambara |
Introduction to Christianity and Jainism
Christianity is a monotheistic religion centered on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, emphasizing salvation through faith and the belief in one God. Jainism, an ancient Indian religion, focuses on non-violence (ahimsa), self-discipline, and liberation through strict ethical principles and ascetic practices. Both faiths offer distinct spiritual paths, with Christianity rooted in the Bible and Jainism grounded in texts like the Agamas.
Historical Origins and Founders
Christianity originated in the 1st century CE in the Roman province of Judea, founded on the teachings of Jesus of Nazareth, who is regarded as the Christ and Son of God. Jainism traces back to ancient India, with its formal establishment attributed to Mahavira in the 6th century BCE, who is considered the 24th Tirthankara in a long lineage of spiritual leaders. The distinct historical origins reflect Christianity's roots in monotheistic Abrahamic traditions, contrasting with Jainism's emphasis on non-theistic spiritual liberation and ascetic practices.
Core Beliefs and Doctrines
Christianity centers on the belief in one God and the salvation of humanity through the life, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ. Jainism emphasizes non-violence (ahimsa), self-discipline, and the liberation of the soul from the cycle of rebirth through strict ethical conduct. While Christianity teaches faith in divine grace for eternal life, Jainism focuses on individual effort to achieve spiritual purity and enlightenment.
Concepts of God and Divinity
Christianity centers on the belief in one omnipotent, omniscient God who embodies love, justice, and mercy, with divinity manifesting uniquely in the Holy Trinity: Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. Jainism rejects the notion of a creator god, emphasizing instead eternal, infinite souls (jivas) that achieve divinity through self-realization and liberation (moksha) by conquering karma and cycle of rebirth. The Christian concept of divinity involves worship and a personal relationship with God, whereas Jain divinity is attained through ethical living, non-violence (ahimsa), and spiritual discipline.
Sacred Texts and Scriptures
Christianity's sacred texts are centered on the Bible, comprising the Old Testament and the New Testament, which include the teachings of Jesus Christ and the history of Israel. Jainism's scriptures are primarily found in the Agamas, which consist of canonical texts articulated by the Tirthankaras, emphasizing non-violence and liberation. Both religions uphold their scriptures as authoritative guides for ethical conduct, spiritual discipline, and doctrinal beliefs.
Rituals and Worship Practices
Christian rituals prominently include baptism, communion, and Sunday church services centered on prayer and hymns, reflecting a focus on scripture and sacraments. Jain worship practices emphasize non-violence (ahimsa), meditation, and rituals like pradakshina (circumambulation) and puja honoring Tirthankaras, with strict adherence to fasting and asceticism. Both traditions use ritual to express devotion, yet Christianity centers on grace through sacraments while Jainism prioritizes self-discipline and liberation through ethical conduct.
Ethical Principles and Moral Teachings
Christian ethical principles center on love, forgiveness, and the Ten Commandments, emphasizing compassion, humility, and salvation through faith in Jesus Christ. Jain moral teachings prioritize non-violence (ahimsa), truthfulness (satya), and asceticism to achieve liberation (moksha) by minimizing harm to all living beings. Both traditions advocate ethical conduct but differ in their metaphysical foundations and approaches to spiritual liberation.
Approaches to Salvation and Liberation
Christianity teaches salvation through faith in Jesus Christ, emphasizing grace, repentance, and divine forgiveness as the pathway to eternal life in Heaven. Jainism promotes liberation (moksha) through strict adherence to non-violence (ahimsa), self-discipline, and karma purification, aiming to free the soul from the cycle of birth and death (samsara). While Christianity centers on a personal relationship with God for salvation, Jainism focuses on self-effort and ethical living to achieve spiritual liberation.
Influence on Society and Culture
Christianity has significantly shaped Western art, law, and social welfare systems, emphasizing charity, community service, and moral teachings rooted in the Bible. Jainism promotes non-violence (ahimsa) and environmental sustainability, influencing Indian culture through vegetarianism, ethical business practices, and grassroots activism. Both religions contribute uniquely to societal values, with Christianity impacting global missions and education, while Jainism fosters ecological consciousness and peaceful coexistence.
Key Differences and Similarities
Christianity centers on the belief in one God and the salvation offered through Jesus Christ's sacrifice, while Jainism emphasizes non-violence (ahimsa) and liberation through self-discipline and karma purification. Both religions teach ethical living and compassion towards others, but Christianity advocates faith in divine grace, whereas Jainism relies on individual effort to attain spiritual enlightenment. Rituals and worship practices differ significantly, with Christianity featuring sacraments and church services, whereas Jainism involves meditation, ascetic practices, and veneration of Tirthankaras.
Christian Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com