A syllable is a fundamental unit of pronunciation consisting of a vowel sound, with or without surrounding consonants, that forms the building blocks of words. Understanding syllables helps improve your reading, writing, and pronunciation skills by breaking down complex words into manageable parts. Explore the rest of this article to learn how syllables influence language and communication.
Table of Comparison
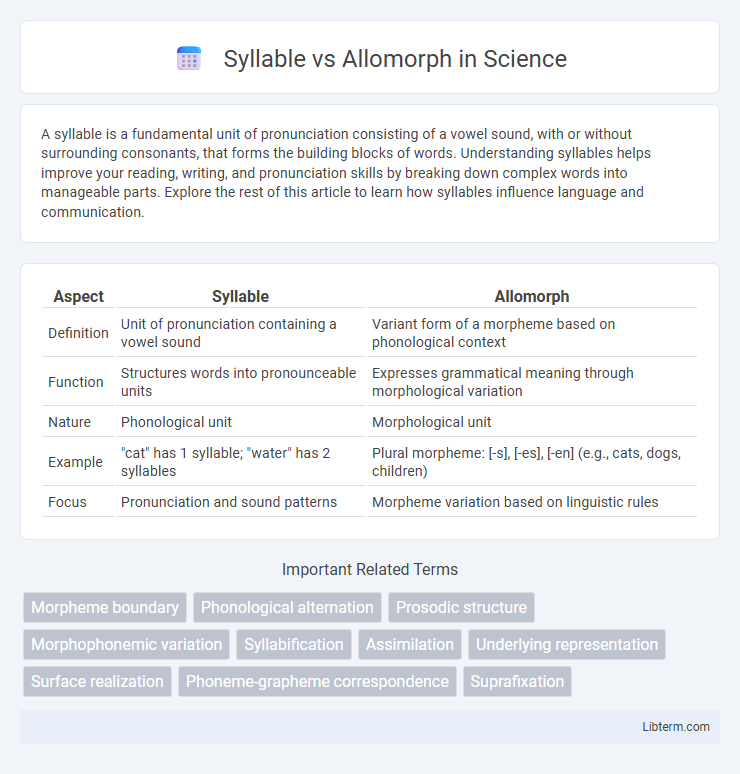
| Aspect | Syllable | Allomorph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unit of pronunciation containing a vowel sound | Variant form of a morpheme based on phonological context |
| Function | Structures words into pronounceable units | Expresses grammatical meaning through morphological variation |
| Nature | Phonological unit | Morphological unit |
| Example | "cat" has 1 syllable; "water" has 2 syllables | Plural morpheme: [-s], [-es], [-en] (e.g., cats, dogs, children) |
| Focus | Pronunciation and sound patterns | Morpheme variation based on linguistic rules |
Introduction to Syllables and Allomorphs
Syllables serve as fundamental units of sound in phonology, typically consisting of a vowel sound with optional surrounding consonants, shaping the rhythm and structure of words. Allomorphs represent the variant forms of a morpheme that appear in different linguistic environments without altering the core meaning, such as the plural morpheme expressed as /s/, /z/, or /Iz/ in English. Understanding syllables aids in distinguishing phonological patterns, while recognizing allomorphs is crucial for analyzing morphological variations in language.
Defining Syllable: Structure and Function
A syllable is a fundamental unit of speech sound consisting of a single vowel sound or vowel nucleus, often accompanied by surrounding consonants, forming the building blocks of words. Its structure typically involves an onset (optional consonants), a nucleus (vowel), and a coda (optional consonants), which together influence the rhythm, stress, and pronunciation in language. Unlike allomorphs, which are variations of a morpheme with semantic or grammatical differences, syllables primarily serve phonological functions related to speech organization and acoustic patterning.
Understanding Allomorph: Morphological Variations
Allomorphs represent morphological variations of a single morpheme, differing in phonological form without altering meaning, such as the English plural morpheme -s appearing as /s/, /z/, or /Iz/. Unlike syllables, which are phonetic units of speech sound organization, allomorphs are rooted in morphophonemic rules governing when specific variant forms occur. Understanding allomorphy is essential for analyzing word formation patterns and morphosyntactic alignment within natural languages.
Key Differences Between Syllable and Allomorph
Syllables are units of pronunciation containing a vowel sound, whereas allomorphs are variant forms of a morpheme that appear in different contexts without changing meaning. Syllables function as phonological building blocks of words, while allomorphs represent morphological variations depending on phonetic or grammatical conditions. The key difference lies in syllables shaping word rhythm and sound structure, whereas allomorphs influence word formation and inflection.
Phonological Aspects of Syllables
Syllables are phonological units consisting of a nucleus, typically a vowel, and optional onset and coda segments, crucial for organizing speech sounds. Allomorphs are morphological variants of a morpheme whose phonological form varies depending on the syllabic environment or neighboring phonemes. The phonological aspects of syllables influence allomorphic variation by conditioning the realization of morphemes to maintain phonotactic constraints and syllable structure.
Morphological Aspects of Allomorphs
Allomorphs represent morphological variations of a single morpheme, differing in phonological form but maintaining consistent semantic meaning, unlike syllables which are simply units of sound without inherent morphological significance. The morphological aspect of allomorphs involves their distribution governed by phonological, morphological, or lexical conditions, reflecting how morphemes adapt to different linguistic environments. Understanding allomorphic variation is crucial for analyzing morphophonemic alternations and the structural organization of languages.
Examples of Syllables in English
Syllables in English serve as fundamental units of pronunciation, exemplified by words like "cat" (one syllable), "banana" (three syllables: ba-na-na), and "strength" (one syllable despite its complexity). Allomorphs represent variations of a morpheme, as seen in the plural morpheme with pronunciations /s/ in "cats," /z/ in "dogs," and /Iz/ in "horses." Understanding syllables aids phonetic analysis, while allomorphs highlight morphological diversity within English word formation.
Examples of Allomorphs in English
Allomorphs are variants of a morpheme that differ in pronunciation but share the same meaning, such as the plural suffix in English, which appears as /s/ in "cats," /z/ in "dogs," and /Iz/ in "horses." Another example includes the past tense morpheme, pronounced as /t/ in "walked," /d/ in "played," and /Id/ in "wanted." These phonetic variations depend on the phonological context and demonstrate how morphemes adapt their form without altering their semantic function.
Role in Linguistic Analysis
Syllables serve as fundamental units of phonological structure, aiding in the analysis of speech rhythm, stress patterns, and phonotactic rules. Allomorphs, as variant forms of a morpheme, provide insight into morphological alternations and grammatical variations within a language. Examining syllables clarifies sound organization, while analyzing allomorphs reveals underlying morphological rules and semantic nuances.
Summary: Syllable vs Allomorph
A syllable is a unit of pronunciation containing a vowel sound, often with surrounding consonants, structuring spoken language into rhythmical segments. An allomorph represents the variant forms of a morpheme that appear in different phonological or morphological contexts without changing meaning. While syllables structure phonetic patterns, allomorphs illustrate morphological variation in word formation within linguistics.
Syllable Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com