Simultaneous actions occur when two or more events happen at the exact same time, creating a dynamic interplay that can significantly impact outcomes. Understanding the concept of simultaneity is crucial in fields like physics, linguistics, and project management to coordinate and analyze concurrent activities effectively. Dive into the rest of the article to explore how simultaneous processes influence various aspects of your daily life and work.
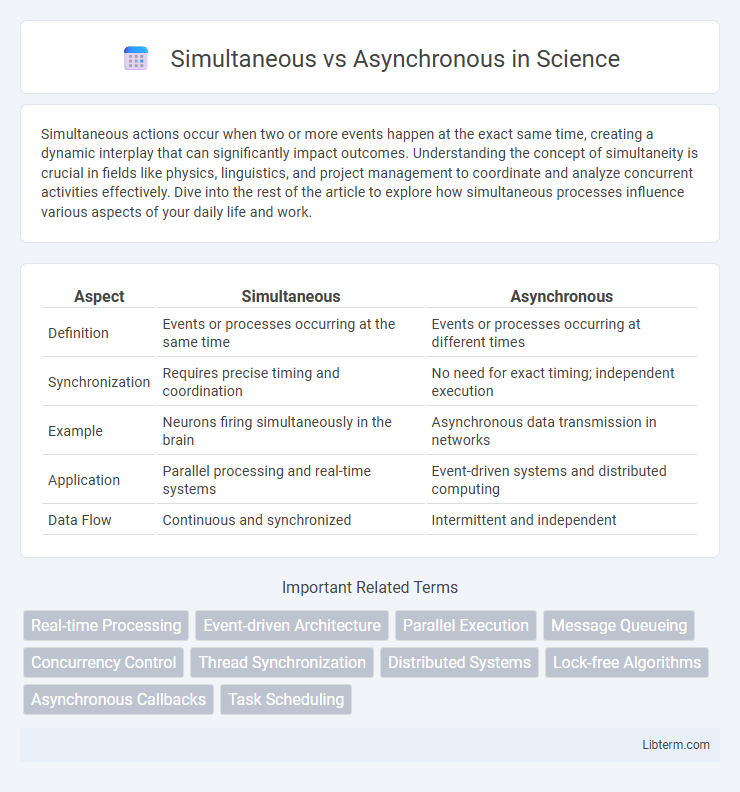
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Simultaneous | Asynchronous |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Events or processes occurring at the same time | Events or processes occurring at different times |
| Synchronization | Requires precise timing and coordination | No need for exact timing; independent execution |
| Example | Neurons firing simultaneously in the brain | Asynchronous data transmission in networks |
| Application | Parallel processing and real-time systems | Event-driven systems and distributed computing |
| Data Flow | Continuous and synchronized | Intermittent and independent |
Introduction to Simultaneous and Asynchronous Processes
Simultaneous processes occur when multiple tasks are executed at the same time, maximizing resource utilization and enabling parallelism within computing environments. Asynchronous processes allow tasks to operate independently without waiting for other tasks to complete, improving system responsiveness and throughput. Understanding the distinction between simultaneous and asynchronous processing is critical in optimizing performance in concurrent and distributed systems.
Definition of Simultaneous Communication
Simultaneous communication refers to the exchange of information where all participants are actively engaged at the same time, enabling real-time interaction and immediate feedback. This communication style is essential in scenarios like video conferences, live chats, and phone calls, where synchronicity enhances understanding and collaboration. Unlike asynchronous communication, which involves delayed responses, simultaneous communication demands continuous attention and instant response, facilitating dynamic and fluid conversations.
Understanding Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication enables participants to engage and respond at their convenience, enhancing flexibility across distributed teams and remote work environments. This method reduces the pressure of immediate replies, supporting deeper thought and more deliberate information exchange through tools like email, messaging apps, and project management platforms. Understanding asynchronous communication is critical for optimizing collaboration efficiency, minimizing interruptions, and balancing diverse time zones in global organizations.
Key Differences Between Simultaneous and Asynchronous
Simultaneous communication occurs in real-time, allowing immediate interaction, while asynchronous communication happens with time delays, enabling participants to respond at their convenience. Key differences include the immediacy of feedback, with simultaneous interactions fostering dynamic, spontaneous exchanges, whereas asynchronous methods support flexibility and thoughtful responses. Tools like video calls exemplify simultaneous communication, whereas emails and message boards are common asynchronous platforms.
Advantages of Simultaneous Interaction
Simultaneous interaction enables real-time communication, promoting immediate feedback and collaboration that enhances problem-solving and decision-making efficiency. It reduces misunderstandings by allowing participants to clarify points instantly during discussions or brainstorming sessions. This mode of interaction fosters stronger engagement and rapport, crucial for teamwork and dynamic environments such as video conferencing and live chat platforms.
Benefits of Asynchronous Methods
Asynchronous methods enhance productivity by allowing tasks to be completed independently without waiting for immediate responses, leading to greater flexibility in time management. They support diverse work schedules and remote collaboration by enabling team members across different time zones to contribute effectively. This approach reduces interruptions and improves focus, resulting in higher-quality outputs and more efficient communication workflows.
Challenges of Simultaneous Approaches
Simultaneous approaches face significant challenges such as synchronization complexity, where coordinating concurrent processes demands precise timing and resource allocation to avoid conflicts and data inconsistency. These methods often require high computational overhead to manage real-time interactions, leading to scalability issues in large systems. Moreover, debugging and error detection become more difficult due to intertwined execution flows and non-deterministic outcomes.
Drawbacks of Asynchronous Solutions
Asynchronous solutions often face challenges such as increased complexity in error handling and debugging due to non-linear execution flows. They can lead to unpredictable latency and resource consumption spikes, impacting system performance and user experience. Moreover, asynchronous communication may cause difficulties in data consistency and synchronization across distributed systems.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Choosing between simultaneous and asynchronous communication depends on your project's urgency and collaboration style. Simultaneous communication offers real-time interaction, ideal for tasks requiring immediate feedback and dynamic discussions. Asynchronous methods provide flexibility, enabling participants to contribute at their convenience, which suits dispersed teams and tasks that benefit from thoughtful responses.
Future Trends in Simultaneous vs. Asynchronous Technologies
Future trends in simultaneous and asynchronous technologies highlight increasing integration with artificial intelligence to enhance real-time collaboration and automated task management. Edge computing advancements facilitate low-latency synchronous interactions, while asynchronous systems benefit from improved data synchronization and offline capabilities. The growing demand for hybrid work environments accelerates innovation in seamless transitions between simultaneous and asynchronous communication modes.
Simultaneous Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com