Diachronic analysis examines how language, culture, or phenomena evolve over time, tracing historical developments and transformations. This approach provides a deeper understanding of changes and continuities within specific contexts or systems. Discover more about how diachronic perspectives can enrich your insights by exploring the rest of this article.
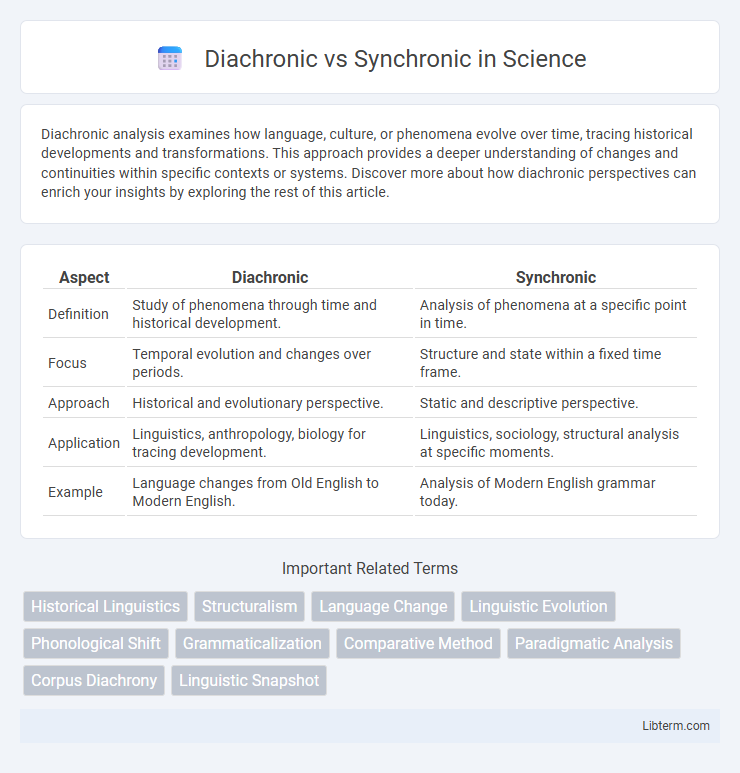
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Diachronic | Synchronic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of phenomena through time and historical development. | Analysis of phenomena at a specific point in time. |
| Focus | Temporal evolution and changes over periods. | Structure and state within a fixed time frame. |
| Approach | Historical and evolutionary perspective. | Static and descriptive perspective. |
| Application | Linguistics, anthropology, biology for tracing development. | Linguistics, sociology, structural analysis at specific moments. |
| Example | Language changes from Old English to Modern English. | Analysis of Modern English grammar today. |
Introduction to Diachronic and Synchronic Approaches
Diachronic approaches analyze language changes over time, tracing historical development and evolution of linguistic features. Synchronic approaches examine language at a specific moment, focusing on its structure and usage without considering historical shifts. Understanding both perspectives provides comprehensive insights into language dynamics and linguistic phenomena.
Defining Diachronic Analysis
Diachronic analysis examines linguistic or cultural phenomena through historical development and changes over time, tracing the evolution of languages, societies, or texts. It contrasts with synchronic analysis, which studies systems at a specific point without considering their history. Understanding diachronic processes is essential for fields like historical linguistics, archaeology, and cultural anthropology to reveal patterns of transformation and continuity.
Understanding Synchronic Analysis
Synchronic analysis examines languages or systems at a specific point in time, emphasizing structure and function without considering historical changes. This approach allows linguists to analyze patterns, usage, and relationships within a language stage, offering insights into grammar, syntax, and semantics as they coexist. Understanding synchronic analysis helps clarify how contemporary language elements interact, enabling more precise descriptions of linguistic phenomena independent of temporal evolution.
Key Differences Between Diachronic and Synchronic
Diachronic analysis examines linguistic or cultural phenomena through time, emphasizing historical development and evolution, while synchronic analysis studies these phenomena at a specific point in time without considering historical context. Key differences include the temporal focus, with diachronic approaches tracing change and language progression, and synchronic approaches highlighting structure and usage in a particular era. Diachronic studies are prevalent in historical linguistics, whereas synchronic studies dominate descriptive linguistics.
Historical Contexts of Diachronic Study
Diachronic study examines language or phenomena through historical contexts, tracing their evolution and transformations over time. This approach allows researchers to understand changes in grammar, vocabulary, and usage by analyzing artifacts, texts, or records from different historical periods. Emphasizing temporal development, diachronic analysis reveals the dynamic processes that have shaped linguistic and cultural histories.
Applications of Synchronic Analysis in Linguistics
Synchronic analysis in linguistics examines language at a specific point in time, enabling detailed study of phonetics, syntax, and semantics within a current context. This approach is crucial for language description, dialectology, and sociolinguistics, as it reveals structural patterns and usage variations without considering historical development. Applications include analyzing contemporary language use in media, education, and AI language processing systems to enhance communication and comprehension accuracy.
Advantages of Diachronic Perspective
The diachronic perspective offers valuable insights into language change by tracing the evolution and historical development of linguistic features over time. It enables researchers to understand how cultural, social, and cognitive factors influence language transformation, providing context for current usage. Studying diachronic linguistics aids in reconstructing ancestral languages and understanding the processes behind semantic shifts and grammaticalization.
Benefits of Synchronic Examination
Synchronic examination offers the benefit of analyzing a language or phenomenon at a specific point in time, providing clear insights into its current structure and usage without historical interference. This method allows for detailed understanding of linguistic relationships, social behaviors, or cultural patterns as they exist simultaneously, facilitating comparisons across different systems or communities. Its focus on contemporaneous data supports practical applications such as language teaching, sociolinguistic analysis, and real-time policy development.
Integrating Diachronic and Synchronic Methods
Integrating diachronic and synchronic methods enhances linguistic analysis by combining historical language change with contemporary language structure. This approach allows researchers to trace the evolution of linguistic features while understanding their current function and usage within specific social contexts. Utilizing both perspectives provides a comprehensive framework for studying language dynamics, addressing how past developments influence present-day linguistic patterns.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Analytical Approach
Selecting between diachronic and synchronic analysis depends on the research objective: diachronic approaches excel in studying historical development and changes over time, providing insights into linguistic or cultural evolution. Synchronic analysis offers a snapshot of structures at a specific point, ideal for understanding systematic functions and relationships within a given period. Optimal research often integrates both methods to capture comprehensive perspectives on language or phenomena dynamics.
Diachronic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com