Animate brings life to static images and characters through dynamic movement and storytelling techniques. Mastering animation enhances your ability to engage audiences across films, games, and digital media with compelling visuals. Discover how to unlock creative potential and elevate your projects by exploring the principles and tools detailed in this article.
Table of Comparison
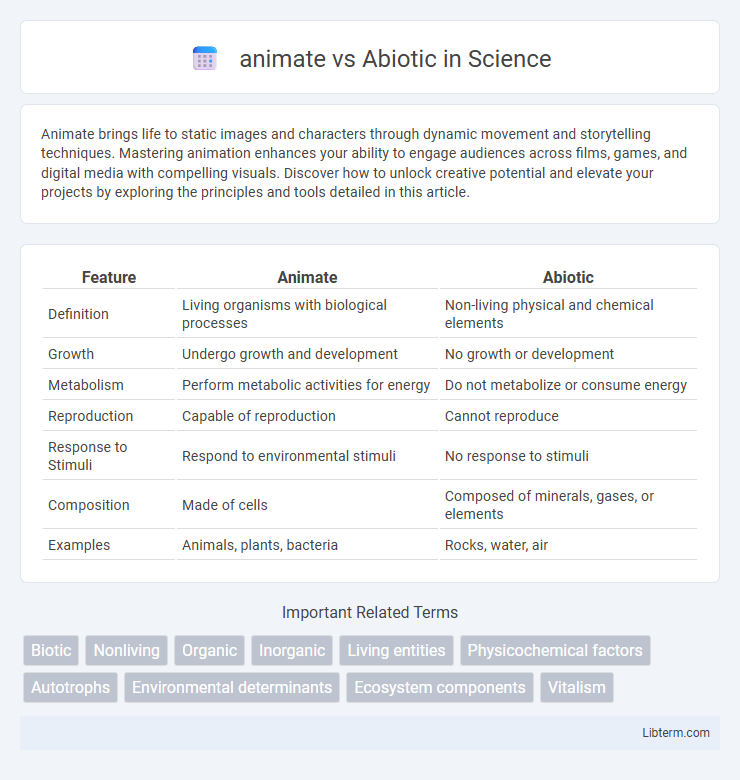
| Feature | Animate | Abiotic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Living organisms with biological processes | Non-living physical and chemical elements |
| Growth | Undergo growth and development | No growth or development |
| Metabolism | Perform metabolic activities for energy | Do not metabolize or consume energy |
| Reproduction | Capable of reproduction | Cannot reproduce |
| Response to Stimuli | Respond to environmental stimuli | No response to stimuli |
| Composition | Made of cells | Composed of minerals, gases, or elements |
| Examples | Animals, plants, bacteria | Rocks, water, air |
Understanding Animate and Abiotic: Key Definitions
Animate entities refer to living organisms characterized by biological processes such as growth, reproduction, and response to stimuli, encompassing animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms. Abiotic elements consist of non-living components of the environment, including minerals, water, air, temperature, and sunlight, which influence ecosystems and biological activity. Understanding the distinction between animate and abiotic factors is essential for ecological studies, environmental science, and the analysis of life-supporting systems.
Core Differences Between Animate and Abiotic Factors
Animate factors encompass living organisms such as plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms that interact with their environment through processes like reproduction, metabolism, and adaptation. Abiotic factors include non-living physical and chemical components like temperature, sunlight, water, soil, and minerals that shape ecosystems by influencing living conditions and resource availability. Core differences lie in animate factors exhibiting biological activity and life functions, whereas abiotic factors remain inanimate and affect habitats without exhibiting life processes.
Types of Animate Components in an Ecosystem
Animate components in an ecosystem include producers, consumers, and decomposers, each playing a crucial role in energy flow and nutrient cycling. Producers like plants and algae convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, forming the ecosystem's foundation. Consumers, ranging from herbivores to carnivores, rely on other organisms for food, while decomposers such as fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the environment.
Examples of Abiotic Elements in Nature
Abiotic elements in nature include non-living components such as sunlight, temperature, water, soil, and atmospheric gases that influence ecosystems without possessing life. Minerals like quartz, rocks, and nutrients in the soil are essential abiotic factors supporting plant growth and shaping habitats. Climate elements such as wind patterns and precipitation levels regulate the distribution and behavior of living organisms within ecosystems.
Importance of Animate Factors in Biological Systems
Animate factors, including animals and microorganisms, play a crucial role in biological systems by facilitating processes such as pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient cycling. These living organisms contribute to ecosystem stability and productivity through their interactions with plants and abiotic elements like soil and climate. The dynamic influence of animate factors ensures biodiversity maintenance and supports complex food webs essential for ecological balance.
Abiotic Influences on Living Organisms
Abiotic factors such as temperature, water availability, sunlight, and soil composition play a crucial role in shaping the distribution, behavior, and survival of living organisms. These non-living environmental elements influence metabolic rates, reproductive cycles, and habitat suitability, directly affecting ecosystem dynamics. Understanding abiotic influences is essential for studying species adaptation and ecological balance.
Interactions Between Animate and Abiotic Elements
Interactions between animate organisms and abiotic elements are crucial for ecosystem functionality, as living beings rely on non-living factors like sunlight, water, and soil nutrients for survival and growth. Plants absorb sunlight and minerals from soil, while animals depend on water and atmospheric oxygen, highlighting the interdependence between biotic and abiotic components. These dynamic interactions regulate energy flow, nutrient cycling, and habitat formation, sustaining biodiversity and environmental balance.
Role of Animate and Abiotic Factors in Ecosystem Balance
Animate factors, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, actively regulate nutrient cycles, energy flow, and population control, ensuring ecosystem stability and resilience. Abiotic factors such as sunlight, temperature, water, and soil composition provide the essential physical environment that supports life processes and influences species distribution. Together, the interplay between animate and abiotic components maintains ecosystem balance by facilitating biological interactions and sustaining habitat conditions.
Effects of Environmental Change on Animate and Abiotic Components
Environmental changes like temperature shifts, pollution, and habitat destruction directly alter animate components by affecting species distribution, reproduction, and survival rates. Abiotic components such as soil quality, water chemistry, and atmospheric conditions experience shifts in nutrient cycling and physical properties due to these disturbances. The interconnectedness between animate and abiotic factors means changes in one can cascade, impacting ecosystem stability and resilience.
Conclusion: Balancing Animate and Abiotic in Nature
Maintaining a balance between animate and abiotic components is essential for ecosystem stability and biodiversity preservation. Animate factors like plants and animals interact closely with abiotic elements such as soil, water, and climate to regulate nutrient cycles and energy flow. Disruptions in either domain can lead to ecological imbalance, highlighting the need for integrated conservation strategies that consider both living organisms and environmental conditions.
animate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com