Quantitative analysis involves the use of mathematical and statistical methods to measure and evaluate data, providing objective insights into trends and patterns. This approach enhances decision-making by transforming complex information into quantifiable metrics that can be systematically assessed. Discover how embracing quantitative techniques can elevate Your understanding and application by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
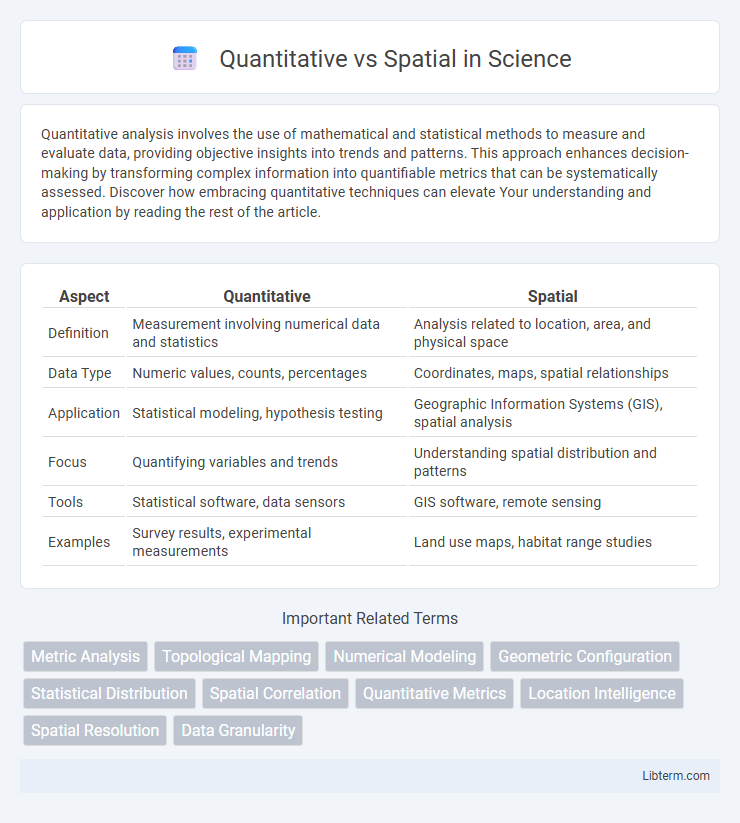
| Aspect | Quantitative | Spatial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement involving numerical data and statistics | Analysis related to location, area, and physical space |
| Data Type | Numeric values, counts, percentages | Coordinates, maps, spatial relationships |
| Application | Statistical modeling, hypothesis testing | Geographic Information Systems (GIS), spatial analysis |
| Focus | Quantifying variables and trends | Understanding spatial distribution and patterns |
| Tools | Statistical software, data sensors | GIS software, remote sensing |
| Examples | Survey results, experimental measurements | Land use maps, habitat range studies |
Introduction to Quantitative and Spatial Analysis
Quantitative analysis involves the systematic examination of numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships using statistical and mathematical models. Spatial analysis focuses on the geographic or locational aspects of data, incorporating techniques such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to analyze spatial relationships and distributions. Combining quantitative and spatial analysis enhances decision-making by integrating numerical precision with spatial context in fields like urban planning, environmental science, and public health.
Defining Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods involve the systematic collection and statistical analysis of numerical data to identify patterns, test hypotheses, and make predictions. These methods prioritize measurable variables and often employ surveys, experiments, or secondary data analysis to generate objective, replicable results. By contrast, spatial methods emphasize the analysis of geographic or spatial data, using tools like GIS to assess the relationships and patterns within physical or human landscapes.
Understanding Spatial Methods
Spatial methods analyze geographic locations and relationships using data mapped in space, enhancing the interpretation of spatial patterns and distributions. Quantitative methods emphasize numerical measurement and statistical analysis, providing precise metrics for hypothesis testing. Understanding spatial methods requires integrating spatial autocorrelation, spatial interpolation, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to accurately capture and interpret spatial dependencies in datasets.
Key Differences Between Quantitative and Spatial Approaches
Quantitative approaches prioritize numerical data analysis, emphasizing statistical methods and measurable variables to identify patterns or correlations. Spatial approaches focus on location-based data, analyzing geographic distribution, spatial relationships, and the physical context of phenomena. The key difference lies in quantitative methods targeting numeric datasets while spatial methods incorporate geographic information system (GIS) tools to visualize and interpret spatial dynamics.
Applications of Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis applies statistical, mathematical, and computational techniques to analyze numerical data for decision-making in finance, healthcare, and market research. It enables precise forecasting, risk assessment, and performance measurement by leveraging large datasets and algorithmic models. Industries such as banking, pharmaceutical research, and supply chain management rely heavily on quantitative methods to optimize operations and strategies.
Applications of Spatial Analysis
Spatial analysis is essential in urban planning, environmental monitoring, and public health, enabling precise location-based decision-making and resource allocation. It leverages geographic information systems (GIS) and remote sensing data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships across spatial datasets. Applications include crime hotspot mapping, habitat suitability modeling, and infrastructure optimization for efficient service delivery.
Advantages of Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods provide precise numerical data that enable statistical analysis and reliable measurement of variables, facilitating objective decision-making. These methods allow for large-scale data collection and replication, enhancing the generalizability and credibility of research findings. The ability to quantify relationships and patterns supports efficient comparison and trend identification across diverse spatial datasets.
Benefits of Spatial Techniques
Spatial techniques enable the analysis of geographic patterns and relationships, providing insights that are impossible with purely quantitative data. These methods enhance decision-making by integrating location-based information, improving urban planning, environmental management, and resource allocation. Utilizing spatial analysis tools allows for more precise visualization and understanding of complex spatial phenomena, driving better outcomes across various industries.
When to Use Quantitative vs Spatial Methods
Quantitative methods are best used when analyzing numerical data, identifying patterns, and measuring relationships through statistical techniques. Spatial methods are ideal for exploring geographic distributions, spatial relationships, and location-based phenomena using mapping and geospatial analysis. Choosing between these approaches depends on whether the primary focus is on numerical measurement or spatial context within the dataset.
Integrating Quantitative and Spatial Approaches
Integrating quantitative and spatial approaches enhances data analysis by combining statistical methods with geographic information systems (GIS) to reveal patterns and relationships in spatial data. This fusion enables precise measurement and visualization of phenomena, supporting better decision-making in urban planning, environmental management, and public health. Leveraging spatial statistics and geospatial analytics improves accuracy and insight beyond traditional quantitative metrics alone.
Quantitative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com