Maladaptive behaviors hinder your ability to adapt effectively to new or challenging situations, often resulting in negative consequences for mental and emotional well-being. These patterns can manifest as avoidance, aggression, or excessive anxiety, disrupting daily life and personal growth. Explore this article to understand how to recognize and address maladaptive behaviors for a healthier mindset.
Table of Comparison
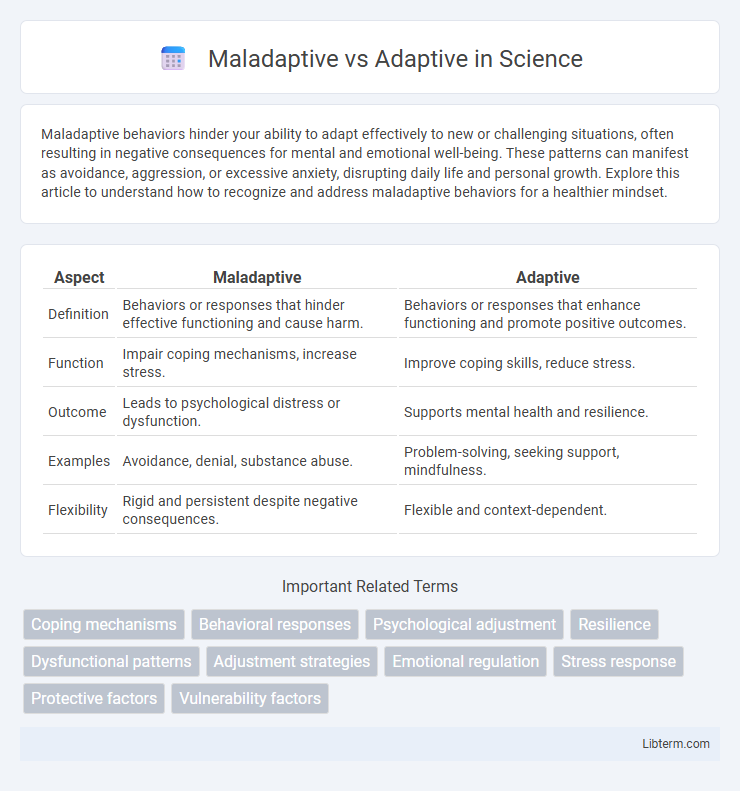
| Aspect | Maladaptive | Adaptive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Behaviors or responses that hinder effective functioning and cause harm. | Behaviors or responses that enhance functioning and promote positive outcomes. |
| Function | Impair coping mechanisms, increase stress. | Improve coping skills, reduce stress. |
| Outcome | Leads to psychological distress or dysfunction. | Supports mental health and resilience. |
| Examples | Avoidance, denial, substance abuse. | Problem-solving, seeking support, mindfulness. |
| Flexibility | Rigid and persistent despite negative consequences. | Flexible and context-dependent. |
Understanding Adaptation: Definitions and Concepts
Maladaptive behaviors hinder effective coping and adjustment to environmental changes, often leading to negative outcomes and decreased well-being. Adaptive behaviors promote positive adjustment by enabling individuals to respond flexibly and constructively to challenges, improving resilience and overall functioning. Understanding adaptation involves recognizing the dynamic interplay between these behaviors and their impact on psychological health and development.
What is Adaptive Behavior?
Adaptive behavior refers to the collection of conceptual, social, and practical skills that individuals use to function effectively in everyday life. These behaviors enable people to meet personal needs, interact successfully with others, and adapt to changing environmental demands. Examples include communication, self-care, social skills, and problem-solving abilities that promote independence and well-being.
Maladaptive Behavior Explained
Maladaptive behavior refers to actions or patterns that inhibit an individual's ability to adjust healthily to stressful situations or demands, often leading to negative consequences in personal, social, or occupational contexts. These behaviors can include avoidance, aggression, or withdrawal, which typically exacerbate problems rather than resolving them. Understanding maladaptive behavior is crucial in psychological assessments and interventions aimed at promoting adaptive coping strategies and mental well-being.
Key Differences Between Adaptive and Maladaptive
Adaptive behaviors promote effective coping and positive adjustment to new or challenging situations, enhancing overall well-being and resilience. Maladaptive behaviors, in contrast, hinder problem-solving and emotional regulation, often exacerbating stress and leading to negative outcomes. Key differences include adaptability to change, impact on mental health, and long-term functionality.
Causes of Maladaptive Responses
Maladaptive responses often stem from unresolved trauma, chronic stress, or negative early life experiences that impair emotional regulation and coping mechanisms. Genetic predispositions and dysfunctional neural pathways also contribute significantly to maladaptive behavior patterns by altering cognitive and emotional processing. Environmental factors such as toxic relationships and persistent adverse conditions exacerbate these responses, reinforcing unhealthy behavioral cycles.
Benefits of Adaptive Strategies
Adaptive strategies enhance resilience by promoting problem-solving skills and emotional regulation, which improve overall mental health and well-being. These approaches facilitate effective coping mechanisms, enabling individuals to navigate stress and challenges constructively. Benefits include increased motivation, better decision-making, and stronger social support networks, contributing to long-term psychological growth.
Examples of Maladaptive vs Adaptive in Daily Life
Maladaptive behaviors in daily life include procrastination that leads to missed deadlines and increased stress or excessive social withdrawal resulting in isolation and decreased support networks. Adaptive behaviors involve time management techniques like creating schedules to meet deadlines and actively seeking social interactions to build and maintain relationships. Both examples highlight how adaptive strategies promote well-being, while maladaptive patterns can hinder personal growth and mental health.
Psychological Impact of Maladaptive Patterns
Maladaptive patterns often lead to increased stress, anxiety, and depression, as they hinder effective problem-solving and emotional regulation. These dysfunctional behaviors reinforce negative thought cycles, impair social relationships, and reduce overall psychological resilience. Conversely, adaptive patterns promote mental well-being by fostering flexibility, coping skills, and positive emotional responses.
Building Adaptive Coping Mechanisms
Building adaptive coping mechanisms involves developing strategies that effectively manage stress and promote resilience, such as problem-solving, emotional regulation, and seeking social support. Unlike maladaptive coping, which includes avoidance, denial, or substance abuse, adaptive coping enhances psychological well-being and long-term mental health. Cultivating mindfulness, cognitive restructuring, and proactive behavior changes are key components that empower individuals to navigate challenges constructively.
Supporting Personal Growth Through Adaptation
Maladaptive behaviors hinder personal growth by reinforcing negative patterns and limiting emotional resilience, while adaptive behaviors promote learning and healthy coping strategies essential for self-improvement. Emphasizing adaptive responses to challenges fosters cognitive flexibility, enhances problem-solving skills, and supports long-term psychological well-being. Understanding the distinction between maladaptive and adaptive mechanisms enables individuals to cultivate mindset shifts that drive sustainable personal development.
Maladaptive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com