Distal refers to a position farther from the center of the body or point of attachment, commonly used in anatomy to describe locations on limbs, such as fingers being distal to the wrist. Understanding distal relationships is crucial in medical diagnosis, rehabilitation, and anatomical study. Explore the rest of the article to learn how the concept of distal applies in various healthcare and biological contexts.
Table of Comparison
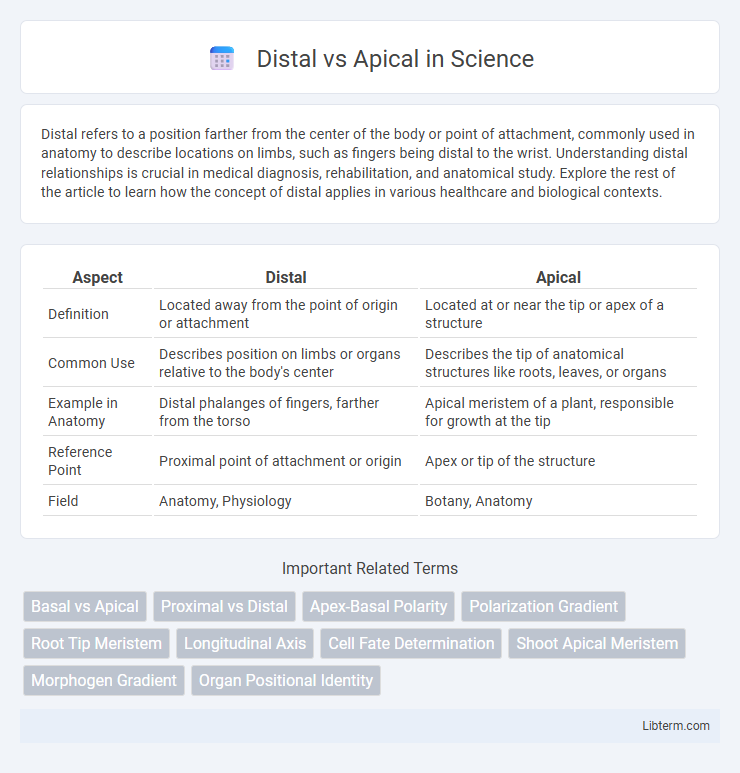
| Aspect | Distal | Apical |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Located away from the point of origin or attachment | Located at or near the tip or apex of a structure |
| Common Use | Describes position on limbs or organs relative to the body's center | Describes the tip of anatomical structures like roots, leaves, or organs |
| Example in Anatomy | Distal phalanges of fingers, farther from the torso | Apical meristem of a plant, responsible for growth at the tip |
| Reference Point | Proximal point of attachment or origin | Apex or tip of the structure |
| Field | Anatomy, Physiology | Botany, Anatomy |
Introduction to Distal and Apical
Distal and apical refer to specific anatomical locations used primarily in dentistry and biology to describe positions along teeth or roots. Distal indicates the surface or direction away from the center of the dental arch, opposite to mesial, while apical denotes the tip or end of the tooth root farthest from the crown. Understanding these terms is essential for accurate dental diagnosis, treatment planning, and communication among professionals.
Definitions: Distal vs Apical
Distal refers to a position farther from the center of the body or point of attachment, often used in anatomical or dental contexts to describe locations away from the midline. Apical pertains to the apex or tip of a structure, such as the tip of a root in a tooth or the end of a plant organ. Understanding the distinction between distal and apical is crucial for precise communication in biology, dentistry, and anatomy.
Anatomical Locations Explained
Distal and apical refer to specific anatomical locations primarily used in dental and anatomical contexts. The distal location indicates the surface or region of a tooth or body part farthest from the midline or point of reference, often referring to the side away from the center of the dental arch. The apical location relates to the apex, usually the tip or end of a structure such as the root of a tooth or the tip of an organ, emphasizing the position at the furthest or terminal point from the base.
Functional Differences
The functional differences between distal and apical surfaces primarily relate to their roles in dental anatomy and physiology. The distal surface, found on the side of a tooth farthest from the midline, is crucial for proper interproximal contact and preventing food impaction between teeth. In contrast, the apical surface, located at the tip of the tooth root, is essential for anchoring the tooth within the alveolar bone and facilitating neurovascular supply through the apical foramina.
Clinical Significance
Distal and apical regions of a tooth play distinct roles in periodontal health, where distal refers to the surface farthest from the midline and apical relates to the tip of the root. Clinically significant differences include disease progression patterns, with apical infections often leading to abscess formation and requiring endodontic treatment, while distal caries can affect adjacent teeth and complicate restorative procedures. Accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies depend on understanding the anatomical nuances between distal and apical involvement in dental pathology.
Common Examples in Practice
Distal and apical are anatomical terms commonly used in dental and medical practice to describe locations relative to a reference point. Distal refers to a position farther from the midline of the body or point of attachment, often seen in dentistry when describing the back surface of a tooth away from the front teeth. Apical pertains to the apex or tip, frequently used in endodontics to describe the tip of a tooth root during root canal procedures.
Importance in Diagnosis
Distal and apical regions of a tooth are crucial in dental diagnosis as they indicate different pathological conditions requiring specific treatment approaches. Distal lesions often highlight issues related to adjacent teeth and occlusal forces, while apical lesions primarily reveal underlying root infections or abscesses critical for endodontic intervention. Accurate differentiation between distal and apical involvement through radiographic imaging optimizes treatment planning and improves patient outcomes.
Challenges in Differentiation
Differentiating distal and apical lesions presents significant challenges due to overlapping radiographic appearances and similar clinical symptoms. Accurate diagnosis requires advanced imaging techniques such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and meticulous clinical examination to identify subtle anatomical variations and lesion localization. Misinterpretation can lead to incorrect treatment planning, emphasizing the need for enhanced diagnostic protocols and clinician expertise in endodontics.
Implications for Treatment
Distal and apical lesions require distinct treatment approaches due to their anatomical locations; distal lesions often involve easier access and removal, while apical lesions may necessitate more complex procedures such as apicoectomy or advanced endodontic therapy. Accurate diagnosis using radiographic imaging is crucial for determining lesion extent and guiding targeted interventions, reducing the risk of treatment failure. Understanding the differences in lesion behavior and healing potential informs selection of appropriate sealing materials and surgical techniques to optimize outcomes.
Summary and Key Takeaways
Distal refers to a position farther from the center of the body or point of attachment, commonly used in anatomical contexts to describe limbs or teeth. Apical relates to the apex or tip of a structure, often indicating the highest or terminal part such as the apex of a tooth or organ. Key takeaways emphasize that distal denotes relative distance along a limb or structure, while apical specifies the precise tip or apex location.
Distal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com