Homochronic cultures emphasize punctuality, scheduling, and completing one task at a time, often valuing structure and order in daily activities. Understanding homochronic behavior can improve your communication and collaboration in multicultural environments. Explore the rest of this article to learn how homochronic time management contrasts with other cultural approaches and its practical implications.
Table of Comparison
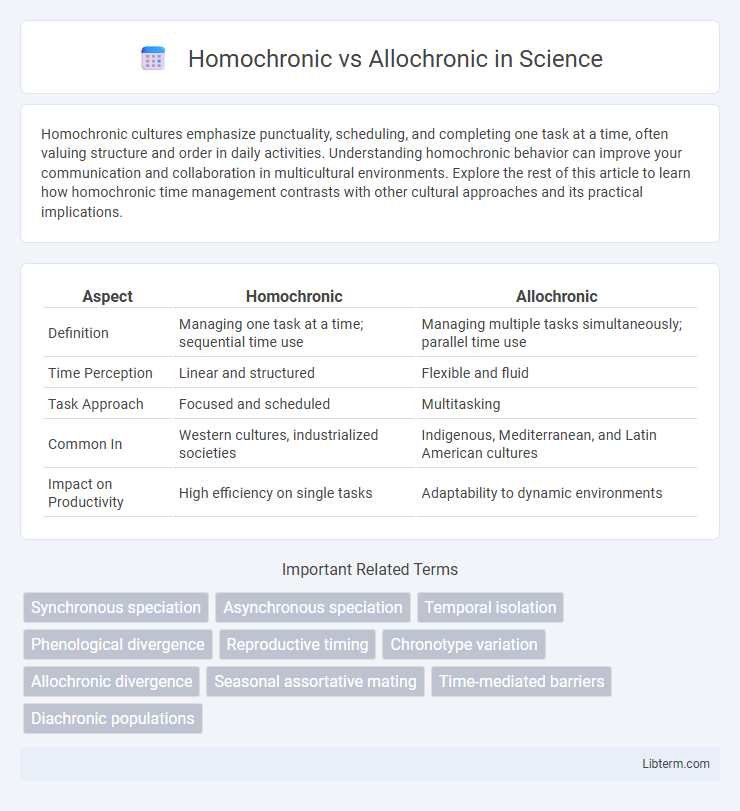
| Aspect | Homochronic | Allochronic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Managing one task at a time; sequential time use | Managing multiple tasks simultaneously; parallel time use |
| Time Perception | Linear and structured | Flexible and fluid |
| Task Approach | Focused and scheduled | Multitasking |
| Common In | Western cultures, industrialized societies | Indigenous, Mediterranean, and Latin American cultures |
| Impact on Productivity | High efficiency on single tasks | Adaptability to dynamic environments |
Introduction to Homochronic and Allochronic Concepts
Homochronic time orientation emphasizes punctuality, schedules, and completing one task at a time, reflecting cultures that value order and linear time management. Allochronic time orientation allows flexibility in time, multitasking, and prioritizes relationships over strict adherence to schedules, common in cultures focused on social connections and fluid time. Understanding homochronic and allochronic concepts is crucial in cross-cultural communication, workplace dynamics, and global collaboration to respect diverse time management preferences.
Defining Homochronic Communication Styles
Homochronic communication styles emphasize punctuality, sequential task completion, and a structured approach to time management, where individuals prefer focusing on one activity at a time. Cultures with homochronic traits value clear schedules, deadlines, and uninterrupted communication flows that align with a linear perception of time. Understanding homochronic communication helps improve cross-cultural interactions by recognizing the importance of time discipline and task-oriented behaviors.
Exploring Allochronic Communication Patterns
Allochronic communication patterns emphasize a flexible approach to time, allowing interactions to adapt dynamically to context and cultural norms. These patterns reflect societies where multitasking and spontaneity are valued, with conversations often overlapping and evolving organically. Understanding allochronic communication enhances cross-cultural interactions by highlighting the importance of temporal fluidity in relationship-building and negotiation processes.
Key Differences Between Homochronic and Allochronic Cultures
Homochronic cultures emphasize strict scheduling, punctuality, and completing one task at a time, reflecting a linear approach to time management primarily found in Western societies such as the United States and Germany. In contrast, allochronic cultures prioritize relationships and flexibility over rigid time structures, often multitasking and handling interruptions fluidly, common in Latin American, African, and Arab cultures. These key differences impact communication styles, workplace dynamics, and social interactions, highlighting how cultural context shapes perceptions and usage of time.
Impact on Workplace Dynamics
Homochronic cultures prioritize strict schedules and tasks, fostering workplace environments with clear deadlines and predictable workflows that enhance productivity and accountability. Allochronic cultures embrace flexibility and multitasking, encouraging creativity and adaptive problem-solving but sometimes causing challenges in time management and coordination. Understanding these cultural time orientations helps organizations design effective communication strategies and collaboration practices that improve team dynamics and reduce conflicts.
Homochronic vs Allochronic in Global Business
Homochronic cultures prioritize punctuality, linear schedules, and task-oriented communication, which enhances efficiency in global business operations by fostering clear timelines and structured meetings. Allochronic cultures emphasize relationships and multitasking, valuing flexibility over strict adherence to schedules, which can lead to adaptive negotiation styles and long-term partnership building in international markets. Understanding the contrast between homochronic and allochronic time orientations is crucial for multinational companies to develop effective communication strategies and avoid cross-cultural misunderstandings.
Cross-Cultural Communication Challenges
Homochronic cultures prioritize punctuality and sequential task completion, valuing clear schedules and deadlines, while allochronic cultures are more flexible with time and multitasking. These differing approaches to time management often cause misunderstandings in cross-cultural communication, as homochronic individuals may perceive allochronic counterparts as disorganized or disrespectful of time constraints. Effective intercultural communication requires recognizing these temporal orientations and adapting communication styles to bridge expectations around time and task organization.
Strategies for Adapting to Different Time Orientations
Adapting to homochronic time orientation involves prioritizing punctuality, structured schedules, and sequential task completion to enhance efficiency and predictability. In contrast, strategies for allochronic time orientation emphasize flexibility, multitasking, and relationship-building, allowing for a more fluid approach to time management that values social interactions over rigid timelines. Understanding these differences enables effective cross-cultural communication and collaboration by aligning expectations with the preferred temporal frameworks of diverse teams.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Case studies comparing homochronic and allochronic cultures highlight time perception differences impacting workplace communication and productivity. For instance, multinational corporations operating in the US (homochronic) and Latin America (allochronic) demonstrate contrasting scheduling approaches, where strict adherence to deadlines in homochronic settings contrasts with the more flexible, relationship-oriented timelines in allochronic cultures. These real-world examples emphasize the necessity for culturally aware management strategies to optimize collaboration across diverse time orientation frameworks.
Conclusion: Navigating Time Perception in Multicultural Settings
Understanding homochronic and allochronic time orientations is crucial for effective communication in multicultural settings, as homochronic cultures prioritize punctuality and sequential task completion while allochronic cultures emphasize flexibility and multitasking. Recognizing these differences helps prevent misunderstandings and fosters collaboration by aligning expectations regarding time management. Successfully navigating these time perceptions enhances cross-cultural relationships and optimizes productivity in diverse environments.
Homochronic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com