Isobar is a global digital marketing agency specializing in innovative brand experiences, digital transformation, and customer engagement strategies. Leveraging data-driven insights and emerging technologies, Isobar crafts personalized campaigns that drive measurable results across multiple platforms. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Isobar can elevate your brand's digital presence.
Table of Comparison
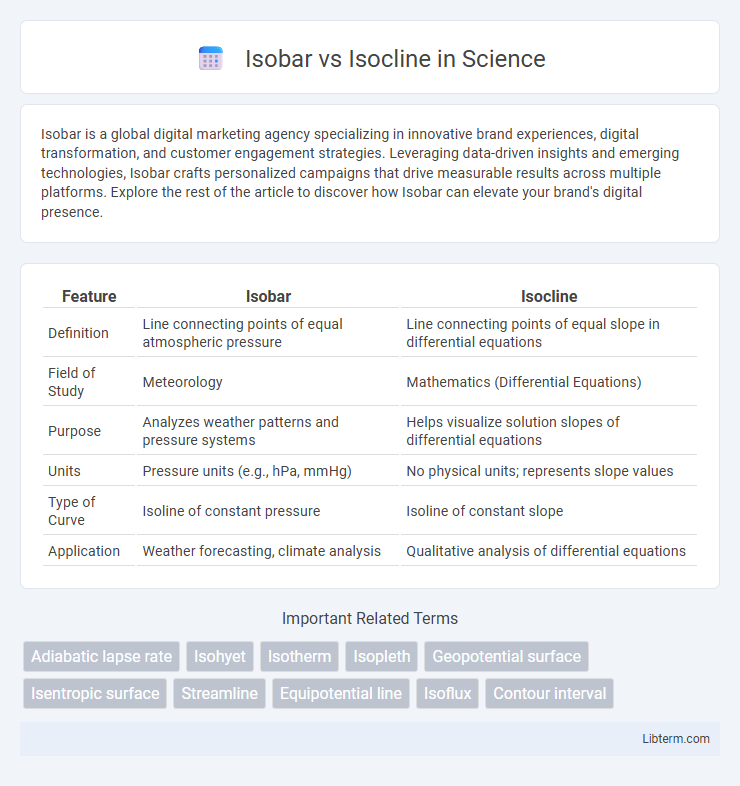
| Feature | Isobar | Isocline |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Line connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure | Line connecting points of equal slope in differential equations |
| Field of Study | Meteorology | Mathematics (Differential Equations) |
| Purpose | Analyzes weather patterns and pressure systems | Helps visualize solution slopes of differential equations |
| Units | Pressure units (e.g., hPa, mmHg) | No physical units; represents slope values |
| Type of Curve | Isoline of constant pressure | Isoline of constant slope |
| Application | Weather forecasting, climate analysis | Qualitative analysis of differential equations |
Introduction to Isobar and Isocline
Isobars represent lines of equal atmospheric pressure on weather maps, helping meteorologists visualize pressure systems and predict wind patterns. Isoclines, commonly used in mathematical and ecological studies, are curves along which a differential equation has a constant slope or where populations experience constant growth rates. Understanding the distinction between isobars in meteorology and isoclines in mathematical modeling enables accurate interpretation of atmospheric conditions and dynamic systems behavior.
Defining Isobar: Meaning and Significance
An isobar is a line on a weather map that connects points of equal atmospheric pressure, measured in millibars or hectopascals. Isobars play a crucial role in meteorology by illustrating pressure patterns that influence wind flow, weather fronts, and storm development. Understanding isobars helps predict weather changes and identify high and low-pressure systems essential for forecasting.
Defining Isocline: Meaning and Importance
Isoclines are curves on a graph representing points where a differential equation's slope or derivative remains constant, crucial for analyzing direction fields in dynamic systems. Defining isoclines helps visualize solution trajectories by highlighting regions of equal slope, enabling better prediction of system behavior and stability. Unlike isobars, which indicate constant pressure, isoclines emphasize mathematical slope consistency essential for qualitative differential equation analysis.
Key Differences Between Isobar and Isocline
Isobars are lines on a weather map connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, helping meteorologists predict wind patterns and weather changes. Isoclines, in contrast, are lines on graphs or maps representing points where the slope of a function is constant, mainly used in mathematical or ecological studies. The key difference lies in their application: isobars are meteorological tools for pressure analysis, while isoclines are mathematical constructs indicating equal rates of change or slope.
Formation and Representation on Maps
Isobars are lines on weather maps connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, formed by measuring pressure at various locations and interpolating values to depict pressure patterns. Isoclines are contours representing equal slope or rate of change in gradients, primarily used in fields like ecology or geography to illustrate areas where a particular variable's rate of change remains constant. On maps, isobars typically appear as smooth, closed loops indicating pressure systems, while isoclines show lines of equal gradient steepness, helping visualize changes in terrain or other variables.
Applications in Meteorology and Geography
Isobars, lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, are essential in meteorology for predicting weather patterns and identifying high and low-pressure systems that influence wind direction and storm development. Isoclines, curves representing equal slope values, find applications in geography and topography to analyze terrain gradient and stability, aiding in landslide risk assessment and landscape evolution studies. While isobars provide insights into dynamic atmospheric processes, isoclines contribute to understanding physical landform characteristics and their impact on environmental processes.
Isobars in Weather Forecasting
Isobars are lines on weather maps connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, essential for predicting wind patterns and storm systems. Closely spaced isobars indicate strong winds, while widely spaced lines suggest calmer conditions, aiding meteorologists in assessing weather severity. This pressure visualization allows accurate forecasting of weather fronts, cyclones, and anticyclones, crucial for public safety and planning.
Isoclines in Ecological and Mathematical Studies
Isoclines in ecological studies represent curves connecting points where the growth rate of a population is zero, helping to analyze species interactions and predict equilibrium states. Mathematically, isoclines are lines on a phase plane where the derivative of a differential equation remains constant, facilitating the understanding of system dynamics and stability. These tools are essential for modeling predator-prey systems, resource competition, and other population dynamics within ecosystems.
Visual Comparison: Isobar vs Isocline Maps
Isobar maps display lines of constant atmospheric pressure, visually representing high and low-pressure systems crucial for weather forecasting. Isocline maps, on the other hand, depict lines of equal slope or rate of change in mathematical or geological contexts, highlighting trends and gradients. The visual comparison between isobar and isocline maps reveals distinct applications: isobars illustrate meteorological pressure patterns, while isoclines emphasize uniform rates of change, making each map type essential for specialized analytical purposes.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Isobar and Isocline
Selecting between isobar and isocline methods depends primarily on the type of data and the problem context; isobars represent lines of constant atmospheric pressure useful in meteorology, while isoclines indicate curves where differential equations have a constant slope, aiding in mathematical analysis. For weather mapping and pressure-related studies, isobars provide clear, actionable insights, whereas isoclines facilitate understanding the behavior of solutions in differential equations. The decision hinges on whether the objective involves physical pressure fields or mathematical solution trajectories.
Isobar Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com