Figurative sense enriches language by conveying meanings beyond the literal interpretation, using metaphors, similes, and symbolism to evoke emotions and create vivid imagery. Understanding figurative expressions enhances your ability to grasp deeper messages and appreciate literary artistry. Explore the rest of the article to master the nuances of figurative language and improve your communication skills.
Table of Comparison
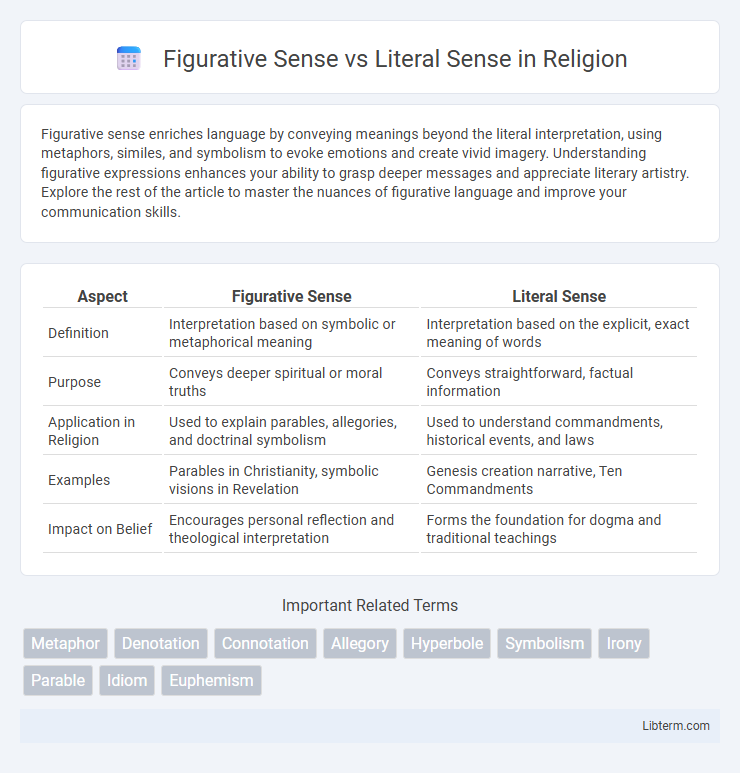
| Aspect | Figurative Sense | Literal Sense |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpretation based on symbolic or metaphorical meaning | Interpretation based on the explicit, exact meaning of words |
| Purpose | Conveys deeper spiritual or moral truths | Conveys straightforward, factual information |
| Application in Religion | Used to explain parables, allegories, and doctrinal symbolism | Used to understand commandments, historical events, and laws |
| Examples | Parables in Christianity, symbolic visions in Revelation | Genesis creation narrative, Ten Commandments |
| Impact on Belief | Encourages personal reflection and theological interpretation | Forms the foundation for dogma and traditional teachings |
Understanding Figurative vs Literal Language
Understanding figurative versus literal language involves recognizing that literal language conveys meanings exactly as stated, while figurative language uses metaphors, similes, and symbolism to express ideas creatively. Figurative sense enhances communication by evoking imagery and emotions, enabling readers to interpret deeper, non-literal meanings beyond the surface text. Mastery of both senses is essential for interpreting literature, rhetoric, and everyday language accurately.
Defining Figurative Sense
Figurative sense refers to interpreting language in a non-literal way, where words or phrases convey meanings beyond their ordinary definitions to create vivid imagery or express complex ideas. It encompasses metaphors, similes, personification, and other rhetorical devices that rely on symbolic or imaginative understanding. This contrasts with literal sense, which involves the direct, explicit meaning of words without embellishment or abstraction.
Defining Literal Sense
The literal sense refers to the primary, straightforward meaning of a text, understood through the exact words without interpretation or symbolic meaning. It involves the factual and explicit content that is directly stated, serving as the foundation for further analysis. Understanding the literal sense is essential for accurate comprehension before exploring figurative or metaphorical layers in language.
Key Differences Between Figurative and Literal Meanings
Figurative sense involves language that deviates from the literal meaning to convey complex ideas through metaphors, similes, and symbolism, enriching expression and evoking emotions. Literal sense refers to the exact, dictionary definitions of words, emphasizing straightforward, concrete meaning without embellishment or interpretation. The key difference lies in figurative language's reliance on imagination and interpretation, while literal language prioritizes clarity and factual accuracy.
Common Types of Figurative Language
Figurative sense involves language that conveys meanings beyond the literal interpretation, enhancing expression and creativity through devices such as metaphors, similes, personification, and hyperbole. Metaphors directly compare two unrelated concepts, similes use "like" or "as" for comparison, personification attributes human traits to non-human objects, and hyperbole exaggerates for emphasis. Understanding these common types of figurative language is essential for interpreting nuanced meanings and enriching communication.
Everyday Examples of Literal Sense
Everyday examples of literal sense include statements like "The sky is blue" or "She drinks water," where words convey their direct, explicit meanings without metaphor or exaggeration. Literal sense is essential for clear communication in routine activities such as giving directions, describing objects, and stating facts. Understanding literal language helps avoid confusion in contexts like instructions, recipes, and safety warnings that rely on precise meanings.
The Role of Context in Meaning
The role of context in determining the meaning of language is crucial for distinguishing between figurative sense and literal sense. Context provides the situational, cultural, and linguistic cues that guide interpretation, enabling listeners or readers to recognize when words or phrases are intended metaphorically rather than literally. Without context, the ambiguity between literal and figurative meanings can lead to misunderstandings, highlighting the importance of surrounding text and real-world knowledge in semantic analysis.
Why Figurative Language Matters in Communication
Figurative language enriches communication by conveying complex ideas and emotions through metaphors, similes, and symbolism, creating deeper connections and engagement. It enhances understanding by appealing to imagination and cultural context, which literal language alone often cannot achieve. This use of figurative expressions allows speakers and writers to communicate abstract or nuanced concepts more effectively and memorably.
Challenges in Interpreting Figurative and Literal Sense
Interpreting figurative and literal sense poses significant challenges due to the inherent ambiguity and contextual dependence of figurative language, which often requires cultural, emotional, and situational awareness to discern implied meanings. Literal sense demands precision and straightforward interpretation, but misunderstandings arise when ambiguity or polysemy blur clear communication. Effective comprehension hinges on the reader's or listener's ability to switch between literal precision and figurative nuance, balancing semantics, pragmatics, and cognitive processing.
Tips for Using Figurative and Literal Language Effectively
Using figurative language effectively involves choosing metaphors, similes, and idioms that enhance imagery and emotional impact without confusing the audience. Literal language should be clear, precise, and straightforward, ensuring that facts and instructions are easily understood. Balancing both senses requires context awareness, audience consideration, and purpose-driven word choice to maximize communication clarity and engagement.
Figurative Sense Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com