Synchronic analysis examines phenomena at a specific point in time, focusing on structure and relationships without considering historical context. This approach is widely used in linguistics, anthropology, and sociology to understand systems as they function in the present moment. Explore the rest of this article to discover how synchronic methods can deepen your understanding of complex systems.
Table of Comparison
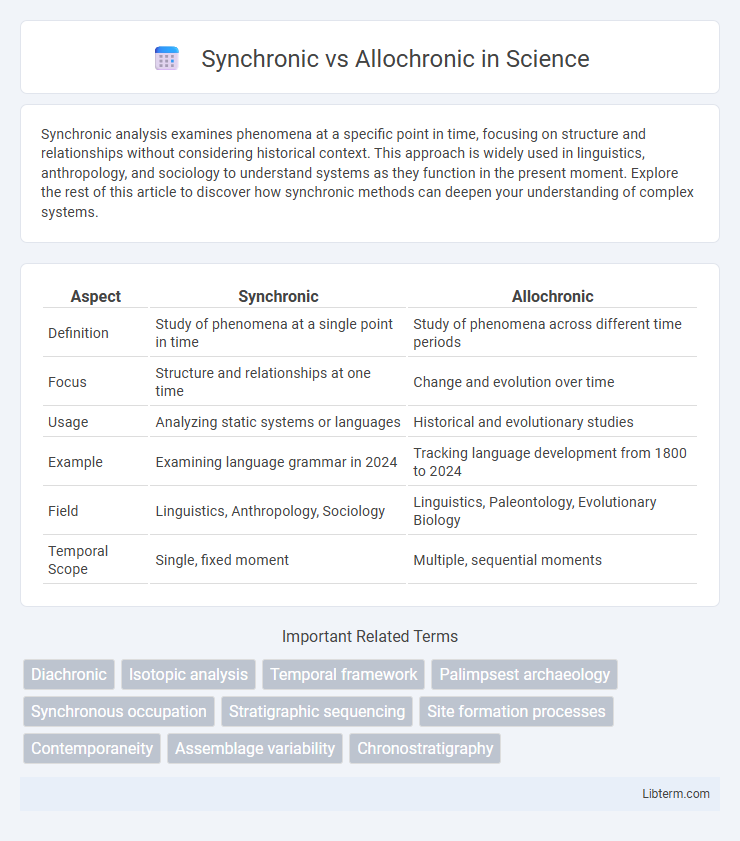
| Aspect | Synchronic | Allochronic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of phenomena at a single point in time | Study of phenomena across different time periods |
| Focus | Structure and relationships at one time | Change and evolution over time |
| Usage | Analyzing static systems or languages | Historical and evolutionary studies |
| Example | Examining language grammar in 2024 | Tracking language development from 1800 to 2024 |
| Field | Linguistics, Anthropology, Sociology | Linguistics, Paleontology, Evolutionary Biology |
| Temporal Scope | Single, fixed moment | Multiple, sequential moments |
Introduction to Synchronic and Allochronic Perspectives
Synchronic perspectives analyze phenomena at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot that captures the structure and relationships within a system without considering historical development. Allochronic perspectives study changes and developments over time, emphasizing temporal dynamics and historical context to understand evolution and transformation. These complementary approaches enable comprehensive analysis by integrating both static snapshots and temporal progression of subjects.
Defining Synchronic Analysis
Synchronic analysis examines a language or cultural phenomenon at a specific point in time, focusing on its structure and usage without considering historical changes. This method enables a detailed understanding of systems as they exist contemporaneously, contrasting with allochronic analysis that studies evolution over periods. Linguists often employ synchronic analysis to identify patterns, rules, and relationships within a language's current state.
Understanding Allochronic Analysis
Allochronic analysis examines changes and developments over time within a specific context, revealing patterns of evolution and transformation. It contrasts with synchronic analysis, which focuses on a specific point or period without considering historical progression. Understanding allochronic analysis enables deeper insights into temporal dynamics and causal factors influencing the subject matter.
Key Differences: Synchronic vs Allochronic
Synchronic analysis examines a subject at a specific point in time, focusing on contemporaneous relationships and structures without considering historical context. Allochronic analysis studies the evolution and changes of a subject across different periods, emphasizing temporal development and historical progression. The key difference lies in synchronic's snapshot approach versus allochronic's diachronic, longitudinal perspective.
Historical Background and Theoretical Origins
Synchronic analysis, rooted in the structural linguistics of Ferdinand de Saussure in the early 20th century, examines languages at a specific point in time without considering historical development. Allochronic analysis, also known as diachronic analysis, traces linguistic changes and evolution over time, drawing from historical linguistics traditions established in the 19th century by scholars like Jacob Grimm and August Schleicher. The theoretical origins of synchronic study emphasize language systems as static structures, whereas allochronic approaches focus on language dynamics and historical transformations.
Applications in Linguistics and Anthropology
Synchronic analysis examines languages or cultures at a specific point in time, enabling linguists to understand structural features and usage patterns without historical context, which is crucial for descriptive linguistics and dialectology. Allochronic analysis studies languages or cultures across different time periods, providing insights into historical language change, language evolution, and cultural transformations, essential for historical linguistics and anthropological research. These complementary approaches facilitate comprehensive understanding of language development and cultural dynamics by combining static snapshots with diachronic perspectives.
Advantages of Synchronic Approaches
Synchronic approaches offer the advantage of analyzing language or phenomena at a specific point in time, enabling precise identification of structural relationships and patterns within that snapshot. This method facilitates a clear understanding of current system states without the complexity of historical changes, making data collection and analysis more straightforward and efficient. Researchers benefit from the ability to compare different elements simultaneously, providing deep insight into the organization and function of the subject under study.
Benefits of Allochronic Analysis
Allochronic analysis provides valuable insights into temporal changes and developmental processes within a given system, allowing researchers to track evolution and identify patterns over time. This method benefits fields like anthropology, linguistics, and ecology by revealing historical dynamics that synchronic analysis may overlook. By examining phenomena across different time periods, allochronic analysis enhances understanding of causality and long-term trends.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Perspective
Synchronic approaches face challenges in capturing temporal changes, often criticized for ignoring historical context and evolution within linguistic or cultural phenomena. Allochronic perspectives struggle with data continuity and comparability, as they rely on diachronic evidence that may be fragmented or inconsistent over time. Both perspectives contend with limitations in fully explaining dynamic systems without integrating insights from the other.
Synchronic and Allochronic: Future Directions and Research
Synchronic and allochronic approaches offer distinct frameworks for analyzing linguistic phenomena either at a single point in time or across historical periods, respectively. Future research prioritizes integrating computational methods and big data analytics to enhance synchronic analysis, enabling real-time linguistic modeling and sociolinguistic variation tracking. Allochronic studies aim to leverage diachronic corpora and machine learning to reconstruct language evolution patterns, informing theoretical linguistics and historical language change predictions.
Synchronic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com