An evaporator plays a crucial role in removing heat from a liquid by converting it into vapor, commonly used in refrigeration and industrial processes. Efficient evaporators enhance system performance by maximizing heat transfer while minimizing energy consumption. Discover how the design and function of evaporators impact your system's efficiency in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
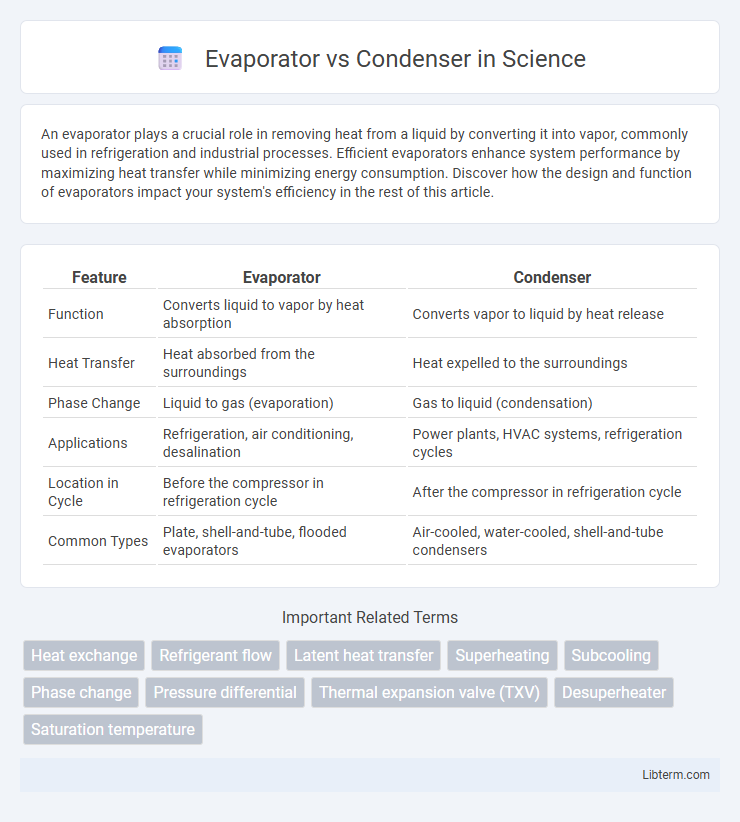
| Feature | Evaporator | Condenser |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts liquid to vapor by heat absorption | Converts vapor to liquid by heat release |
| Heat Transfer | Heat absorbed from the surroundings | Heat expelled to the surroundings |
| Phase Change | Liquid to gas (evaporation) | Gas to liquid (condensation) |
| Applications | Refrigeration, air conditioning, desalination | Power plants, HVAC systems, refrigeration cycles |
| Location in Cycle | Before the compressor in refrigeration cycle | After the compressor in refrigeration cycle |
| Common Types | Plate, shell-and-tube, flooded evaporators | Air-cooled, water-cooled, shell-and-tube condensers |
Introduction to Evaporators and Condensers
Evaporators and condensers are critical components in thermal and refrigeration systems, with evaporators facilitating the phase change of a liquid into vapor by absorbing heat, while condensers enable the conversion of vapor back into liquid by releasing heat. Evaporators maximize heat absorption through surface area and efficient fluid flow, commonly found in air conditioning, refrigeration, and industrial processes. Condensers utilize cooling mediums like air or water to remove latent heat from vapor, ensuring system efficiency and maintaining desired pressure and temperature conditions.
Understanding the Basics: What is an Evaporator?
An evaporator is a key component in refrigeration systems where a liquid refrigerant absorbs heat and changes into a vapor, enabling cooling by extracting heat from the surrounding environment. It operates at low pressure and temperature, facilitating the phase change necessary for heat absorption. Understanding the evaporator's function is essential for grasping how cooling mechanisms work in air conditioners, refrigerators, and heat pumps.
Understanding the Basics: What is a Condenser?
A condenser is a heat exchanger device that condenses vapor into liquid by cooling it, typically used in refrigeration, air conditioning, and power plants. It transfers heat from the refrigerant vapor to the surrounding air or water, facilitating the phase change from gas to liquid. Understanding the condenser's role is essential for optimizing thermal systems and ensuring efficient energy transfer.
Core Functions: How Evaporators Work
Evaporators function by absorbing heat from a liquid, causing it to evaporate and transform into vapor, which is essential in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. The core process involves the liquid refrigerant entering the evaporator at low pressure and temperature, where it absorbs heat from the surrounding environment or fluid, leading to phase change. This heat absorption cools the environment while the vaporized refrigerant moves to the compressor for the next cycle.
Core Functions: How Condensers Work
Condensers function by removing heat from refrigerant vapor, transforming it into a high-pressure liquid as part of the HVAC cycle. Heat dissipation occurs through air or water-cooled mechanisms, enabling efficient latent heat transfer essential for refrigeration and air conditioning systems. This cooling process contrasts with evaporators, which absorb heat to vaporize the liquid refrigerant, highlighting the condenser's role in the thermal regulation loop.
Key Differences Between Evaporators and Condensers
Evaporators absorb heat to convert liquid into vapor, playing a crucial role in refrigeration cycles by facilitating the cooling process. Condensers release heat to turn vapor back into liquid, essential for transferring heat away from the system in air conditioning and industrial applications. The primary difference lies in their thermal function: evaporators operate at low pressure and temperature to absorb heat, while condensers function at high pressure and temperature to dissipate heat.
Applications of Evaporators in Various Industries
Evaporators play a crucial role in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing by enabling efficient concentration and drying of liquids without compromising product quality. In the dairy industry, evaporators concentrate milk and whey, while in chemical plants, they remove solvents to recover valuable compounds. Their ability to handle heat-sensitive materials makes evaporators indispensable for producing concentrates, extracts, and purified products across diverse industrial applications.
Common Uses of Condensers Across Sectors
Condensers play a vital role in industries such as power generation, HVAC, refrigeration, and chemical processing by efficiently converting vapor into liquid to facilitate heat exchange and energy conservation. In power plants, condensers condense steam from turbines to maximize energy efficiency, while in refrigeration systems, they expel heat absorbed from the cooled space. The chemical and petrochemical sectors utilize condensers for distillation and solvent recovery processes, making these devices essential across diverse applications requiring thermal management and phase change.
Efficiency Considerations: Evaporators vs Condensers
Evaporators maximize efficiency by absorbing heat rapidly from the surrounding environment, utilizing a large surface area and optimal refrigerant flow to enhance thermal transfer. Condensers operate efficiently by expelling heat through effective refrigerant phase change and maintaining consistent airflow, which reduces energy consumption in compressors. The balance of evaporator and condenser performance directly impacts overall system efficiency, with proper sizing and maintenance crucial for minimizing energy losses.
Choosing the Right Component: Factors to Consider
Selecting between an evaporator and a condenser depends on the specific refrigeration or HVAC system requirements, such as desired heat transfer direction and temperature control. Consider factors like thermal load, system pressure, and fluid compatibility to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency. Proper sizing and material selection also influence durability and maintenance needs in diverse environmental conditions.
Evaporator Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com