Patrilineal descent traces family lineage through the male line, determining inheritance and social status based on paternal ancestry. This system influences cultural practices, property rights, and family naming conventions across many societies. Discover how patrilineal structures shape your identity and societal roles by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
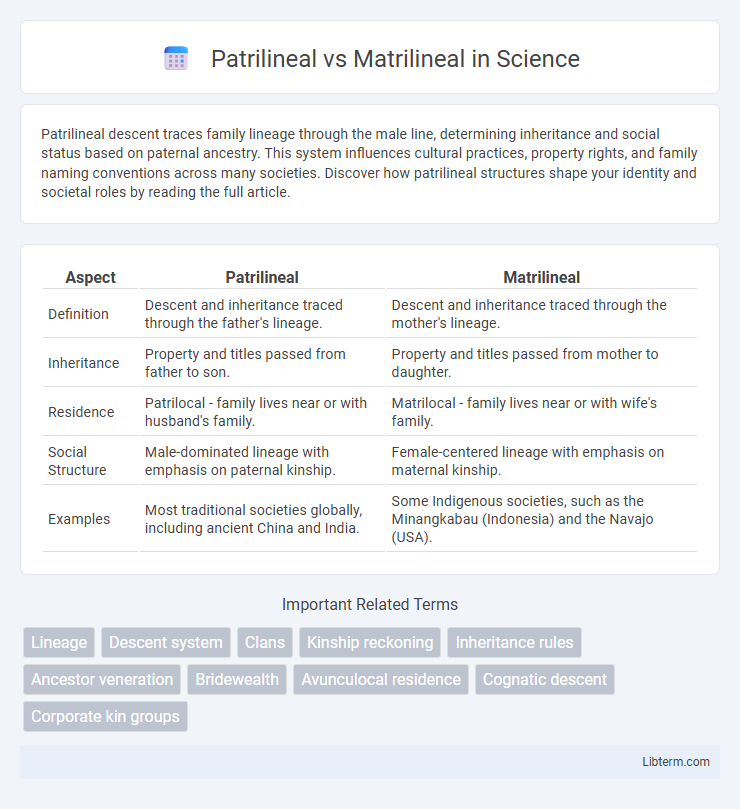
| Aspect | Patrilineal | Matrilineal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent and inheritance traced through the father's lineage. | Descent and inheritance traced through the mother's lineage. |
| Inheritance | Property and titles passed from father to son. | Property and titles passed from mother to daughter. |
| Residence | Patrilocal - family lives near or with husband's family. | Matrilocal - family lives near or with wife's family. |
| Social Structure | Male-dominated lineage with emphasis on paternal kinship. | Female-centered lineage with emphasis on maternal kinship. |
| Examples | Most traditional societies globally, including ancient China and India. | Some Indigenous societies, such as the Minangkabau (Indonesia) and the Navajo (USA). |
Introduction to Lineal Descent Systems
Lineal descent systems classify kinship based on the tracing of ancestry, where patrilineal descent follows the male lineage and matrilineal descent traces through the female lineage. Patrilineal systems emphasize inheritance, family name, and social status passed from father to children, prevalent in societies such as many traditional Asian and African cultures. Matrilineal systems prioritize maternal connections for inheritance and clan membership, commonly found among groups like the Iroquois and the Minangkabau of Indonesia.
Defining Patrilineal Descent
Patrilineal descent is a kinship system where lineage, inheritance, and family identity are traced exclusively through the male line, typically from father to son. This form of descent shapes social structure, property rights, and succession within many cultures, emphasizing male ancestry. Patrilineality often influences clan membership, marital residence, and the transmission of family names, distinguishing it from matrilineal systems that follow the female line.
Understanding Matrilineal Descent
Matrilineal descent traces lineage and inheritance exclusively through the mother's line, emphasizing maternal relatives in family structure and social identity. This system often influences property rights, clan membership, and succession, contrasting with patrilineal descent, which follows the father's lineage. Understanding matrilineal descent requires examining its role in shaping kinship patterns, cultural norms, and gender dynamics within various societies worldwide.
Key Differences Between Patrilineal and Matrilineal Societies
Patrilineal societies trace descent, inheritance, and family lineage through the male line, emphasizing the father's ancestry and male heirs. In contrast, matrilineal societies prioritize the mother's lineage for inheritance, social status, and clan membership, often granting women central roles in family and tribal structures. These key differences influence property rights, residence patterns, and social responsibilities differently between the two systems.
Inheritance Patterns in Patrilineal Cultures
Inheritance patterns in patrilineal cultures prioritize the transfer of property, titles, and family name through the male lineage, ensuring that assets pass from father to son or the nearest male relative. This system reinforces the patriarchal structure by concentrating wealth and social status within the male members of the family, often limiting inheritance rights for women. Patrilineal inheritance is prevalent in societies such as traditional Arab, Jewish, and many Hindu communities, where lineage and descent are traced through the male line.
Property and Wealth Transmission in Matrilineal Communities
In matrilineal communities, property and wealth are transmitted through the female line, ensuring inheritance passes typically from mothers to daughters, which supports the stability of female kin groups. This system often results in women having significant control over family resources and land, contrasting with patrilineal societies where male lineage governs wealth transfer. Such matrilineal inheritance patterns influence social organization, economic roles, and power dynamics by prioritizing maternal kinship ties in property succession.
Gender Roles in Lineal Societies
Patrilineal societies typically emphasize male authority and inheritance through the father's lineage, reinforcing traditional gender roles where men hold dominant positions in family and community decision-making. Matrilineal societies trace descent through the mother's line, often granting women significant social power and inheritance rights, which can lead to more balanced or female-centered gender roles. These differing systems profoundly shape family dynamics, property rights, and leadership structures within lineal societies.
Social Organization and Kinship Structure
Patrilineal social organization traces descent and inheritance through the male line, emphasizing male authority and lineage continuity, often leading to patriarchal kinship structures with strong patrilocal residence patterns. Matrilineal systems, by contrast, define kinship and inheritance through the female line, promoting maternal uncles' roles in lineage authority and frequently supporting matrilocal or avunculocal residence arrangements. These contrasting kinship frameworks profoundly influence social roles, inheritance rights, and familial alliances within different cultural contexts.
Global Examples of Patrilineal and Matrilineal Systems
Patrilineal systems, where lineage and inheritance are traced through the father's line, are predominant in regions such as the Middle East, South Asia, and parts of Africa, exemplified by countries like Saudi Arabia, India, and Nigeria. Matrilineal systems, tracing descent through the mother's line, are observed in societies such as the Khasi in India, the Minangkabau of Indonesia, and the Navajo Nation in the United States. These distinct kinship patterns influence property rights, social organization, and cultural identity within their respective communities.
Modern Shifts in Descent Patterns
Modern shifts in descent patterns reveal an increasing fluidity between patrilineal and matrilineal systems, driven by changing social norms and gender roles. Contemporary societies show trends where inheritance, residence, and lineage affiliations often blend elements from both patrilineal and matrilineal traditions to accommodate evolving family dynamics. Urbanization, globalization, and legal reforms further accelerate the transformation of traditional descent patterns, reflecting a complex interplay between cultural heritage and modern identity.
Patrilineal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com