Graphemes are the smallest units of writing that represent sounds in a language, serving as the building blocks of written communication. Understanding graphemes is essential for decoding words and developing strong reading skills. Discover how graphemes influence language structure and improve your literacy by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
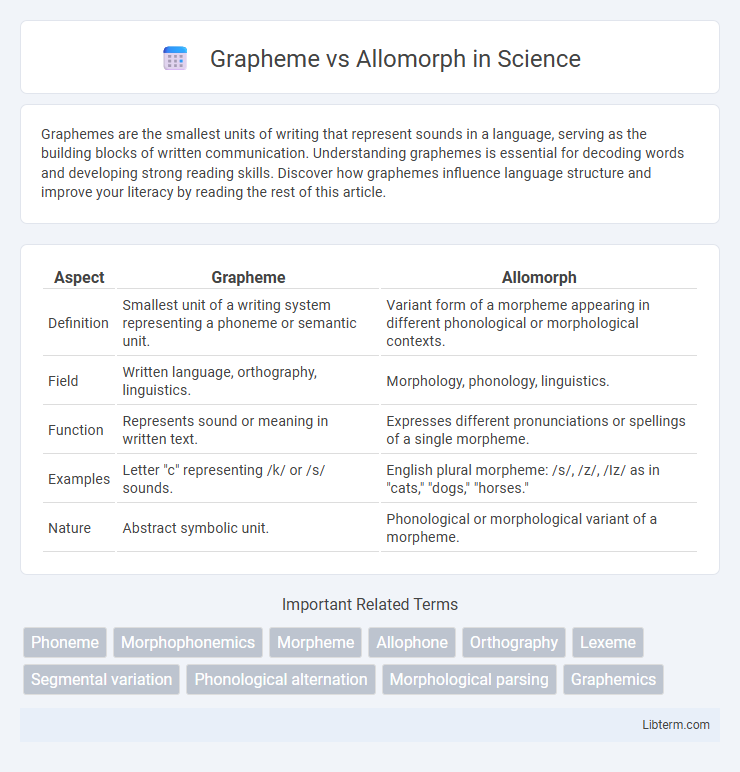
| Aspect | Grapheme | Allomorph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smallest unit of a writing system representing a phoneme or semantic unit. | Variant form of a morpheme appearing in different phonological or morphological contexts. |
| Field | Written language, orthography, linguistics. | Morphology, phonology, linguistics. |
| Function | Represents sound or meaning in written text. | Expresses different pronunciations or spellings of a single morpheme. |
| Examples | Letter "c" representing /k/ or /s/ sounds. | English plural morpheme: /s/, /z/, /Iz/ as in "cats," "dogs," "horses." |
| Nature | Abstract symbolic unit. | Phonological or morphological variant of a morpheme. |
Introduction to Graphemes and Allomorphs
Graphemes are the smallest units of written language that represent phonemes, serving as fundamental symbols in alphabets and writing systems. Allomorphs are variant forms of a morpheme that differ in pronunciation or spelling depending on linguistic context, yet they share the same semantic function. Understanding graphemes and allomorphs is essential for analyzing the relationship between written symbols and morphemic variations in language structure.
Defining Grapheme: The Building Block of Writing
A grapheme is the smallest unit of writing that represents a phoneme or meaningful sound in a language, such as letters in the English alphabet. It serves as a fundamental building block in orthographic systems, encoding spoken language into visual symbols for reading and writing. Unlike allomorphs, which are variants of a morpheme affecting pronunciation, graphemes function as consistent graphical representations independent of phonetic variation.
Understanding Allomorph: The Morphological Variant
Allomorphs are morphological variants of a single morpheme that differ in phonetic form but retain the same semantic function, such as the plural morpheme expressed as /s/, /z/, or /Iz/ in "cats," "dogs," and "horses." Graphemes represent individual letters or letter combinations in a writing system, while allomorphs pertain to spoken language morphology. Understanding allomorphs involves recognizing how context influences morpheme pronunciation without changing meaning, essential for linguistic analysis and language learning.
Key Differences Between Grapheme and Allomorph
A grapheme is the smallest unit of a writing system representing a phoneme, while an allomorph is a phonetic variant of a morpheme that differs in pronunciation without changing meaning. Graphemes are visual symbols such as letters or characters, whereas allomorphs occur in speech as different pronunciations of the same morpheme depending on phonological or morphological context. Understanding the key differences involves recognizing that graphemes belong to orthography, while allomorphs pertain to phonology and morphology in linguistics.
Representation in Written vs Spoken Language
Graphemes are the smallest units of written language that represent sounds or phonemes, serving as visual symbols in alphabets and scripts. Allomorphs are variants of a morpheme that differ in pronunciation but convey the same semantic meaning, occurring in spoken language as phonetically distinct forms. While graphemes correspond to fixed visual representations, allomorphs reflect the dynamic and context-dependent nature of spoken word formation and pronunciation.
Linguistic Functions of Grapheme and Allomorph
Graphemes serve as the smallest units in a writing system, representing phonemes and enabling the visual encoding of language for effective communication and literacy development. Allomorphs function as variant forms of a morpheme that manifest depending on phonological or morphological context, aiding in the nuanced expression of grammatical relationships and meaning in spoken language. The linguistic function of graphemes centers on consistent symbol representation, while allomorphs contribute to morphological flexibility and phonetic adaptation within a language's syntactic structure.
Examples of Graphemes in Various Languages
Graphemes serve as the smallest units of writing in languages, representing phonemes through symbols such as letters or characters. For example, the English alphabet uses graphemes like "c," "h," and the digraph "ch," while the Japanese writing system employs kanji characters like "Shan " (yama) and kana scripts such as "ka" (ka). Understanding graphemes across diverse linguistic systems, including Arabic script's letters like "b" (ba) and Devanagari's letters like "k" (ka), highlights their role in encoding phonological information visually.
Illustrative Allomorphs Across Languages
Illustrative allomorphs vary significantly across languages, reflecting diverse phonological and morphological systems. For example, the English plural morpheme appears as /s/, /z/, or /Iz/, depending on phonetic context, while in Arabic, a single root may manifest multiple allomorphic patterns through vowel changes and affixation. These variations contrast with graphemes, which represent consistent orthographic units, highlighting the complexity of allomorphy in spoken language morphology.
Importance in Linguistic Analysis and Literacy
Graphemes represent the smallest units of written language, critical for decoding and literacy development, while allomorphs are variant forms of morphemes affecting meaning and grammatical function. Understanding grapheme distinctions enables accurate phoneme-grapheme mapping essential for reading skills, whereas analyzing allomorphs aids in morphological awareness and vocabulary acquisition. Linguistic analysis leveraging both graphemes and allomorphs improves comprehension of language structure and enhances educational strategies for literacy instruction.
Conclusion: Grapheme vs Allomorph in Language Structure
Graphemes function as the smallest units of written language, representing specific phonemes or sounds, whereas allomorphs are variations of a single morpheme that differ in pronunciation or form without changing meaning. The distinction highlights graphemes' role in orthographic representation compared to allomorphs' role in morphological variation within the spoken language. Understanding both concepts is essential for analyzing language structure, as graphemes anchor phoneme-grapheme correspondence and allomorphs illuminate morphological flexibility and phonological context.
Grapheme Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com