Empirical evidence relies on observation and experimentation to validate theories and claims, making it a cornerstone of scientific research. By focusing on measurable and reproducible data, empirical methods ensure that conclusions are grounded in real-world experience rather than speculation. Discover how empirical approaches can strengthen your understanding by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
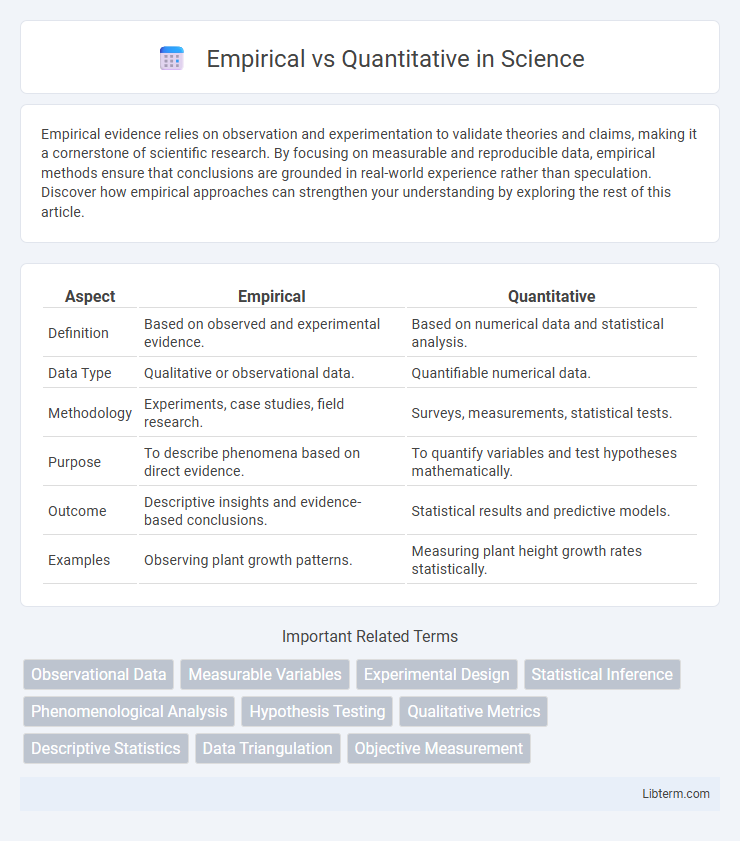
| Aspect | Empirical | Quantitative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Based on observed and experimental evidence. | Based on numerical data and statistical analysis. |
| Data Type | Qualitative or observational data. | Quantifiable numerical data. |
| Methodology | Experiments, case studies, field research. | Surveys, measurements, statistical tests. |
| Purpose | To describe phenomena based on direct evidence. | To quantify variables and test hypotheses mathematically. |
| Outcome | Descriptive insights and evidence-based conclusions. | Statistical results and predictive models. |
| Examples | Observing plant growth patterns. | Measuring plant height growth rates statistically. |
Introduction to Empirical and Quantitative Research
Empirical research relies on observed and measured phenomena, gathering data through direct or indirect observation to generate knowledge. Quantitative research emphasizes numerical data and statistical analysis to quantify relationships and test hypotheses in a structured manner. Both methodologies are foundational in scientific inquiry, with empirical research providing the basis for data collection and quantitative research focusing on data measurement and analysis.
Defining Empirical Research
Empirical research involves collecting data through direct or indirect observation and experimentation to generate evidence-based conclusions about phenomena. It relies on systematic methods such as surveys, case studies, and fieldwork to gather qualitative and quantitative information that reflects real-world experiences. By focusing on actual data rather than theory alone, empirical research validates hypotheses through measurable and observable outcomes.
Understanding Quantitative Research
Quantitative research employs numerical data and statistical methods to test hypotheses and measure variables, ensuring precise and objective analysis. It relies on structured instruments like surveys and experiments to gather quantifiable evidence that supports generalizable conclusions. Understanding quantitative research enhances the ability to interpret data trends, validate theories, and support decision-making with empirical rigor.
Key Differences Between Empirical and Quantitative Approaches
Empirical research relies on observation and experience to gather data, emphasizing qualitative insights and real-world evidence. Quantitative research focuses on numerical data, employing statistical methods to measure and analyze variables systematically. The key difference lies in empirical approaches prioritizing observable phenomena, while quantitative techniques emphasize measurable and quantifiable data for hypothesis testing.
Methodologies Used in Empirical Studies
Empirical studies primarily use methodologies centered on direct observation, experimentation, and data collection from real-world contexts to derive insights and validate hypotheses. Common methods include case studies, field experiments, ethnography, and longitudinal observations, which emphasize qualitative data and contextual understanding. This approach contrasts with purely quantitative methods by integrating experiential data to complement statistical analysis, enhancing the richness and applicability of research findings.
Quantitative Research Methods and Tools
Quantitative research methods involve the systematic collection and analysis of numerical data to identify patterns, test hypotheses, and make predictions. Tools commonly used include surveys with structured questionnaires, statistical software like SPSS or R for data analysis, and experiments that manipulate variables to measure outcomes. Emphasizing objectivity and replicability, quantitative research provides measurable evidence to support decision-making across various disciplines.
Data Collection Techniques: Empirical vs Quantitative
Empirical data collection techniques involve direct observation, experimentation, and qualitative assessments to gather information based on sensory experience. Quantitative data collection relies on structured methods such as surveys, questionnaires, and statistical measurements to acquire numerical data for analysis. Both approaches emphasize accuracy but differ in their focus on subjective insight versus objective quantification.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Approach
Empirical research relies on direct observation and experimentation, offering strengths such as real-world data collection and context-specific insights, but it faces limitations like potential observer bias and challenges in replicability. Quantitative research excels in statistical analysis and generalizability through numerical data, providing precise measurement and hypothesis testing, yet it may overlook nuanced variables and lack depth in understanding complex phenomena. Balancing empirical richness and quantitative rigor enables comprehensive analysis but requires careful consideration of methodological constraints inherent to each approach.
Practical Applications Across Various Fields
Empirical research relies on observation and experimentation to gather data, making it essential in fields like psychology and medicine for developing evidence-based treatments. Quantitative methods, using statistical and numerical analysis, are critical in economics, finance, and engineering to model trends and predict outcomes accurately. Integrating empirical data with quantitative techniques enhances decision-making and innovation across disciplines such as social sciences, healthcare, and technology.
Choosing the Right Research Method for Your Study
Selecting the appropriate research method hinges on the study's objectives and data type; empirical research relies on direct observation or experience, ideal for qualitative insights and real-world contexts. Quantitative research emphasizes numerical data and statistical analysis, suited for hypothesis testing and measuring variables. Matching your research questions with these characteristics ensures robust, valid, and actionable results.
Empirical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com