Gradual changes allow processes to evolve smoothly over time, minimizing disruptions and maximizing adaptation. This approach is often used in technology updates, environmental policies, and learning methodologies to ensure steady progress. Explore the rest of the article to discover how gradual strategies can benefit your projects and daily life.
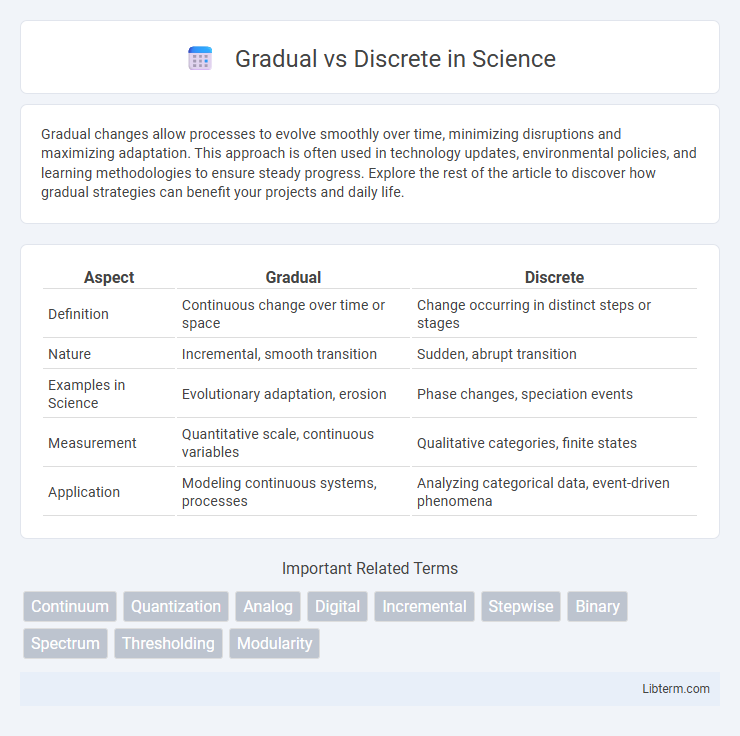
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Gradual | Discrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous change over time or space | Change occurring in distinct steps or stages |
| Nature | Incremental, smooth transition | Sudden, abrupt transition |
| Examples in Science | Evolutionary adaptation, erosion | Phase changes, speciation events |
| Measurement | Quantitative scale, continuous variables | Qualitative categories, finite states |
| Application | Modeling continuous systems, processes | Analyzing categorical data, event-driven phenomena |
Understanding Gradual and Discrete Concepts
Gradual concepts involve continuous changes where variations occur smoothly over a spectrum, such as temperature or color gradients, allowing for nuanced distinctions. Discrete concepts, in contrast, consist of distinct, separate categories without intermediate states, like binary code or species classification, enabling clear-cut differentiation. Understanding the distinction between gradual and discrete concepts is crucial for accurate data analysis, decision-making, and problem-solving across scientific, mathematical, and cognitive domains.
Key Differences Between Gradual and Discrete Processes
Gradual processes involve continuous, incremental changes over time, such as soil erosion or mountain formation, reflecting steady transformation without abrupt shifts. Discrete processes occur in distinct steps or stages, exemplified by cell division or digital signal processing, characterized by clear boundaries between phases. Understanding these key differences aids in selecting appropriate models for environmental studies, biology, and information systems.
Real-World Examples of Gradual vs Discrete Changes
Plant growth exemplifies gradual change, where height and leaf number increase incrementally over time, reflecting continuous development. In contrast, the metamorphosis of a caterpillar into a butterfly represents a discrete change, involving distinct and sudden transformation stages. Urban expansion often occurs gradually through successive construction phases, while volcanic eruptions cause discrete, abrupt alterations to the landscape.
Advantages of Gradual Approaches
Gradual approaches offer enhanced flexibility, allowing continuous adaptation and fine-tuning over time to meet evolving needs. They promote better risk management by enabling incremental implementation, which minimizes potential disruptions and facilitates early detection of issues. This method encourages sustained learning and improvement through iterative feedback loops, resulting in more robust and optimized outcomes.
Benefits of Discrete Methods
Discrete methods offer precise control over each individual step, enabling clear and exact outcomes in digital systems or algorithmic processes. These methods enhance computational efficiency by simplifying complex problems into distinct, manageable units that are easier to analyze and optimize. Their ability to handle sharp changes and non-continuous data makes discrete techniques indispensable in fields such as computer science, operations research, and digital signal processing.
Gradual vs Discrete in Technology and Engineering
Gradual vs discrete approaches in technology and engineering influence system design and signal processing, where gradual changes enable smoother transitions and better adaptability, such as in analog circuits or continuous control systems. Discrete methods, characterized by distinct, separate steps or states, are fundamental in digital electronics, binary data processing, and microcontroller operations. Choosing between gradual and discrete depends on application requirements for precision, responsiveness, and system complexity.
Educational Perspectives: Gradual Learning vs Discrete Steps
Gradual learning in education emphasizes continuous knowledge acquisition and skill development through incremental progress, fostering deeper understanding and long-term retention. Discrete steps involve breaking down content into clearly defined units or modules, allowing focused mastery of specific concepts before advancing. Both approaches optimize cognitive load management and can be strategically integrated to enhance pedagogical effectiveness.
Psychological Impact: Adjusting to Gradual or Discrete Change
Gradual change allows the mind to adapt incrementally, reducing stress and fostering resilience through manageable adjustments over time. Discrete change often triggers acute psychological responses such as anxiety or shock, as individuals confront sudden shifts without prior mental preparation. Understanding these impacts helps tailor support strategies that align with the pace and nature of change, enhancing overall mental well-being.
Choosing Between Gradual and Discrete Solutions
Choosing between gradual and discrete solutions depends on the project's complexity and desired flexibility. Gradual solutions offer continuous adjustment and scalability, ideal for evolving environments, while discrete solutions provide definitive, fixed outcomes suitable for clear-cut applications. Evaluating specific use cases and long-term goals ensures optimal selection for efficiency and effectiveness.
Future Trends: Integrating Gradual and Discrete Models
Future trends in machine learning emphasize integrating gradual and discrete models to enhance adaptability and precision in complex decision-making systems. Hybrid frameworks leverage gradual models' ability to handle uncertainty with discrete models' strengths in clear-cut categorization, facilitating more robust predictive analytics and real-time data processing. This integration promises advancements in fields like autonomous systems, natural language processing, and dynamic resource allocation by optimizing computational efficiency and interpretability.
Gradual Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com