Parasitism is a biological relationship where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of another, the host, often causing harm without immediate death. This interaction plays a crucial role in ecosystems by influencing population dynamics and driving evolutionary adaptations. Explore the rest of this article to understand how parasitism shapes the natural world and affects your environment.
Table of Comparison
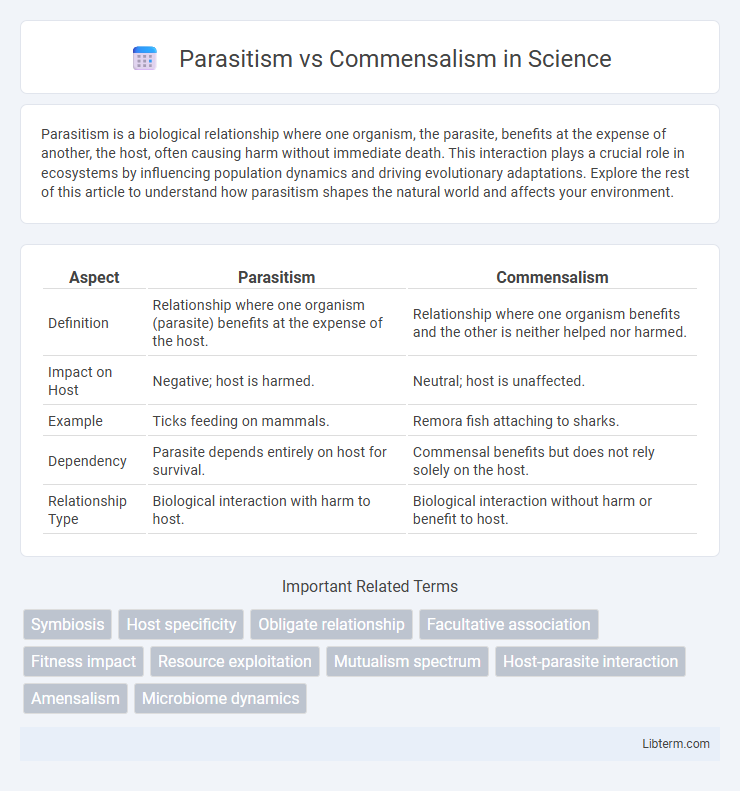
| Aspect | Parasitism | Commensalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relationship where one organism (parasite) benefits at the expense of the host. | Relationship where one organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed. |
| Impact on Host | Negative; host is harmed. | Neutral; host is unaffected. |
| Example | Ticks feeding on mammals. | Remora fish attaching to sharks. |
| Dependency | Parasite depends entirely on host for survival. | Commensal benefits but does not rely solely on the host. |
| Relationship Type | Biological interaction with harm to host. | Biological interaction without harm or benefit to host. |
Understanding Symbiotic Relationships
Parasitism involves one organism benefiting at the expense of another, often causing harm to the host, as seen in ticks feeding on mammals. Commensalism describes a relationship where one species benefits while the other remains unaffected, such as barnacles attaching to whales without harming them. Understanding these symbiotic relationships highlights ecological balance and the diverse strategies organisms use for survival.
Defining Parasitism
Parasitism is a symbiotic relationship where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the host, often causing harm or disease. The parasite relies on the host for resources such as nutrients or habitat, sometimes leading to weakened host health or reduced reproductive success. This contrasts with commensalism, where one organism benefits without affecting the other.
Understanding Commensalism
Commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits while the other remains unaffected, exemplified by barnacles attaching to whale skin for transportation and food scraps without harming the host. This interaction contrasts with parasitism, where the parasite gains at the host's expense, often causing harm or disease. Understanding commensalism helps clarify ecosystem dynamics by highlighting relationships that maintain species coexistence without negative impacts.
Key Differences Between Parasitism and Commensalism
Parasitism involves one organism benefiting at the expense of another, often causing harm or disease to the host, while commensalism benefits one organism without affecting the other. In parasitism, the parasite relies on the host for nutrients or habitat, leading to a detrimental impact, whereas in commensalism, the commensal organism gains shelter, support, or transportation without causing harm. The key difference lies in the effect on the host: parasitism results in negative consequences, whereas commensalism maintains a neutral balance.
Examples of Parasitism
Examples of parasitism include the relationship between ticks and mammals, where ticks feed on the host's blood, causing harm and potential disease transmission. Another example is the parasitic interaction between tapeworms and their vertebrate hosts, where the tapeworm absorbs nutrients at the host's expense, leading to malnutrition. Parasitism also occurs with mistletoe plants attaching to tree branches, extracting water and nutrients while negatively affecting the host tree's growth.
Examples of Commensalism
Examples of commensalism include barnacles attaching to whales, benefiting from transportation and food scraps without harming the host. Another common example is the relationship between cattle egrets and grazing animals, where egrets feed on insects disturbed by the movement of livestock. Epiphytic plants growing on trees also illustrate commensalism by gaining access to sunlight without affecting the host tree.
Impacts on Host Organisms
Parasitism negatively impacts host organisms by extracting nutrients or resources, often causing harm, disease, or weakened immunity. In contrast, commensalism involves one species benefiting while the host remains unaffected, experiencing neither harm nor gain. The host in parasitic relationships endures stress or damage, whereas in commensal interactions, the host's physiological functions continue normally without disruption.
Ecological Roles of Parasitism and Commensalism
Parasitism plays a crucial ecological role by regulating host population dynamics, often controlling species abundance and maintaining ecosystem balance. Commensalism contributes to biodiversity by allowing one species to benefit without harming the host, often facilitating resource utilization and habitat sharing. Both interactions influence community structure, with parasitism impacting health and survival while commensalism promotes coexistence and niche differentiation.
Evolutionary Perspectives
Parasitism drives evolutionary arms races by prompting hosts to develop defense mechanisms while parasites evolve strategies to overcome them, enhancing survival and reproductive success. Commensalism often leads to stable associations where commensal species benefit without harming or benefiting the host, potentially paving the way for mutualism over evolutionary time. These interactions shape species adaptations, influencing biodiversity and ecological dynamics through selective pressures and coevolutionary processes.
Importance in Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
Parasitism and commensalism play critical roles in biodiversity and ecosystem health by influencing species interactions and population dynamics. Parasitism regulates host populations and drives evolutionary adaptations, while commensalism enhances habitat complexity and resource availability without harming hosts. Together, these relationships maintain ecological balance, promote species coexistence, and support ecosystem resilience.
Parasitism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com