Essential skills and knowledge form the foundation for success in any field, ensuring you can navigate challenges effectively and seize opportunities. Mastering these core competencies boosts confidence and opens doors to advanced learning and career growth. Explore the rest of the article to discover how to develop and apply essential qualities in your personal and professional life.
Table of Comparison
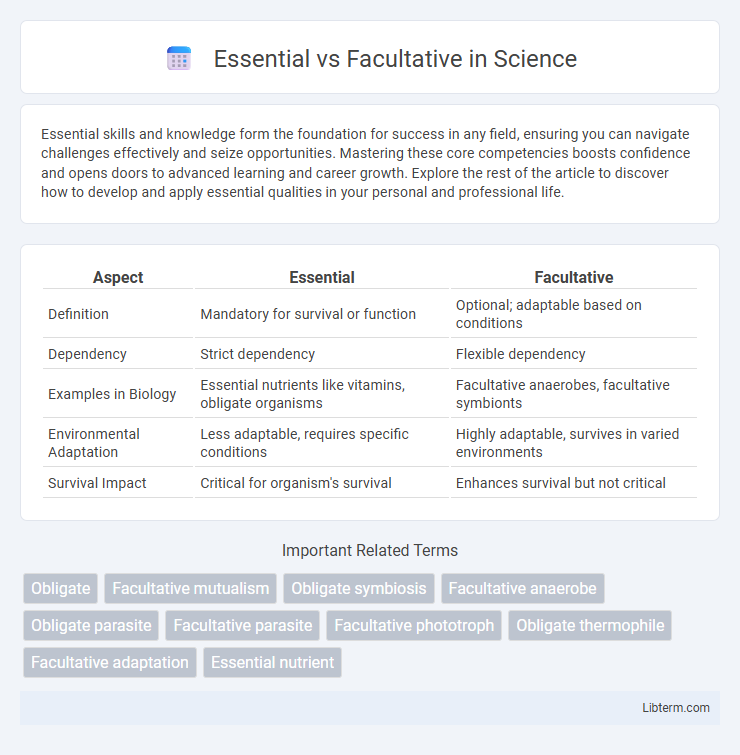
| Aspect | Essential | Facultative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mandatory for survival or function | Optional; adaptable based on conditions |
| Dependency | Strict dependency | Flexible dependency |
| Examples in Biology | Essential nutrients like vitamins, obligate organisms | Facultative anaerobes, facultative symbionts |
| Environmental Adaptation | Less adaptable, requires specific conditions | Highly adaptable, survives in varied environments |
| Survival Impact | Critical for organism's survival | Enhances survival but not critical |
Introduction to Essential and Facultative Concepts
Essential concepts refer to elements or conditions strictly required for the survival, growth, or functionality of an organism or system, such as essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals necessary for human health. Facultative concepts describe those elements or organisms that can adapt to varying conditions but are not strictly necessary, for example, facultative anaerobes that can survive with or without oxygen. Understanding the distinction between essential and facultative types is critical in biology and environmental science for assessing adaptability and survival strategies.
Defining Essential: Core Characteristics
Essential traits represent the core characteristics indispensable for an organism's survival and reproduction, such as fundamental metabolic functions and genetic codes. These traits are conserved across species and remain stable despite environmental variations, emphasizing their critical role in maintaining biological integrity. In contrast, facultative traits exhibit flexibility, adapting to environmental conditions rather than defining the organism's basic identity.
What Does Facultative Mean?
Facultative refers to organisms or behaviors that are flexible and can adapt to different conditions but are not strictly necessary for survival or function. In biology, facultative traits allow species to switch between modes of feeding, reproduction, or habitat preference depending on environmental factors. This adaptability contrasts with essential characteristics, which are mandatory for an organism's existence.
Key Differences: Essential vs Facultative
Essential organisms require specific nutrients or environmental conditions to survive, such as obligate aerobes needing oxygen for growth. Facultative organisms can adapt to varying conditions, thriving with or without certain factors, like facultative anaerobes that grow in both oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor environments. The key difference lies in reliance: essential organisms depend strictly on certain elements, while facultative organisms exhibit metabolic flexibility.
Biological Contexts: Essential and Facultative Examples
Essential nutrients, such as vitamins and amino acids, are critical for an organism's survival because they cannot be synthesized internally and must be obtained from the environment, exemplified by humans requiring essential amino acids like lysine. Facultative traits or behaviors, such as facultative anaerobic bacteria switching between aerobic and anaerobic respiration, allow organisms to adapt flexibly to changing environmental conditions without being strictly dependent on one mode of metabolism. In biological contexts, essential genes encode fundamental functions necessary for cell viability, whereas facultative genes provide adaptability, like facultative parasitism observed in certain nematodes that can survive independently or as parasites.
Importance in Microbiology and Ecology
Essential and facultative organisms play crucial roles in microbiology and ecology by influencing nutrient cycles and ecosystem dynamics. Essential microbes are indispensable for specific biochemical processes such as nitrogen fixation or cellulose degradation, supporting ecosystem productivity and stability. Facultative organisms exhibit metabolic flexibility, allowing them to adapt to fluctuating environmental conditions and contribute to microbial diversity and resilience.
Industrial and Medical Applications
Essential microorganisms play a critical role in industrial applications by driving key biochemical processes like fermentation in pharmaceutical manufacturing, enhancing the production of antibiotics and vaccines. Facultative organisms offer flexibility in medical applications, adapting to both aerobic and anaerobic environments, which is vital for bioremediation and infection control strategies. The selective use of essential and facultative microbes optimizes efficiency and efficacy in producing medical compounds and maintaining industrial bioprocess stability.
Evolutionary Implications
Essential genes are critical for an organism's survival and are highly conserved across species, indicating their fundamental evolutionary importance. Facultative genes, which are non-essential under normal conditions, provide adaptive advantages by enabling organisms to respond to environmental changes and stressors, contributing to evolutionary flexibility. The balance between essential and facultative genes shapes evolutionary trajectories by maintaining core biological functions while allowing genetic innovation and adaptation.
Case Studies: Essential and Facultative Organisms
Case studies of essential and facultative organisms highlight distinct survival dependencies, where essential organisms require specific environmental factors or symbiotic relationships for growth, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria in legume roots. Facultative organisms demonstrate metabolic flexibility, thriving under varied conditions, exemplified by facultative anaerobes like Escherichia coli that grow with or without oxygen. Comparative analysis of microbial behavior in different habitats reveals critical insights into ecological adaptation and biotechnological applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Essential and Facultative Approaches
Choosing between essential and facultative approaches depends on the specific ecological or biological context, where essential methods are mandatory for survival or function, and facultative ones offer flexibility and adaptability. Essential strategies ensure baseline stability and consistent outcomes, while facultative approaches enable responsiveness to environmental variability, enhancing resilience. Balancing both approaches can optimize overall effectiveness by combining reliability with adaptive potential.
Essential Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com